Global Banking and Financial Stability1. The Role of Global Banking in the World Economy
Global banking institutions include commercial banks, investment banks, universal banks, central banks, and cross-border financial intermediaries. These institutions perform several core functions that support global economic growth:
1.1 Capital Allocation
Banks collect deposits and channel them into loans for businesses, households, and governments. Efficient capital allocation ensures that productive sectors—manufacturing, technology, infrastructure—receive the funding they need to expand.
1.2 Facilitating Global Trade
Banks finance trade through letters of credit, export financing, and currency exchange. International transactions require trust, documentation, and risk management, which banks provide by acting as intermediaries.
1.3 Payment Systems
Modern banking supports real-time payments, cross-border remittances, SWIFT messaging, and digital fund transfers. These systems form the highway on which global money flows.
1.4 Risk Management and Hedging
Banks design instruments such as derivatives, currency swaps, and interest-rate futures, helping businesses manage forex, commodity, and credit risks. This stabilizes global supply chains and investment strategies.
2. The Architecture of Global Financial Stability
Financial stability means the system continues functioning even when faced with shocks—like economic downturns, geopolitical events, or market volatility. Several pillars support this:
2.1 Robust Banking Regulations
After the 2008 financial crisis, global regulators introduced stronger frameworks:
Basel III norms improved capital adequacy and liquidity requirements.
Stress testing ensures banks can survive market shocks.
Macroprudential regulations prevent systemic risks like credit bubbles.
These safeguards ensure banks hold enough capital and liquidity to absorb losses.
2.2 Central Bank Oversight
Central banks like the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, Bank of England, RBI, and others play a major role in maintaining stability by:
Setting interest rates
Controlling inflation
Providing emergency funding through lender-of-last-resort facilities
Supervising financial institutions
Regulating payment systems
Their decisions directly affect borrowing costs, credit supply, currency values, and overall financial stability.
2.3 International Institutions
Bodies such as the IMF, World Bank, Bank for International Settlements (BIS), and Financial Stability Board (FSB) create global standards, provide financial aid during crises, and coordinate cross-border regulations. Their involvement becomes crucial during sovereign debt crises and currency collapses.
3. Key Risks to Global Banking Systems
Despite advancements in regulation, global banks face several systemic risks:
3.1 Credit Risk
The possibility that borrowers fail to repay loans. High default rates—especially in corporate or real-estate sectors—can weaken bank balance sheets.
3.2 Liquidity Risk
When banks cannot meet short-term obligations due to insufficient cash. Liquidity crises often trigger bank runs or emergency central bank interventions.
3.3 Market Risk
Changes in interest rates, currency prices, or asset valuations can reduce the value of a bank’s holdings. Sudden rate hikes or stock market crashes may cause large unrealized losses.
3.4 Operational and Cyber Risk
Digitalization increases the risk of cyberattacks on banks, potentially disrupting payment systems or exposing customer data. Technology failures also pose operational threats.
3.5 Contagion Risk
Because banks are interconnected, the failure of one major bank or a country’s financial system can create chain reactions globally. This was seen during:
The 2008 Lehman Brothers collapse
The 2011 Eurozone debt crisis
The 2023 regional bank failures in the U.S.
Interconnectedness magnifies both strength and vulnerability.
4. The Drivers of Financial Stability in the Current Global Environment
4.1 Strong Bank Balance Sheets
Global banks today hold higher capital buffers and liquidity reserves. This increases their ability to withstand market shocks.
4.2 Digital Transformation in Banking
Technology improves efficiency, risk monitoring, and compliance. Real-time data analytics help banks detect stress early and manage exposures more effectively.
4.3 Banking Consolidation
Mergers create larger, stronger banks with diversified operations. This reduces individual institution risk but can also create “too-big-to-fail” challenges.
4.4 Improved Crisis Management Frameworks
Many countries now have:
Deposit insurance
Resolution mechanisms for failing banks
Better stress tests
Contingency funding arrangements
These tools reduce panic and ensure orderly handling of distressed institutions.
5. Emerging Challenges for Global Financial Stability
5.1 Geopolitical Tensions
Trade wars, sanctions, and military conflicts affect currency stability, commodity prices, and cross-border capital flows.
5.2 Inflation and Interest Rate Volatility
High inflation forces central banks to raise rates. Rapid hikes increase borrowing costs and can strain banking sectors—especially in emerging markets.
