Global IPO & SME IPO TrendsIntroduction
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) have always been a symbol of ambition, growth, and transformation. They represent the moment when a company decides to move beyond private ownership and open its doors to the public capital markets. IPOs not only provide companies with capital for expansion but also give investors an opportunity to participate in wealth creation.
Over the last few decades, IPOs have evolved significantly, shaped by globalization, technological change, regulatory reforms, and shifting investor behavior. In addition to traditional large-cap IPOs, the rise of Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) IPOs has been a defining trend in recent years, especially in developing markets like India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa.
This paper explores global IPO trends and SME IPO dynamics, examining how the landscape has transformed, the challenges and opportunities it presents, and what the future holds.
Part I: The Global IPO Landscape
1. Historical Overview
Early IPOs: The concept of public share issuance dates back to the 1600s with the Dutch East India Company, which allowed investors to buy shares in overseas trade.
20th Century Boom: IPOs became mainstream in the U.S. and Europe during the industrial boom, with companies in oil, steel, and manufacturing driving listings.
Dot-Com Bubble (1990s-2000s): Technology IPOs surged in the late 1990s, many without strong fundamentals, leading to the dot-com crash in 2000.
Post-2008 Era: After the global financial crisis, IPO markets slowed but revived with technology giants like Facebook, Alibaba, and Uber entering the public space.
2. Regional IPO Hotspots
United States: Still the largest IPO market by value. Nasdaq and NYSE dominate global tech and unicorn listings.
China & Hong Kong: Became global leaders in IPO volumes, especially in technology, fintech, and manufacturing. Hong Kong has been a preferred listing destination for Chinese firms.
Europe: More selective, with strong activity in London, Frankfurt, and Amsterdam.
India: A rising star, with both large-cap IPOs and booming SME IPOs. Retail participation is strong.
Middle East: Saudi Arabia’s Aramco IPO (2019) became the world’s largest, showing the region’s growing importance.
3. Global IPO Trends in Numbers
IPO activity tends to move in cycles, often tied to macroeconomic conditions, liquidity availability, and investor sentiment.
2020-2021: Record IPO activity, fueled by low interest rates, stimulus-driven liquidity, and tech growth during COVID-19.
2022-2023: IPO slowdown due to inflation, interest rate hikes, and geopolitical tensions (Ukraine war, US-China rivalry).
2024-2025: Signs of revival, with AI, EV, renewable energy, and fintech companies leading the pipeline.
Part II: Factors Shaping IPO Markets
1. Macroeconomic Environment
Interest Rates: Low rates encourage risk-taking and IPOs; high rates deter them.
Liquidity: Abundant global liquidity fuels IPO demand.
Geopolitics: Wars, trade disputes, and regulatory crackdowns influence cross-border IPOs.
2. Sectoral Trends
Technology: AI, semiconductors, SaaS, and fintech dominate listings.
Green Energy: EVs, solar, wind, and hydrogen IPOs attract ESG-focused investors.
Healthcare & Biotech: Rising due to pandemic learnings and aging populations.
Consumer & Retail: Still strong, but facing disruptions from e-commerce.
3. Regulatory Environment
The U.S. SEC, Europe’s ESMA, and Asian regulators have tightened disclosure norms.
China has restricted overseas listings of sensitive tech companies.
India’s SEBI has become stricter but supportive of SME and tech listings.
Part III: Rise of SME IPOs
1. Why SME IPOs Matter
SMEs are the backbone of most economies, contributing 30–60% of GDP in many countries.
Access to capital markets allows SMEs to reduce dependence on banks and private equity.
SME IPOs democratize wealth creation by involving retail investors.
2. India as a Case Study
India has emerged as a global leader in SME IPOs.
Platforms like NSE Emerge and BSE SME Exchange have hosted hundreds of SME listings.
Retail investors flock to SME IPOs due to small ticket sizes and potential for multi-bagger returns.
In 2023–2025, SME IPOs in India often delivered stronger short-term gains than large IPOs.
3. Global SME IPO Landscape
China: Has STAR Market for tech-driven SMEs.
Europe: AIM (Alternative Investment Market) in London supports SME listings.
U.S.: Nasdaq SmallCap and OTC markets exist, but venture capital dominates.
Africa & Middle East: Nascent SME IPO frameworks are being developed.
4. Key Challenges
Liquidity Issues: SME IPOs often face thin trading volumes.
Governance: Risk of weak disclosure and manipulation.
Investor Education: Retail investors sometimes underestimate risks.
Part IV: Investor Behavior & Market Psychology
1. Institutional vs Retail Investors
Institutional investors dominate large-cap IPOs.
Retail investors are increasingly active in SME IPOs.
Behavioral biases — such as FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) — drive oversubscriptions.
2. IPO Pricing & Valuation Dynamics
Companies often price aggressively, leading to mixed post-listing performance.
The “listing pop” culture attracts traders seeking quick gains.
3. The Role of Anchor Investors
Anchor investors provide credibility to IPOs and influence demand.
Part V: Risks and Challenges in IPO Markets
Volatility: IPOs are highly sensitive to market sentiment.
Regulatory Crackdowns: Sudden changes (like China’s tech crackdown) disrupt IPO pipelines.
Post-IPO Underperformance: Many IPOs fail to sustain valuations beyond the first year.
Speculative Bubbles: Retail-driven hype can inflate SME valuations unsustainably.
Part VI: The Future of IPOs & SME IPOs
1. Technology’s Role
Digital Platforms: E-IPO applications and online brokerages increase retail participation.
Blockchain & Tokenized IPOs: A possible future trend where companies raise funds via tokenized shares.
AI in Valuation: Algorithms now play a role in IPO pricing and demand analysis.
2. ESG & Sustainable Finance
Investors increasingly prefer companies with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) credentials.
Green IPOs (renewable energy, EV, sustainability tech) will dominate.
3. Globalization vs Protectionism
While globalization pushes for cross-border listings, geopolitics may encourage companies to list domestically.
India, China, and Middle East will become more self-reliant IPO hubs.
4. SME IPOs Outlook
SME IPOs will expand rapidly in Asia and Africa, where small businesses dominate.
Regulatory reforms and investor education will decide sustainability.
Conclusion
The global IPO market is a mirror of the world economy, reflecting growth cycles, technological revolutions, and investor sentiment. While traditional large-cap IPOs continue to capture headlines, the rise of SME IPOs represents a deeper democratization of finance.
SMEs, once constrained by limited access to capital, are now using public markets to scale up, attract visibility, and create wealth for investors. Markets like India, China, and the Middle East are emerging as epicenters of SME IPO growth, while the U.S. and Europe remain leaders in large-cap listings.
Going forward, IPO trends will be shaped by AI, ESG, fintech innovations, and shifting geopolitics. Investors and regulators must balance opportunity with caution, especially in SME IPOs where risks are higher but so are the rewards.
In short, IPOs — both global and SME-focused — will continue to remain a critical engine of capital formation, innovation funding, and wealth creation in the evolving global economy.
Learntotrade
Healthcare & Pharma StocksIntroduction
Healthcare and pharmaceutical (pharma) stocks represent one of the most vital and resilient segments of global equity markets. Unlike cyclical sectors such as automobiles or real estate, healthcare is a necessity-driven industry—people require medical care, medicines, and treatments regardless of economic ups and downs. This inherent demand creates a unique investment landscape where growth, stability, and innovation intersect.
Pharma and healthcare stocks include a wide variety of companies—ranging from multinational giants like Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Novartis to Indian leaders such as Sun Pharma, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, and Cipla. The sector also encompasses hospitals, diagnostic chains, biotech innovators, medical device manufacturers, and health-tech startups.
This write-up provides a deep 360-degree analysis of healthcare & pharma stocks, covering their structure, business drivers, global trends, risks, opportunities, and investment strategies.