5.3 Shadow Banking Risks
Non-bank financial institutions—hedge funds, fintech lenders, investment funds—play a growing role but operate with less regulation. Their instability can spill into the banking system.
5.4 Climate and Sustainability Risks
Climate-related disasters, ESG compliance pressures, and the transition to green economies impact credit portfolios, insurance markets, and investment strategies.
5.5 Digital Currencies and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
While innovation brings opportunities, it also poses risks:
Volatile crypto markets
Lack of regulatory frameworks
Potential loss of monetary policy control
Cyber-vulnerabilities
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) may reshape global banking in unpredictable ways.
6. The Path Forward: Strengthening the Future of Global Finance
Ensuring long-term global financial stability requires coordinated efforts across governments, banks, international organizations, and the private sector. Key priorities include:
6.1 Strengthening Regulation and Supervision
Continuous evolution of Basel norms, cyber-resilience frameworks, and cross-border regulatory cooperation is essential.
6.2 Enhancing Financial Inclusion
Stable banking systems must serve not just corporates but also small businesses and individuals. Digital banking, UPI-type platforms, and low-cost financial services reduce inequality and strengthen economies.
6.3 Building Resilient Digital Infrastructure
Banks must invest heavily in cybersecurity, cloud reliability, AI-driven risk analysis, and fraud prevention.
6.4 Sustainable and Responsible Banking
Green financing, climate-risk assessment, and ESG compliance will increasingly shape global credit flows and stability metrics.
6.5 Crisis Preparedness
Regular stress tests, liquidity buffers, and emergency response frameworks help ensure rapid containment of shocks without widespread disruption.
Conclusion
Global banking is the lifeline of modern economies, facilitating capital flow, trade, investment, and innovation. Financial stability depends on well-regulated, well-capitalized, and well-supervised banking institutions that can withstand economic and geopolitical shocks. As globalization deepens and new risks like cyber threats, climate change, and digital currencies emerge, maintaining stability will require constant vigilance, updated regulatory frameworks, and resilient financial infrastructure. Ultimately, the strength of the global banking system shapes the strength of the global economy, influencing growth, employment, and prosperity for billions of people.
Microsoft Corp Shs Cert Deposito Arg Repr 0.03333333 Shs
No trades
Trade ideas
PERFECT MSFT SHORTWe have a really strong timeframe alignment on NASDAQ:MSFT , presenting us with a great shorting opportunity.
Weekly
If we start top down from the weekly, MSFT had a strong and fast rally but has faced strong rejection on the upper side of its long term upward channel. Price may now look to retrace to its previous long-term swing high after this rejection. We also see volatility constriction through Bollinger Bands, indicating potential for large price moves and volume to occur soon.
Daily
On the daily chart we see a strong rejection of the daily 50 ema and resistive levels after a downside breakout.
Hourly
For the entry on the 1hr timeframe we are looking at a large head and shoulder formation, with a trend rejection and a strong rejection of the 1hr 100ema.
I am targeting the previous long-term swing high at 470 as my singular TP.
Goodluck-nfa.
MSFT — Bullish Structure Intact Above 373.22, Targeting 739.88.Microsoft remains in a well-defined long-term bullish structure despite the current pullback from the 0.40–0.50 Fibonacci resistance cluster. The recent decline appears corrective in nature and does not signal any structural weakness as long as the stock preserves its main support foundation.
Key Support (Primary Structural Level): 373.22
The level at 373.22 represents the most critical demand zone on the chart.
It marks:
The origin of the previous bullish impulse,
A zone of strong institutional accumulation,
The base that
continues to anchor the long-term trend.
As long as price stays above 373.22, the broader upward cycle remains intact.
Fibonacci Expansion Targets (Long-Term Investor Levels)
The current impulsive leg projects the following upside targets:
483.97 (0.333)
509.67 (0.40)
548.04 (0.50)
593.32 (0.618)
643.96 (0.75)
701.51 (0.90)
739.88 (1.00 — primary long-term extension)
These levels correspond to strategic zones where institutional models anticipate consolidation or profit-taking.
Market Structure & Investor Outlook
The long-term trend remains strongly bullish.
The current pullback is normal retracement behavior.
Secondary demand pockets sit at 446.75 and 413.75 if the pullback deepens.
Macro structure remains fully intact above 373.22.
Bullish Continuation Scenario (Base Case)
If MSFT holds above 483.97 and regains momentum, the price can progress through:
509 → 548 → 593 → 643 → 701 → 739.88
This represents the natural continuation path of the current expansion.
Bearish Scenario (Limited & Non-Structural)
The only valid bearish scenario for now is a return to retest the key support at 373.22.
This move would represent:
A technical retest,
A liquidity sweep,
A refresh of institutional demand, not a trend reversal
As long as price holds 373.22, the long-term bullish structure remains unchanged.
Conclusion
Microsoft continues to demonstrate strong long-term structural integrity.
The only bearish possibility is a corrective move back toward the 373.22 support, after which the broader trend is expected to resume toward the long-term targets: 509, 548, 593, 643, 701, and 739.88.
MSFT Holding a Tight Range — Levels I’m Watching for Nov 26
MSFT spent most of the session stuck inside that tight 475–478 pocket. It never really committed in either direction, and when a stock trades like this, it usually means bigger players are positioning quietly ahead of the next move. The recovery off the morning shakeout was solid, but every attempt toward 478 kept getting absorbed. That kind of steady rejection usually hints that there’s something sitting overhead — not sellers necessarily, but hedging pressure.
On the 15-minute view, you can see how controlled the move has been. Nothing impulsive, nothing sloppy. Just slow buying with shallow pullbacks, then that familiar hesitation right under the ceiling. The candles toward the end of the day say a lot: smaller bodies, slower pace, and a clear unwillingness to push into that resistance.
If you check the 1-hour GEX chart I uploaded below, the reason for that hesitation becomes pretty obvious. There are heavy call walls stacked right above price. That whole stretch from 479 into the low 480s is packed with hedging resistance, which usually acts like a lid until volume picks up. Below price, the GEX landscape is cleaner — good put support around 470 and deeper at 465 — which explains why MSFT hasn’t been eager to unwind.
So for Nov 26, I’m mainly watching two things:
A clean break above 478 gives MSFT a chance to move into 479, and if that gets taken out with real momentum, then 482.5 becomes the next logical magnet. But if price stays stuck under that band, it’s just more coiling.
If MSFT loses 475 and stays below it, then the market probably wants to revisit 472 or even 470 to reload.
Option Angle
Calls only make sense if price can finally get above 478 with strength — that’s where the air pockets sit between GEX levels. MSFT usually moves quickly when it clears a hedging cluster.
Puts only make sense if 475 breaks cleanly. Below that, 472 and 470 open up. If MSFT stays above 475, puts decay fast because the structure leans bullish.
Disclaimer
This is not financial advice. It’s just my personal view based on chart behavior and options data. Always trade your own plan and manage your risk.
MSFT: another 1-2, 1-2 countMSFT: I count MSFT as starting a new 5-wave sequence at the 2022 bear market low and have completed Waves 1, 2, and i of 3.
Wave 2 corrected a bit more than 38.2% and Wave ii of 3 so far has corrected 38.2% as well. It's common for a Wave 2 to correct 50% so both degrees of Wave 2 are short.
MSFT is a long-term hold for me and I see no reason to be concerned.
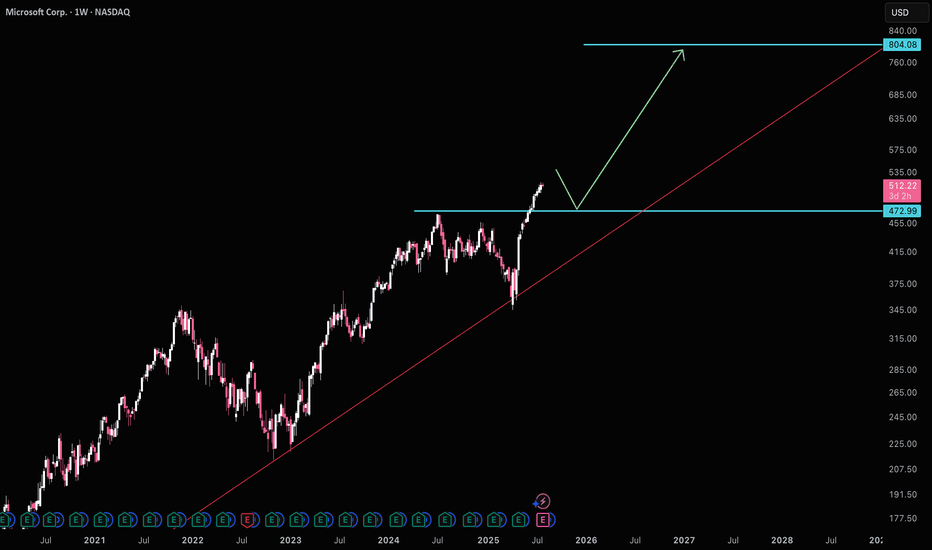
MSFT: PAST RESISTANCE = FUTURE SUPPORTMSFT pierced above resistance on a weekly chart. Last week, it fell back to that area of resistance. We can observe this principal gong forward: PAST RESISTANCE = FUTURE SUPPORT .