1. Structure of Healthcare & Pharma Sector
The healthcare & pharma ecosystem can be broadly divided into:
A. Pharmaceuticals
Generic drugs: Off-patent medicines manufactured at lower costs. (e.g., Sun Pharma, Teva)
Branded drugs: Patented products with high margins. (e.g., Pfizer, Novartis)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs): Raw drug materials, where India and China dominate.
Contract Research & Manufacturing Services (CRAMS): Outsourcing R&D and manufacturing.
B. Biotechnology
Companies focused on genetic engineering, cell therapies, and monoclonal antibodies.
High-risk but high-reward investments (e.g., Moderna, Biocon).
C. Hospitals & Healthcare Services
Hospital chains (Apollo, Fortis, Max Healthcare).
Diagnostics (Dr. Lal PathLabs, Metropolis, Thyrocare).
Health insurance companies.
D. Medical Devices & Technology
Imaging equipment, surgical tools, wearables (Medtronic, Siemens Healthineers).
Digital health platforms and telemedicine providers.
E. Global vs. Domestic Markets
Global players dominate innovation-driven drug discovery.
Indian players dominate generics, APIs, and affordable healthcare solutions.
2. Key Growth Drivers
A. Rising Global Healthcare Spending
Worldwide healthcare spending is projected to cross $10 trillion by 2030.
Ageing populations in developed nations and increasing middle-class healthcare demand in emerging economies fuel growth.
B. Lifestyle Diseases
Diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disorders, and obesity are increasing.
Continuous demand for chronic therapy drugs.
C. Patents & Innovation
Innovative drugs with patent protection ensure high profit margins.
Pipeline of oncology, rare disease, and immunology drugs is expanding.
D. COVID-19 Acceleration
Pandemic showcased the sector’s importance.
Vaccine manufacturers, diagnostics, and hospital chains saw exponential growth.
E. Government Policies & Healthcare Access
India’s Ayushman Bharat scheme, US Medicare expansion, and Europe’s universal healthcare systems are pushing accessibility.
F. Digital Transformation
Telemedicine, AI-based diagnostics, robotic surgeries, and wearable devices.
Creates new sub-segments for investors.
3. Risks & Challenges
A. Regulatory Risks
FDA (US), EMA (Europe), and CDSCO (India) have stringent regulations.
Compliance failures lead to import bans, plant shutdowns, and fines.
B. Patent Expirations
Blockbuster drugs lose exclusivity after 10–15 years.
Leads to generic competition and margin erosion.
C. Pricing Pressure
Governments cap drug prices to maintain affordability.
Generic drug prices are constantly under pressure.
D. R&D Uncertainty
Only 1 in 10,000 drug molecules successfully reaches the market.
High R&D costs with uncertain returns.
E. Geopolitical & Supply Chain Issues
China controls key raw materials (APIs).
Any disruption impacts global supply.
4. Global Leaders in Healthcare & Pharma
A. Pharma Giants
Pfizer (US): COVID-19 vaccine, oncology, cardiovascular drugs.
Johnson & Johnson (US): Diversified pharma, medical devices, consumer healthcare.
Novartis (Switzerland): Oncology, gene therapy.
Roche (Switzerland): Diagnostics and cancer treatments.
AstraZeneca (UK): Cardiovascular and respiratory therapies.
B. Biotechnology Leaders
Moderna & BioNTech: mRNA vaccine technology.
Gilead Sciences: HIV and hepatitis treatments.
Amgen: Biologic drugs.
C. Indian Leaders
Sun Pharma: Largest Indian pharma company, strong in generics.
Dr. Reddy’s: APIs, generics, biosimilars.
Cipla: Strong in respiratory segment.
Biocon: Pioneer in biosimilars.
Apollo Hospitals: Leading hospital chain.
Metropolis & Dr. Lal PathLabs: Diagnostics leaders.
5. Market Trends
A. Consolidation & M&A
Big pharma acquiring biotech startups.
Indian firms expanding globally via acquisitions.
B. Biosimilars & Biologics
Biologics (complex drugs made from living organisms) are the future.
Biosimilars (generic versions of biologics) gaining ground after patent expiry.
C. Personalized Medicine
Genetic testing enables customized treatments.
Oncology leading the way.
D. Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery
AI reduces time and costs in clinical trials.
Companies like Exscientia and BenevolentAI working with pharma giants.
E. Medical Tourism
India, Thailand, and Singapore attract patients globally due to cost advantage.
Growth in hospital and diagnostic sector.
6. Investment Perspective
A. Defensive Nature
Healthcare is non-cyclical—stable demand even in recessions.
Acts as a hedge in uncertain markets.
B. Growth Potential
Emerging markets like India offer double-digit growth.
Biotech and innovation-driven companies can deliver multibagger returns.
C. Dividends & Stability
Big pharma firms are cash-rich and provide regular dividends.
Stable revenue models for hospitals and insurers.
D. Valuation Metrics
Investors should analyze:
R&D pipeline: Future drug launches.
Regulatory compliance: FDA approvals, audits.
Debt levels & cash flow: Capital-intensive sector.
Market presence: US, Europe, and India exposure.
7. Indian Market Outlook
Pharma exports: India supplies 20% of global generics by volume.
Domestic healthcare: Rising insurance penetration and government spending.
Diagnostics: High growth with preventive healthcare awareness.
Hospital chains: Consolidation and increasing private equity investments.
API manufacturing push: Government incentives to reduce dependency on China.
8. Future Opportunities
Gene Therapy & CRISPR: Revolutionary treatments for genetic disorders.
mRNA Technology: Beyond vaccines, applicable in cancer therapies.
Wearable Health Tech: Smartwatches, glucose monitors, cardiac sensors.
Telemedicine: Remote healthcare becoming mainstream.
AI in Healthcare: Faster drug discovery, predictive healthcare analytics.
9. Risks for Investors
Litigation Risks: Patent disputes, product liability lawsuits.
Currency Fluctuations: Export-driven Indian pharma firms face forex risk.
Competition: Generic wars in the US and EU.
Policy Shifts: Government price controls can reduce profitability.
10. Investment Strategies
A. Long-Term Play
Biotech & R&D-driven pharma are long-term investments (10–15 years).
Examples: Biocon, Moderna, Roche.
B. Defensive Allocation
Hospitals, insurance, and generic pharma are safer bets for portfolio stability.
C. Thematic Investing
Focus on oncology, biosimilars, digital health, or telemedicine themes.
D. Diversification
Spread across global pharma (Pfizer, J&J), Indian generics (Sun, Cipla), and hospitals (Apollo, Fortis).
Conclusion
Healthcare & pharma stocks represent a unique mix of stability, growth, and innovation. The sector is driven by non-cyclical demand, global healthcare spending, lifestyle diseases, and constant innovation in biotechnology. At the same time, it faces challenges like regulatory hurdles, pricing pressures, and patent expirations.
For investors, healthcare and pharma provide defensive positioning in uncertain times and long-term multibagger opportunities in high-growth biotech and digital health. In India, the sector is set to grow rapidly with rising domestic demand, government support, and increasing global market share.
In essence, investing in healthcare & pharma stocks is not just about chasing profits—it is about betting on the future of human health and well-being.
Hedge Funds & Alternative AssetsIntroduction
Financial markets are far more than just stocks and bonds. While traditional assets like equities, fixed income, and cash dominate the portfolios of most retail investors, the world of professional money management goes much deeper. Sophisticated investors – pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, high-net-worth individuals, and endowments – often turn to hedge funds and alternative assets for higher returns, risk diversification, and exposure to strategies unavailable in public markets.
Hedge funds and alternative assets have grown into multi-trillion-dollar industries, shaping global capital flows and influencing everything from commodities to real estate, from startups to distressed debt. Understanding them is crucial not only for investors but also for policymakers, economists, and anyone who wants to grasp the modern financial ecosystem.
In this write-up, we’ll explore:
What hedge funds are and how they operate.
The structure, strategies, and risks of hedge funds.
The rise of alternative assets beyond traditional investing.
Key categories of alternative investments: private equity, venture capital, real estate, commodities, infrastructure, collectibles, and digital assets.
The benefits and challenges of investing in alternatives.
The future outlook of hedge funds and alternative assets in an evolving financial landscape.
Part 1: Hedge Funds – An Inside Look
What is a Hedge Fund?
A hedge fund is a pooled investment vehicle that collects capital from accredited investors or institutions and deploys it using advanced strategies to generate returns. Unlike mutual funds, hedge funds face fewer regulatory restrictions, giving managers the freedom to use leverage, derivatives, short-selling, and global asset classes.
The term “hedge” comes from the early days when hedge funds primarily aimed to “hedge” market risk by taking offsetting positions. For example, buying undervalued stocks while shorting overvalued ones. Over time, hedge funds expanded far beyond hedging, into aggressive return-seeking strategies.
Key Characteristics
Exclusivity – Available only to high-net-worth individuals (HNIs), accredited investors, and institutions.
Fee Structure – Typically the famous “2 and 20” model: 2% management fee + 20% performance fee.
Flexibility – Can invest in equities, bonds, currencies, commodities, private deals, derivatives, etc.
Leverage & Shorting – Unlike mutual funds, hedge funds can borrow heavily and profit from falling prices.
Limited Liquidity – Lock-in periods are common; investors may need to stay invested for months or years.
Hedge Fund Structures
Master-Feeder Structure: Commonly used for global funds. Offshore investors put money into a feeder fund, which channels into a master fund that manages the portfolio.
Limited Partnership (LP) Model: Most funds are structured as LPs, where the manager is the General Partner (GP) and investors are Limited Partners.
Major Hedge Fund Strategies
Equity Long/Short – Buy undervalued stocks, short overvalued ones.
Global Macro – Bet on big-picture economic trends: currencies, interest rates, commodities. Famous example: George Soros’ bet against the British pound in 1992.
Event-Driven – Profit from mergers, bankruptcies, spin-offs (e.g., merger arbitrage).
Relative Value Arbitrage – Exploit mispricings between related securities.
Distressed Debt – Buy debt of bankrupt companies at deep discounts and profit from recovery.
Quantitative/Algo – Use statistical models, AI, and algorithms for trading.
Multi-Strategy – Diversify across several hedge fund strategies to balance risks.
Hedge Fund Risks
Leverage Risk – Borrowing amplifies losses as much as gains.
Liquidity Risk – Lock-in periods restrict withdrawals; assets may also be hard to sell.
Operational Risk – Complex operations, fraud cases (e.g., Bernie Madoff), and mismanagement.
Market & Strategy Risk – A wrong macro bet or flawed quantitative model can cause massive losses.
Role in Financial Markets
Hedge funds are often criticized for being opaque and excessively risky. Yet, they add liquidity, efficiency, and price discovery to markets. They are influential players in global finance, with total assets under management (AUM) estimated around $4.5 trillion (2024).
Part 2: Alternative Assets – Beyond the Traditional
What are Alternative Assets?
Alternative assets are investment classes outside of traditional stocks, bonds, and cash. They often involve unique structures, illiquidity, and higher risk but offer diversification and the potential for superior returns.
Why Alternatives?
Diversification – Low correlation with traditional markets reduces portfolio volatility.
Higher Returns – Private equity, venture capital, and hedge funds have historically outperformed public markets.
Inflation Hedge – Real assets like real estate, commodities, and infrastructure preserve value.
Access to Innovation – Venture capital and private markets provide exposure to startups before they go public.
Part 3: Major Categories of Alternative Assets
1. Private Equity (PE)
Private equity involves investing in private companies (not listed on stock exchanges) or buying public companies and taking them private.
Buyouts – Acquiring controlling stakes in established businesses.
Growth Equity – Funding expansion of mid-stage firms.
Turnarounds – Investing in struggling companies and restructuring them.
PE funds usually have long horizons (7–10 years) and target internal rates of return (IRR) higher than public equities.
2. Venture Capital (VC)
VC focuses on startups and early-stage businesses with high growth potential. Investors take equity in exchange for capital. While risky, successful investments (e.g., early Amazon, Google, Tesla) deliver extraordinary returns.
Stages:
Seed funding
Series A, B, C rounds
Pre-IPO funding
3. Real Estate
Investing in physical properties (residential, commercial, industrial) or through REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts). Real estate offers rental income and appreciation, and acts as a hedge against inflation.
4. Commodities
Gold, oil, agricultural products, and industrial metals are classic alternatives. Commodities provide diversification, inflation protection, and are heavily influenced by geopolitics and supply-demand shocks.
5. Infrastructure
Long-term projects like roads, airports, energy grids, renewable power plants. Infrastructure assets are attractive for their stability, inflation-linked returns, and essential role in economies.
6. Hedge Funds (as Alternative Assets)
Though discussed separately above, hedge funds themselves are a key segment of alternatives, given their non-traditional, high-risk-return profiles.
7. Collectibles & Art
Luxury watches, fine wine, rare art, vintage cars, and even sports memorabilia. These assets have emotional value and scarcity-driven returns but are highly illiquid and speculative.
8. Digital Assets (Crypto, NFTs, Tokenized Assets)
Bitcoin, Ethereum, decentralized finance (DeFi), and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have emerged as a new frontier. While volatile, digital assets represent an alternative asset class of the future, tied to blockchain technology and financial innovation.
Part 4: Benefits & Challenges
Benefits
Portfolio Diversification: Alternatives reduce reliance on equity/bond cycles.
Return Potential: PE and VC have delivered double-digit returns historically.
Inflation Hedge: Real assets preserve purchasing power.
Access to Growth: Exposure to innovation, infrastructure, and global macro themes.
Challenges
Illiquidity: Lock-in periods can span 5–10 years.
High Fees: 2% management + 20% profit sharing is common.
Complexity: Requires due diligence, specialized knowledge, and access.
Accessibility: Usually open only to accredited or institutional investors.
Risk: Alternatives can suffer steep losses (e.g., crypto crashes, failed startups).
Part 5: The Future of Hedge Funds & Alternatives
The world of alternatives is rapidly evolving:
Institutional Adoption – Pension funds and sovereign wealth funds are allocating larger portions to PE, VC, and hedge funds.
Retail Access – With democratization through ETFs, tokenization, and platforms, retail investors are slowly entering alternatives.
Technology-Driven Strategies – AI, machine learning, and blockchain are reshaping hedge funds and digital assets.
Sustainability Focus – ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) considerations are becoming central to alternative investments.
Globalization – Emerging markets, especially BRICS nations, are driving demand for infrastructure and private equity.
Conclusion
Hedge funds and alternative assets represent the sophisticated side of global investing. While traditional markets remain the backbone of wealth creation, alternatives provide the “alpha” – the chance for superior returns and diversification. Hedge funds, with their flexible strategies, seek to exploit inefficiencies in markets, while alternatives like private equity, venture capital, real estate, and digital assets open doors to growth opportunities unavailable in public equities.
However, they are not for everyone. Their complexity, illiquidity, and risks require expertise, patience, and a long-term view. For investors who can access them, hedge funds and alternative assets will remain vital tools for navigating a world of financial uncertainty, technological disruption, and global shifts.
The financial markets of the future will likely be a blend of traditional and alternative assets, with hedge funds continuing to push the boundaries of innovation and risk-taking. In the end, they reflect the broader evolution of capitalism itself – seeking returns wherever opportunity arises, from Wall Street to Silicon Valley to the blockchain.
Alternative Assets & The Digital EconomyIntroduction
The 21st century global financial landscape has changed dramatically. Traditional investments such as stocks, bonds, and gold still hold their ground, but new opportunities have emerged. Investors today are increasingly exploring alternative assets – a class of investments beyond conventional equity and debt. At the same time, the rise of the digital economy has reshaped how we trade, invest, create value, and measure wealth.