It is not a guaranteed ruling, but it is a principle that is time-tested and there is some evidence that psychological levels do exist in the markets. Maybe this one will pan out.
:)
Midterm Stock Forecast for MicrosoftNASDAQ:MSFT appears set for a healthy correction from $472 to $420, consistent with H1 overextension and cooling RSI. Despite powerful fundamentals—Azure growth, AI integration, and strong enterprise demand—the stock is pricing in perfection. A move to $420 would offer a balanced risk-reward area as markets reassess AI monetization timelines.
Capital Flows: Concept and Characteristics1. Concept of Capital Flows
Definition
Capital flows refer to the movement of financial resources between countries. These resources include investments in financial markets, real assets, loans, and banking transfers. The underlying motivation behind these flows is to seek higher returns, diversify risks, fund economic development, or benefit from interest rate differentials and exchange rate expectations.
In macroeconomic terms, capital flows form the capital account and financial account of a country’s balance of payments (BoP). When foreign investors invest in a country, it records capital inflows. When domestic investors invest abroad, it results in capital outflows.
Types of Capital Flows
Capital flows can be broadly categorized into two major types:
A. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
FDI involves long-term investments where a foreign entity acquires ownership or controlling stake in a domestic company. Examples include:
Setting up factories
Buying significant equity in a foreign company
Mergers and acquisitions
FDI is typically stable, growth-enhancing, and associated with technology transfer and employment generation.
B. Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI)
These are investments in financial assets such as stocks, bonds, and other securities without acquiring management control. FPIs are highly liquid and sensitive to:
Interest rates
Market sentiment
Global financial conditions
Due to their volatility, FPIs are often called hot money flows.
C. Other Capital Flows
Bank loans and deposits
External commercial borrowings (ECBs)
Sovereign bond purchases
Remittances (often classified separately)
Short-term speculative flows
2. Importance of Capital Flows in the Global Economy
A. Financing Development
Capital flows help developing economies fill investment gaps. Low domestic savings often restrict capital formation, and foreign investment helps fund infrastructure, manufacturing, and services.
B. Enhancing Financial Market Efficiency
Global capital flows integrate financial markets, increasing liquidity and improving price discovery. This allows companies to raise funds more efficiently and reduces the cost of capital.
C. Boosting Productivity and Innovation
FDI brings new technologies, management practices, and skills that enhance productivity. Exposure to global competition also pushes domestic firms to innovate and modernize.
D. Supporting Balance of Payments Stability
Capital inflows help countries finance current account deficits. For example, if a nation imports more than it exports, foreign investments can help cover the gap.
E. Influencing Exchange Rates
Large inflows appreciate the domestic currency, while outflows lead to depreciation. Exchange rate movements, in turn, influence trade competitiveness and inflation.
3. Characteristics of Capital Flows
Capital flows vary in size, stability, duration, and impact. The following are key characteristics that define their behavior:
A. Mobility
In today’s digital, globalized financial system, capital flows are highly mobile. Investors can shift funds across borders with the click of a button. This mobility increases liquidity but also contributes to volatility.
For instance:
Rising US interest rates may trigger outflows from emerging markets within hours.
A geopolitical tension may cause investors to rapidly move towards safe-haven assets like gold or US Treasury bonds.
B. Volatility
Not all capital flows are stable. Portfolio investments, short-term loans, and speculative flows are extremely sensitive to:
Global interest rate changes
Investor sentiment
Currency movements
Political stability
A sudden reversal of flows can trigger financial instability, known as capital flight. Emerging markets are especially vulnerable because their financial systems are relatively smaller and more fragile.
C. Risk–Return Driven
The direction of capital flows is predominantly determined by risk–return calculations. Investors compare:
Interest rate differentials (e.g., “carry trade”)
Expected currency changes
Economic growth prospects
Political risks
Financial stability metrics
Countries with stable policies, higher returns, and sound macroeconomics attract more inflows.