Both concepts are intertwined: digitalization has given rise to entirely new asset classes like cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and tokenized securities, while alternative assets have found new avenues of liquidity and global participation through technology.
This write-up will provide a comprehensive explanation of:
What alternative assets are and why they matter.
The rise of the digital economy and its impact on finance.
Key categories of alternative assets, both traditional (like real estate, private equity) and digital-native (like crypto, tokenized assets).
How digital technology is disrupting and democratizing investment access.
The risks, challenges, and future trends in this space.
1. Understanding Alternative Assets
Definition
Alternative assets are investments that do not fall into the traditional categories of stocks, bonds, or cash. They typically include:
Private Equity (PE)
Venture Capital (VC)
Hedge Funds
Real Estate
Commodities
Collectibles (art, wine, classic cars, watches, rare coins)
Infrastructure investments
Digital Assets (cryptocurrencies, NFTs, tokenized securities, DeFi instruments)
Key Features of Alternative Assets
Illiquidity: Many alternative assets are harder to sell quickly compared to listed stocks.
Diversification: They offer exposure to uncorrelated markets, reducing overall portfolio risk.
Higher Risk–Higher Reward: Alternatives often have greater return potential but come with higher risks.
Limited Accessibility: Traditionally, only institutional investors or ultra-high-net-worth individuals (UHNWIs) could access them.
Complex Valuation: Unlike stocks with daily prices, alternatives often require professional valuation.
Growth of Alternative Investments
According to Preqin, global alternative assets under management (AUM) surpassed $13 trillion in 2023 and are projected to hit $23 trillion by 2027. Investors are allocating more funds to alternatives because low interest rates, inflationary pressures, and volatile equity markets demand diversification.
2. The Rise of the Digital Economy
Defining the Digital Economy
The digital economy refers to economic activity driven by online platforms, digital services, data, and technology-enabled financial instruments. It is powered by the internet, cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and mobile networks.
The digital economy includes:
E-commerce (Amazon, Alibaba, Flipkart)
FinTech (PayPal, Stripe, PhonePe, UPI in India)
Digital Assets & Blockchain
Gig & Platform Economy (Uber, Airbnb, Fiverr)
Digital Payments & CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies)
Metaverse & Virtual Reality Economies
Why It Matters
In 2023, the digital economy contributed over 15% of global GDP, and this share is rapidly expanding.
Countries like China, the U.S., and India are leading digital adoption, with digital payments, online marketplaces, and AI-driven services shaping consumer behavior.
Digital platforms lower entry barriers, allowing small investors to participate in markets previously reserved for large institutions.
3. Categories of Alternative Assets in the Digital Era
A. Traditional Alternatives
Private Equity (PE)
Involves investing directly into private companies (not listed on stock exchanges).
Digital platforms now allow fractional ownership of private equity funds.
Example: Growth of Indian unicorns like BYJU’s, Paytm, and OYO funded by PE & VC.
Venture Capital (VC)
Focused on startups and high-growth technology companies.
Heavily tied to the digital economy (AI, EVs, green tech, SaaS).
Example: Sequoia, Tiger Global, and SoftBank Vision Fund investments.
Real Estate
Traditionally considered a safe-haven asset.
Digital disruption: tokenized real estate, REITs, and crowdfunding platforms like Fundrise.
Example: In India, fractional real estate platforms allow small investors to buy Grade A commercial properties.
Hedge Funds
Pooled investment vehicles using complex strategies.
Digital algorithms, AI, and data-driven trading dominate hedge fund strategies today.
Commodities
Gold, oil, silver, agricultural products.
Tokenization and digital trading platforms make commodities accessible to retail investors.
Collectibles & Luxury Assets
Art, fine wine, vintage cars, sneakers, rare watches.
Platforms like Masterworks (art) and Rally Rd (collectibles) enable fractional ownership.
B. Digital-First Alternatives
Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, and thousands of altcoins.
Represent decentralized, blockchain-based assets.
Used as both speculative investments and stores of value (digital gold).
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens)
Unique blockchain-based digital certificates representing ownership of art, music, video, or virtual goods.
NFT boom (2020–2022) showed how digital scarcity could create new asset markets.
Tokenized Securities
Stocks, bonds, and real estate represented as blockchain tokens.
Offer 24/7 trading, fractional ownership, and lower transaction costs.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
Blockchain-based lending, borrowing, yield farming, and liquidity pools.
Competes with traditional banking and asset management.
Metaverse Assets
Virtual real estate (Decentraland, Sandbox).
Virtual fashion, avatars, and in-game economies.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Issued by central banks, combining government backing with blockchain technology.
Example: India’s Digital Rupee pilot launched by RBI in 2023.
4. How the Digital Economy is Disrupting Alternative Assets
Democratization of Access
Tokenization allows small investors to own fractions of expensive assets (e.g., a $1M artwork split into $1,000 tokens).
Platforms like AngelList democratize startup investing.
Liquidity Enhancement
Historically illiquid assets (private equity, real estate, art) can now be traded 24/7 via digital marketplaces.
Global Participation
Cross-border investments made easier via blockchain and digital payment systems.
Data-Driven Valuation
AI, big data, and predictive analytics help investors evaluate risks in private and alternative markets.
Smart Contracts & Transparency
Blockchain ensures transparency, security, and automated execution of investment contracts.
5. Risks and Challenges
Regulatory Uncertainty
Cryptocurrencies face bans, restrictions, or unclear legal frameworks in many countries.
Tokenized securities need alignment with securities law.
Volatility
Digital assets like Bitcoin can swing 20–30% in a single day.
Fraud & Scams
Rug pulls, Ponzi schemes, and fake NFTs highlight risks in the digital ecosystem.
Liquidity Risks
Despite tokenization, some markets still lack active buyers and sellers.
Technology Risks
Hacks, smart contract bugs, and cyber-attacks can lead to losses.
Valuation Complexity
NFTs, collectibles, and private companies often lack standardized valuation metrics.
6. Case Studies
Bitcoin as Digital Gold
In 2020–2021, Bitcoin was adopted by institutions like Tesla and MicroStrategy as a treasury asset.
Illustrates how digital assets can move into mainstream finance.
Masterworks (Art Fractionalization)
Investors can buy shares of multimillion-dollar artworks, previously only accessible to wealthy collectors.
Real Estate Tokenization in India
Platforms enabling retail investors to own Grade A commercial properties for as little as ₹25,000.
DeFi Lending
Platforms like Aave and Compound allow peer-to-peer lending with interest rates higher than traditional banks.
7. Future Trends
Hybrid Finance (TradFi + DeFi)
Traditional institutions will increasingly adopt blockchain to tokenize bonds, stocks, and real estate.
Mainstream Adoption of CBDCs
Countries will roll out CBDCs for faster cross-border trade and financial inclusion.
Artificial Intelligence in Alternative Investing
AI will optimize portfolio allocation, fraud detection, and asset valuation.
Green & Sustainable Alternatives
ESG-focused alternative investments will attract trillions of dollars.
Metaverse & Web3 Expansion
Virtual worlds will create new forms of ownership, commerce, and alternative assets.
Democratization Continues
Even small retail investors will be able to invest in PE, VC, and art via tokenization.
Conclusion
Alternative assets and the digital economy are two powerful forces reshaping modern finance. Alternative assets provide diversification, unique opportunities, and higher return potential, while the digital economy offers platforms, tools, and innovations that make these investments more accessible, liquid, and global.
From cryptocurrencies to tokenized real estate, from NFTs to private equity digital platforms, the investment landscape is no longer confined to Wall Street or Dalal Street. However, with great opportunities come great risks—regulation, volatility, and fraud remain serious challenges.
Looking ahead, the fusion of alternative investments with digital innovation will define the next era of global finance. Investors who adapt to these changes and understand both the opportunities and risks will be best positioned to benefit in this evolving financial ecosystem.
Commodity Market TrendsIntroduction
The commodity market is one of the oldest forms of trade in human history. From ancient barter systems to modern-day electronic exchanges, commodities such as gold, silver, oil, grains, and livestock have always played a central role in global trade. Unlike stocks and bonds, which represent ownership of a company or debt obligations, commodities are tangible goods that people consume, use in manufacturing, or trade for value preservation.
Commodity market trends reflect how prices move over time, influenced by demand, supply, economic growth, geopolitics, climate, and investor behavior. Understanding these trends is vital for traders, investors, businesses, and policymakers because commodities impact everything—from inflation to national security.
In this essay, we’ll explore commodity market trends in detail, covering:
Types of commodities
Factors influencing commodity prices
Historical evolution of commodity trends
Current global trends
Sector-wise commodity insights
Role of technology and trading platforms
India’s role in global commodity markets
Risks and challenges
Future outlook
1. Types of Commodities
Commodities are broadly classified into two categories:
A. Hard Commodities
These are natural resources that must be mined or extracted.
Energy: Crude oil, natural gas, coal, uranium
Metals: Gold, silver, platinum, copper, aluminum
B. Soft Commodities
These are agricultural products or livestock.
Grains: Wheat, rice, corn, barley, soybeans
Cash crops: Cotton, coffee, sugar, cocoa, rubber
Livestock: Cattle, hogs, poultry
Each commodity has unique demand-supply cycles, trading methods, and price drivers, which create distinctive trends.
2. Factors Influencing Commodity Market Trends
Commodity trends are shaped by multiple interrelated factors.
A. Supply and Demand
A poor monsoon can reduce India’s wheat and rice production, pushing prices higher.
Rising industrial demand in China increases the global price of copper and steel.
B. Economic Growth
Strong GDP growth increases energy demand (oil, coal, gas).
Slowdowns reduce consumption and depress prices.
C. Geopolitical Events
Wars in oil-producing regions like the Middle East push crude prices up.
Trade sanctions disrupt supply chains, creating shortages.
D. Inflation and Currency Value
Commodities, especially gold and silver, are seen as a hedge against inflation.
A weaker US dollar generally boosts commodity prices since most are dollar-denominated.
E. Technological Advancements
Shale oil extraction revolutionized US energy supply.
Precision farming and GM crops increase agricultural yields.
F. Speculation and Investment Flows
Commodities are part of hedge funds’ and ETFs’ portfolios.
Heavy speculation can exaggerate short-term price swings.
3. Historical Evolution of Commodity Trends
Commodity markets have evolved through distinct eras:
A. Ancient and Medieval Period
Gold and silver were primary stores of value.
Spices, silk, and cotton drove global trade routes like the Silk Road.
B. Industrial Revolution (18th–19th Century)
Coal became central to powering factories and railways.
Agricultural markets expanded with colonial trade networks.
C. 20th Century
Oil replaced coal as the dominant energy source.
The Bretton Woods system (post-WWII) tied currencies to gold, which influenced commodity flows.
D. 21st Century
Commodities became financialized—futures, options, ETFs.
Climate change, ESG investing, and green energy are reshaping commodity dynamics.
4. Current Global Commodity Market Trends
A. Energy Commodities
Crude Oil – Prices remain volatile due to OPEC policies, US shale production, and geopolitics (Russia-Ukraine conflict, Middle East tensions).
Natural Gas – LNG demand is rising in Asia, especially India and China, while Europe shifts away from Russian supply.
Coal – Despite clean energy policies, coal demand remains strong in emerging markets like India due to electricity needs.
B. Metals
Gold – Functions as a safe-haven asset during inflation, recession fears, or geopolitical tension.
Silver – Dual role as industrial metal and safe haven. Solar panel demand is pushing industrial consumption.
Copper – Known as "Dr. Copper" because it reflects economic health. Demand is surging from EVs, batteries, and infrastructure.
Aluminum & Nickel – Essential in renewable energy technologies and lightweight transport manufacturing.
C. Agricultural Commodities
Grains – Climate change, supply chain disruptions, and fertilizer shortages drive volatility.
Coffee & Cocoa – Affected by weather shocks (El Niño) and global consumer demand.
Sugar & Cotton – Linked to biofuel trends, textile demand, and monsoon performance in India.
5. Sector-Wise Commodity Insights
A. Energy Sector
Oil demand is plateauing in developed countries but surging in Asia.
Renewable-linked commodities like lithium, cobalt, and rare earths are gaining importance.
B. Precious Metals
Gold remains the world’s ultimate crisis hedge.
Silver and platinum are benefiting from the green energy transition.
C. Base Metals
Copper and aluminum are crucial for infrastructure and EV adoption.
Supply disruptions in Africa and South America impact availability.
D. Agriculture
Population growth increases long-term demand for food commodities.
Climate change increases unpredictability—extreme droughts, floods, and pests.
6. Technology and Commodity Trading
Electronic Trading Platforms (MCX, CME, ICE) have made commodity markets global and fast-paced.
AI and Data Analytics help forecast weather impacts, demand patterns, and price trends.
Blockchain improves traceability in agricultural and mining commodities.
Algo-Trading has increased speculative flows and high-frequency trading.
7. India’s Role in Commodity Markets
India is both a major producer and consumer of commodities:
Gold & Silver: India is the second-largest consumer of gold, driven by cultural and investment demand.
Crude Oil: India imports over 85% of its crude needs, making it vulnerable to global price shocks.
Agriculture: Leading producer of rice, wheat, sugarcane, and cotton.
Coal: India is the second-largest coal producer but still imports due to quality mismatches.
Exchanges: MCX (Multi Commodity Exchange) and NCDEX (National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange) are the leading Indian platforms.
Government policies—like MSP (Minimum Support Price), import-export bans, and subsidies—also strongly influence domestic commodity trends.
8. Risks and Challenges in Commodity Markets
Price Volatility – Rapid swings can hurt producers, consumers, and investors.
Geopolitical Tensions – Wars, sanctions, and trade wars disrupt supply chains.
Climate Change – Unpredictable weather patterns affect agriculture and energy demand.
Technological Risks – Cyberattacks on trading platforms and supply chain disruptions.
Regulatory Risks – Changes in taxation, subsidies, and environmental laws affect trade.
9. Future Outlook for Commodity Market Trends
A. Energy Transition
The world is shifting towards renewables, EVs, and green hydrogen.
Demand for lithium, cobalt, nickel, and copper will surge.
B. Digital Commodities
Data, carbon credits, and even water rights may emerge as tradable commodities.
C. Inflation Hedge Investments
Investors will continue to use gold and silver as hedges against economic uncertainty.
D. Agriculture & Food Security
With rising global population (expected 10 billion by 2050), agriculture commodities will remain critical.
Precision farming, vertical farming, and biotech seeds will shape future supply.
E. India’s Growing Role
As one of the fastest-growing economies, India’s demand for energy, metals, and food will strongly influence global trends.
10. Conclusion
The commodity market is the backbone of the global economy, deeply tied to human survival, industrial growth, and financial systems. Its trends are not just numbers on a chart—they reflect global consumption patterns, political events, and technological changes.
In today’s interconnected world, understanding commodity market trends is essential for:
Traders who seek profit from price movements.
Businesses that need raw materials for production.
Governments that must ensure stability and security.
Investors looking for safe havens and diversification.
From gold and oil to wheat and copper, commodities are the foundation of every nation’s economic journey. As we move into a future shaped by green energy, climate change, and digitalization, the role of commodities will only grow stronger.
👉 In summary, the next era of commodity market trends will be defined by energy transition, technological disruption, and geopolitical rebalancing, making it one of the most exciting and unpredictable spaces in global trade.