D. Impact on Currency and Exchange Rates
Large capital inflows strengthen the domestic currency because foreign investors must purchase local currency to invest. This can lead to:
Cheaper imports
More expensive exports
On the other hand, capital outflows weaken the currency, sometimes resulting in inflationary pressures.
E. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Nature
Capital flows differ in duration:
FDI is long-term, stable, and less likely to exit suddenly.
Portfolio flows are short-term and highly reversible.
Short-term debts increase vulnerability during crises.
Countries with higher shares of short-term external debt face greater risks during global financial shocks.
F. Pro-Cyclicality
Capital flows often move in tandem with global economic cycles:
During global booms, flows rush into emerging markets seeking higher returns.
During recessions or crises, investors retreat to safer assets (“flight to safety”).
This pro-cyclical nature can amplify economic fluctuations in recipient countries.
G. Influence of Global Liquidity Conditions
Global financial conditions, especially monetary policies of major central banks like the US Federal Reserve and ECB, heavily influence the magnitude and direction of capital flows.
For example:
Low interest rates in the U.S. push investors toward emerging markets for higher yields.
Tightening monetary policy triggers widespread outflows.
H. Policy Sensitivity
Capital flows respond quickly to changes in:
Tax policies
Capital control regulations
FDI norms
Banking sector reforms
Political developments
Stable and transparent policies attract long-term capital, while unpredictable regulations discourage investors.
I. Impact on Domestic Financial Stability
Large capital inflows can create:
Asset bubbles (stocks, real estate)
Credit booms
Over-leveraging
Similarly, sharp outflows can lead to:
Currency crashes
Stock market declines
Liquidity shortages
Thus, managing capital flows is crucial to financial stability.
4. Policy Tools to Manage Capital Flows
Countries use several strategies to handle volatile capital movements:
A. Capital Controls
Restrictions on inflows or outflows to reduce vulnerabilities.
Examples:
Limits on foreign ownership
Taxes on short-term flows
Minimum holding periods
B. Exchange Rate Interventions
Central banks may buy or sell foreign currency to stabilize exchange rates.
C. Macroprudential Policies
Limits on external borrowing
Stress tests for banks
Higher reserve requirements
D. Building Forex Reserves
Large reserves help soften the impact of outflows and boost investor confidence.
Conclusion
Capital flows are a vital engine of global economic growth and integration. They help countries access investment, improve productivity, strengthen financial markets, and support development. At the same time, their volatility, mobility, and sensitivity to global events pose significant risks, especially for developing economies.
Understanding the concept, types, and characteristics of capital flows is essential for designing effective policies that maximize benefits while reducing vulnerabilities. Proper management of these flows enables countries to achieve sustainable economic growth and maintain financial stability in a highly interconnected world.
Why is Microsoft Stock $MSFT dropping hard?Microsoft just did what every impatient trader hates… after a massive rally, the candles are shrinking, emotions are rising, and here comes the correction everyone said ‘couldn’t happen.’ Today I’ll show you—using pure supply and demand—why MSFT is being magnetically pulled back into the monthly demand imbalance like a toddler to a candy shop. No fundamentals, no drama… just price action, imbalances, and patience. Let’s dive in.
Microsoft Monthly Supply & Demand Analysis
After Apple’s strong monthly correction setup, Microsoft (MSFT) is showing the exact same pattern — but even cleaner.
This is what I love when I teach traders to learn to trade stocks using pure price action and supply and demand imbalances. You don’t need news, earnings, or any guru opinion — everything is already priced in at the higher timeframes. Just like I explained in the Supply and Demand Free Course , the bigger timeframes tell you what the professionals already did months ago.
Let’s break it down.
Candles Shrinking = Momentum Weakening
Fast-forward to mid/late 2025:
- The wide-bodied candles disappeared
- Small-bodied candles appeared
- Then came the big bearish candle
This is classic momentum decay. This is exactly when most traders start acting emotionally:
- They zoom into 5-minute charts
- Their IQ drops by 50 points
- They forget the trend
- They forget the imbalance
- They become chart zombies
But price action never lies — we’re simply seeing exhaustion after a massive markup.