CPI Data Impact (Consumer Price Index)1. Introduction to CPI
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is one of the most widely watched economic indicators in the world. At its core, CPI measures the average change over time in the prices that consumers pay for a basket of goods and services. This basket includes everyday essentials such as food, clothing, housing, transportation, healthcare, and entertainment. In simpler terms, CPI is a tool used to track inflation — the rise in the general price level of goods and services.
The reason CPI data carries such weight is because it directly affects the cost of living. When CPI rises, it means the purchasing power of money falls — people need more money to buy the same amount of goods and services. On the other hand, when CPI remains stable or falls, it signals controlled inflation or even deflation.
Every month, governments release CPI figures, and these numbers instantly capture the attention of central banks, investors, businesses, and the general public. This is because CPI not only reflects the current state of the economy but also guides crucial decisions related to interest rates, wages, investment strategies, and fiscal policies.
2. How CPI is Calculated
To understand its impact, it’s important to know how CPI is put together.
Basket of Goods & Services: Authorities create a list of items that represent what an average household typically consumes.
Food & Beverages
Housing & Utilities
Apparel
Transportation
Medical care
Recreation
Education
Miscellaneous goods
Weightage: Each category gets a weight based on its importance in household expenditure. For example, housing and food usually carry higher weights.
Data Collection: Price data is collected from retail stores, service providers, and online markets across the country.
Index Formula: The prices are compared with a base year (say 2010 = 100). If the index rises from 100 to 110, it means there has been a 10% increase in the price level.
Types of CPI Measures:
Headline CPI: Includes all items, even volatile ones like food and fuel.
Core CPI: Excludes food and energy because they fluctuate too much, giving a clearer picture of long-term inflation.
This method ensures CPI reflects the average change in prices felt by consumers, making it a direct measure of inflation.
3. Importance of CPI in the Economy
CPI data is not just about numbers; it has real-world implications:
Purchasing Power: CPI determines how much money is worth in terms of goods and services. If salaries don’t keep pace with rising CPI, people feel poorer.
Wages & Pensions: Many countries link wage hikes, pensions, and social security payments to CPI to protect citizens against inflation.
Tax Brackets: Some tax systems adjust brackets according to CPI so that inflation doesn’t push taxpayers unfairly into higher tax categories.
Business Planning: Companies use CPI to set prices, negotiate contracts, and forecast demand.
Government Policy: Policymakers rely on CPI to shape monetary and fiscal decisions.
4. CPI Data and Central Banks
One of the biggest reasons CPI data is so powerful is its influence on central banks. Institutions like the Federal Reserve (US), RBI (India), ECB (Europe), and BOJ (Japan) watch CPI numbers closely because inflation control is their primary responsibility.
If CPI is too high: Central banks usually raise interest rates to reduce money supply, making borrowing costlier and cooling down demand.
If CPI is too low or negative (deflation): They lower rates or inject liquidity to stimulate spending and investment.
For example, if US CPI comes in much higher than expected, markets immediately anticipate the Fed may raise interest rates. This triggers huge shifts in stock, bond, and forex markets.
5. Impact of CPI on Different Asset Classes
CPI data doesn’t stay in economics textbooks; it directly shakes global markets every time it’s released. Let’s explore the impact across major asset classes:
a. Stock Markets
High CPI (Inflation rising fast): Bad for stock markets in the short term. High inflation raises costs for companies (raw materials, wages, energy) and squeezes profit margins. Investors fear higher interest rates, which reduce future corporate earnings.
Low or stable CPI: Good for equities, as it signals controlled inflation, stable demand, and predictable interest rates.
Sectoral Impact:
Consumer staples (FMCG) may survive inflation better because people always buy essentials.
Technology and growth stocks suffer because their valuations depend on low interest rates.
Banks and financials sometimes benefit as higher rates improve lending margins.
b. Bond Markets
Bonds are highly sensitive to CPI data.
Rising CPI = Higher inflation = Future interest rates may rise = Bond prices fall.
Lower CPI = Bonds rally as investors expect stable or falling interest rates.
For example, a surprise jump in US CPI can cause a sharp sell-off in Treasury bonds within minutes.
c. Forex Market
CPI is a key driver of currency values.
Higher CPI = Expectation of rate hikes = Stronger currency.
Lower CPI = Rate cuts or dovish stance = Weaker currency.
Example: If India’s CPI jumps unexpectedly, the market may anticipate RBI rate hikes, strengthening the Indian Rupee against the US Dollar.
d. Commodities (Gold, Oil, etc.)
Gold: Seen as an inflation hedge. When CPI is high, investors rush to gold to preserve value.
Oil & Energy: Often the cause of rising CPI (fuel inflation). Their prices can rise further when CPI signals strong demand or supply constraints.
Food Commodities: High CPI often reflects higher food prices, influencing futures markets in grains, soybeans, sugar, etc.
6. CPI Data and Investors’ Behavior
CPI releases are like shockwaves in financial markets. Investors, traders, and analysts prepare days in advance for these numbers.
Expectations vs. Reality: If actual CPI matches forecasts, markets remain calm. But if CPI is higher or lower than expected, markets react violently.
Short-Term Traders: Use CPI releases for quick moves in forex, stocks, and commodities.
Long-Term Investors: Adjust portfolios based on CPI trends, shifting from growth stocks to defensive assets during inflationary times.
Hedging Strategies: Many hedge funds use derivatives like futures, options, and inflation-linked bonds to guard against CPI surprises.
7. Case Studies of CPI Shocks
a. US CPI in 2021-2022 (Post-COVID Inflation Spike)
After COVID-19, supply chain disruptions and stimulus spending caused US CPI to soar to 40-year highs. The Federal Reserve was forced to raise interest rates aggressively, leading to a global stock market correction, bond sell-offs, and a stronger US dollar.
b. India’s CPI and RBI Actions
India often battles food inflation due to monsoon impacts. A spike in food prices raises CPI quickly, forcing RBI to tighten monetary policy. This directly impacts borrowing rates for businesses and housing loans.
c. Eurozone Energy Crisis (2022)
The Russia-Ukraine conflict led to soaring energy prices in Europe. CPI in countries like Germany and the UK hit record highs, pushing the European Central Bank and Bank of England into aggressive rate hikes.
8. CPI Data in Global Context
CPI is universal, but its impact varies:
Developed Economies: Focus on core CPI, as food and energy form smaller shares of expenditure.
Developing Economies: Headline CPI is more important, since food and fuel dominate consumption.
Global Markets: US CPI carries the heaviest weight because the US Dollar is the world’s reserve currency. A higher-than-expected US CPI can shake global equity, forex, and commodity markets.
9. CPI vs. Other Inflation Measures
WPI (Wholesale Price Index): Tracks price changes at wholesale level; often a leading indicator of CPI.
PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditure, US): A broader measure used by the Fed.
GDP Deflator: Measures price changes across the economy, not just consumers.
CPI remains the most relatable and widely followed measure since it directly reflects household expenses.
10. How Traders Use CPI in Analysis
Volume & Price Action: Traders look at how markets react immediately after CPI release (volatility spikes).
Forward Guidance: They link CPI trends with central bank statements to predict interest rate cycles.
Technical + Fundamental Mix: Many combine CPI-driven sentiment with technical chart patterns for entries and exits.
Options Trading: CPI days often see huge spikes in implied volatility; options traders profit from straddles or strangles.
11. Criticism and Limitations of CPI
While CPI is powerful, it has limitations:
The basket of goods may not reflect actual consumption of all groups (urban vs. rural, rich vs. poor).
It doesn’t always capture asset inflation (like rising real estate prices).
Substitution bias: If beef prices rise, consumers may switch to chicken, but CPI still reflects beef inflation.
Globalization: Many goods are imported, so CPI may reflect international price shifts more than local demand.
12. Conclusion
CPI data is one of the most important numbers in economics. It is not just about tracking inflation but also about shaping central bank decisions, guiding government policies, influencing financial markets, and affecting every household’s cost of living.
A single CPI release can shake stock markets, move bond yields, strengthen or weaken currencies, and shift commodity prices. For investors and traders, understanding CPI is crucial because it links economic fundamentals to market movements.
In the modern interconnected world, where inflationary shocks in one country can spread globally, CPI has become more than just a domestic indicator — it is a global barometer of economic health. Whether you are a policymaker, investor, business owner, or simply a consumer, CPI impacts your daily financial reality in one way or another.
Cryptocurrency & Digital Assets1. Introduction
In the past decade, finance has seen a revolution that goes beyond banks, stock markets, and traditional currencies. This revolution is called cryptocurrency and digital assets. What started as a niche experiment with Bitcoin in 2009 has now become a global phenomenon worth trillions of dollars. Cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), and blockchain-based assets are redefining money, ownership, and trust in the digital era.
To understand this world, we need to cover not only the technical foundation but also the real-world applications, benefits, challenges, and risks. Let’s explore.
2. What Are Digital Assets?
At the core, a digital asset is anything of value stored electronically. This can include documents, music, art, or data. But in financial terms, digital assets refer to assets that exist purely in digital form and can be owned, transferred, or traded.
Examples:
Cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum)
Stablecoins (USDT, USDC)
Security tokens (digital representation of real-world securities)
NFTs (unique digital collectibles/art)
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Digital assets are usually recorded and verified using blockchain technology, which ensures transparency, immutability, and decentralization.
3. What is Cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a type of digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange, store of value, or unit of account. It is secured by cryptography, making it difficult to counterfeit or double-spend.
Key Features:
Decentralization – Not controlled by a single authority like banks or governments.
Blockchain-based – Transactions are recorded on a distributed ledger.
Cryptographic Security – Ensures authenticity and prevents fraud.
Peer-to-Peer Transactions – People can send money directly without intermediaries.
Global & Borderless – Works across countries with internet access.
4. The Origin of Cryptocurrencies
The story begins in 2008 when an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto released a whitepaper:
“Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.”
The idea was to create money outside of government control, relying on cryptography and decentralized networks.
In 2009, Bitcoin was launched. It introduced blockchain technology as a transparent ledger, enabling trust without banks.
From there:
2015: Ethereum introduced smart contracts.
2017–2018: ICO (Initial Coin Offering) boom.
2020–2021: Rise of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) and NFTs.
2022–2023: Market corrections, regulations, and institutional adoption.
2024 onward: Growth of CBDCs, tokenization, and AI integration.
5. How Cryptocurrencies Work
To understand cryptocurrencies, let’s break down the components:
a) Blockchain Technology
A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records all transactions.
Each block contains transaction data, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash.
Once added, blocks cannot be altered (immutability).
b) Mining & Consensus Mechanisms
Proof of Work (PoW): Used by Bitcoin. Miners solve puzzles to validate transactions.
Proof of Stake (PoS): Used by Ethereum 2.0. Validators stake coins to secure the network.
Other mechanisms: Delegated Proof of Stake, Proof of Authority, etc.
c) Wallets & Keys
To own cryptocurrency, you need a digital wallet.
Wallets use private keys (your password to access funds) and public keys (your address to receive funds).
d) Transactions
When you send Bitcoin, your transaction is broadcasted to the network.
Miners/validators verify and record it on the blockchain.
Once confirmed, it becomes permanent.
6. Types of Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin (BTC):
First cryptocurrency, digital gold.
Mainly used as a store of value.
Ethereum (ETH):
Introduced smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
Backbone of DeFi and NFTs.
Stablecoins (USDT, USDC, DAI):
Pegged to stable assets like the US dollar.
Reduce volatility, widely used in trading.
Altcoins (Litecoin, Ripple, Cardano, Solana, etc.):
Offer various improvements or innovations over Bitcoin/Ethereum.
Utility Tokens:
Used within specific platforms (e.g., Binance Coin, Chainlink).
Security Tokens:
Represent ownership in real assets (stocks, real estate).
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs):
Unique digital items (art, music, in-game assets).
7. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs became mainstream in 2021 when digital art sold for millions.
Unlike cryptocurrencies (fungible, interchangeable), NFTs are unique and indivisible.
Examples:
Digital artwork (Beeple’s $69 million sale)
Collectibles (NBA Top Shot)
In-game items (Axie Infinity)
Music rights & virtual real estate
NFTs represent a revolution in digital ownership.
8. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is a financial ecosystem built on blockchain, without intermediaries like banks.
Key elements:
Lending & Borrowing Platforms (Aave, Compound)
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) (Uniswap, PancakeSwap)
Yield Farming & Liquidity Mining
Synthetic Assets & Derivatives
Benefits:
Open to anyone with internet.
Transparent and programmable.
Higher returns compared to traditional banking.
9. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Governments are developing their own digital money, called CBDCs.
Unlike cryptocurrencies, CBDCs are centralized and backed by national banks.
Examples:
China’s Digital Yuan (e-CNY)
India’s Digital Rupee (pilot launched by RBI)
European Union exploring Digital Euro
CBDCs aim to combine the efficiency of digital assets with the trust of government money.
10. Advantages of Cryptocurrencies & Digital Assets
Decentralization – Reduced dependency on banks/governments.
Fast & Cheap Transactions – Cross-border payments in seconds.
Financial Inclusion – Access for unbanked populations.
Transparency – Blockchain records are public and verifiable.
Ownership Control – You truly own your assets (self-custody).
Innovation & Programmability – Smart contracts enable new business models.
Global Access – Works anywhere with internet.
Potential for High Returns – Many investors see massive growth.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets are more than just speculative investments—they represent a new paradigm for money, ownership, and trust in the digital age. While risks exist, the opportunities for innovation, financial inclusion, and global economic transformation are immense.
From Bitcoin’s vision of decentralized money to NFTs redefining art and CBDCs reshaping government-issued currency, the world of digital assets is evolving rapidly. We are witnessing a once-in-a-generation shift that could impact how humans trade, invest, and interact for decades to come.
Multi-Time Frame Analysis (MTF) — Explained SimplyWant to level up your trading decisions? Mastering Multi-Time Frame Analysis helps you see the market more clearly and align your trades with the bigger picture.
Here’s how to break it down:
🔹 What is MTF Analysis?
It’s the process of analyzing a chart using different time frames to understand market direction and behavior more clearly.
👉 Example: You spot a trade setup on the 15m chart, but you confirm trend and structure using the 1H and Daily charts.
🔹 Why Use It?
✅ Avoids tunnel vision
✅ Aligns your trades with the larger trend
✅ Confirms or filters out weak setups
✅ Helps you find strong support/resistance zones across time frames
🔹 The 3-Level MTF Framework
Use this to structure your chart analysis effectively:
Higher Time Frame (HTF) → Trend Direction & Key Levels
📅 (e.g., Daily or Weekly)
Mid Time Frame (MTF) → Structure & Confirmation
🕐 (e.g., 4H or 1H)
Lower Time Frame (LTF) → Entry Timing
⏱ (e.g., 15m or 5m)
🚀 If you’re not using MTF analysis, you might be missing critical market signals. Start implementing it into your strategy and notice the clarity it brings.
💬 Drop a comment if you want to see live trade examples using this method!
GBPUSD LIVE TRADE AND EDUCATIONAL BREAKDOWN FOR BEGINNERS 218PIPGBP/USD holds recovery gains near 1.3350 as US Dollar loses further ground
GBP/USD is trading near 1.3350 in Wednesday’s European session, extending Tuesday's 1% rally. The pair capitalizes on renewed US Dollar sell-off even as risk sentiment turns negative. Fedspeak and trade talks remain in focus.
WEEKLY ANALYSIS FOR BITCOIN/BT/BTCBitcoin is one everyone's radar with analysts expecting another bullish run. Prices are definitely looking bullish and I'm on board with the thesis that new highs will soon be delivered, but for now I'm bearish on the next week and think you can enter on better prices.
WEEKLY ANALYSIS TO HELP YOUR TRADING: Nasdaq, NQ, NAS100A pretty accurate week from my last video analysis if I do say so myself.
This week, I'm anticipating more bullish price action, however, there's also a strong chance for an inside bar which could have price working within last week's trading range. Based on the levels discussed in this video, price has reason to try and close bullish yet again, so I'll be watching price action for entries into longs and managing my risk accordingly.
Happy Trading,
The Meditrader
EURUSD LIVE TRADE AND EDUCATIONAL BREAKDOWNEUR/USD remains offered around 1.1350
EUR/USD trades well on the defensive for the second day in a row, revisinting the mid-1.1300s on the back of the continuation of the upside impulse in the US dollar. The move followed firmer US PMI data and news indicating the White House may be considering tariff cuts on Chinese imports.
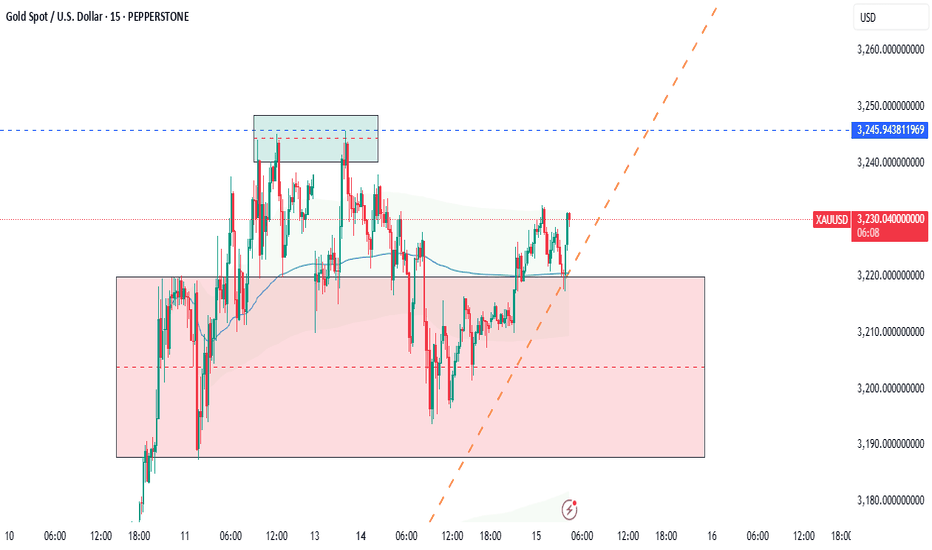
XAU LIVE TRADE AND EDUCATIONAL BREAKDOWNGold price approaches $3,300 mark amid persistent safe-haven demand
Gold price continues scaling new record highs through the Asian session on Wednesday and has now moved well within striking distance of the $3,300 round-figure mark. Persistent worries about the escalating US-China trade war and US recession fears amid the ongoing US tariff chaos continue to boost demand for gold.
GOLD LIVE TRADE AND EDUCATIONAL BREAKDOWN 18K PROFITGold price retains its positive bias above $3,200 amid US-China trade war, bearish USD
Gold price regains positive traction as US tariff uncertainty continues to underpin safe-haven assets. Bets for aggressive Fed rate cuts in 2025 keep the USD depressed and also benefit the XAU/USD pair.
EURUSD LIVE TRADE AND EDUCATIONAL BREAK DOWN SHORTEUR/USD bounces off 1.1300, Dollar turns red
After bottoming out near the 1.1300 region, EUR/USD now regains upside traction and advances to the 1.1370 area on the back of the ongoing knee-jerk in the US Dollar. Meanwhile, market participants continue to closely follow news surrounding the US-China trade war.
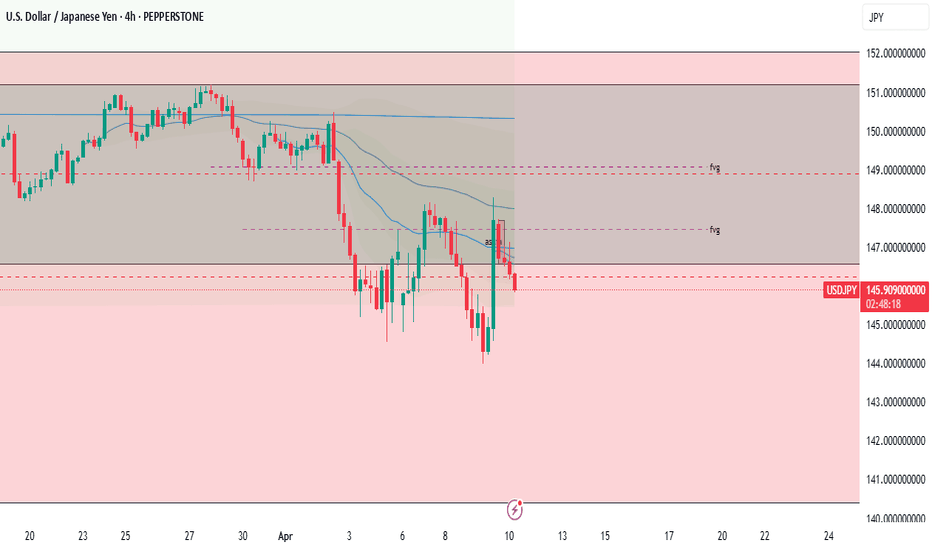
USDJPY SHORT LIVE TRADE AND EDUCATIONAL BREAKDOWNUSD/JPY tumbles below 147.00, awaits US CPI for fresh impetus
USD/JPY has come under intense selling presure and drops below 147.00 in the Asian session on Thursday. The US-China trade war escalation and the divergent BoJ-Fed policy expectations underpin the Japanese Yen and weigh heavily on the pair amid a renewed US Dollar downtick. US CPI awaited.
EURUSD LIVE TRADE EDUCATIONAL BREAK DOWNEUR/USD holds gains below 1.1000 ahead of US CPI release
EUR/USD is tirmimng gains while below 1.1000 in the European session on Thursday. The Euro gains on the German coalition deal and Trump's 90-day pause on reciprocal tariffs. Meanwhile, the US Dollar finds demand on profit-booknig ahead of the US CPI data release.
XAU QUICK SHORT TRADE LIVE TRADE AND EDUCATIONAL BREAKDOWN Gold price (XAU/USD) touches a fresh weekly top, around the $3,132-3,133 area heading into the European session as concerns about escalating US-China trade tensions continue to drive safe-haven flows. Moreover, fears that tariffs would hinder economic growth and boost inflation turn out to be another factor that benefits the precious metal's status as a hedge against rising prices. Apart from this, bets for multiple interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve (Fed) push the non-yielding higher for the second successive day.
XAU LONG LIVE TRADE AND EDUCATIONAL BREAKDOWN Gold extends rally to $3,050 area as safe-haven flows dominate markets
Gold preserves its bullish momentum and trades near $3,050 in the second half of the day. Further escalation in the trade conflict between the US and China force markets to remain risk-averse midweek, allowing the precious metal to capitalize on safe-haven flows.
EURUSD LONG 100 PIP MOVE LIVE TRADE AND EDUCATIONAL BREAK DOWNEUR/USD trades decisively higher on the day above 1.1000 on Wednesday as the US Dollar (USD) stays under persistent selling pressure on growing fears over a recession as a result of the US trade war with China. Later in the American session, the Federal Reserve will release the minutes of the March policy meeting.
EURUSD LIVE TRADE 100 PIP MOVE EUR/USD trades decisively higher on the day above 1.1000 on Wednesday as the US Dollar (USD) stays under persistent selling pressure on growing fears over a recession as a result of the US trade war with China. Later in the American session, the Federal Reserve will release the minutes of the March policy meeting.