MSFT Selling Pressure Activated — Time to Short!🔥 MSFT Bearish Profit Playbook — Thief-Style Layer Attack Activated! 🔥
Asset: MSFT — Microsoft Corporation (NASDAQ)
Style: Swing / Day-Trade Playbook 📉💼
📉 Plan: Bearish Pressure Play — Smart Sell-Side Thief Approach
Microsoft is showing potential exhaustion on the upside, and this setup focuses on a structured bearish move using a layered sell-limit strategy (Thief Layer Method) 😎🕵️♂️.
🎯 Entry Strategy (Thief Layer Method)
Using the thief-style multi-layer approach, we stack multiple sell-limit orders at different levels to catch premium liquidity:
Sell Limit Layers:
$500, $490, $480
(You can increase or adjust layers based on your own risk tolerance.)
This method aims to fade upward pushes, catching price exhaustion during liquidity grabs.
🛑 Stop Loss (Risk Control)
This is the Thief SL @ $510 🛑
Note: Dear Ladies & Gentlemen (Thief OG’s), I’m not recommending that you use only my stop-loss. It’s your money — your rules. Manage your risk like a pro. 💼⚠️
🎯 Target (Exit Zones)
We are aiming toward strong support zones + potential oversold zones where bearish momentum may slow.
Main Target: $450
Trap may form — escape with profits before the market police catch us 🚓💨
Note: Dear Ladies & Gentlemen (Thief OG’s), I’m not recommending using only my target. Exit where you feel safe and profitable. 🏦✨
📊 Market Summary (Clean, TV-Safe Explanation)
Bearish attempt based on overextended zones
Layered entries help clip premium during upside wicks
Targeting liquidity pockets near support
SL above structural invalidation
Setup respects TradingView House Rules: No financial advice, no promises, no signals, educational thief-style humor only ✔️
🔗 Related Pairs to Watch (Correlation Insights)
Because MSFT is a heavyweight in tech + NASDAQ index weighting:
1️⃣ NASDAQ:QQQ (NASDAQ 100 ETF)
Strongly correlated
If QQQ rejects from local resistance → MSFT bearish play strengthened
QQQ weakness = tech sector weakness
2️⃣ AMEX:SPY (S&P500 ETF)
Broader market risk sentiment
SPY pullback often pressures mega-caps like MSFT
3️⃣ NASDAQ:AAPL (Apple Inc.)
Moves similarly during liquidity rotations
Apple weakness = added pressure to mega-cap tech basket
4️⃣ NASDAQ:NVDA (Nvidia Corp.)
High-beta tech name
When NVDA loses momentum, MSFT downside probability increases through sector rotation
5️⃣ NASDAQ:GOOGL (Alphabet Inc.)
If large-cap tech corrects collectively, MSFT rarely moves opposite
Perfect correlation watch ⚡
Watching these pairs helps confirm bearish bias through sector-wide confirmation, not isolated signals.
✨ “If you find value in my analysis, a 👍 and 🚀 boost is much appreciated — it helps me share more setups with the community!”
⚠️ Disclaimer:
This is a thief-style trading strategy just for fun.
Educational only — not financial advice. Trade at your own risk. 😄🕵️♂️
MSFT WARNING!Here is a closer view of the chart I posted back on Oct 5, 2024, for a nice profitable -25% drawdown.
This time will be far more profitable.
Here is a breakdown of the chart.
- Up against a 38-year trendline.
- A rare 5-wave rising wedge.
- A H & S with a head test
- Big Ass Gap Below
- Double top M pattern that CRACKED!
- Rising Bearish Wedge.
This is just getting started!
Bulls, if you didn't make your money in MSFT yet and are trying to squeeze a little bit more profits bc you are too damn greedy. Then you deserve what you get next.
THANK YOU for getting me to 5,000 followers! 🙏🔥
Let’s keep climbing.
If you enjoy the work:
👉 Boost
👉 Follow
👉 Drop a solid comment
Let’s push it to 6,000 and keep building a community grounded in truth, not hype.
Microsoft Wave Analysis – 20 November 2025- Microsoft broke support levels 500.00, 490.00
- Likely to fall to support level 465.00
Microsoft recently broke the support zone between the support levels 500.00, 490.00 (low of wave A from September) and the 38.2% Fibonacci correction of the upward impulse from April.
The breakout of this support zone accelerated the C-wave of the active ABC correction (4) from July.
Microsoft can be expected to fall further to the next support level 465.00, target price for the completion of the active C-wave.
Caution Ahead: Strong Financials, but Market Conditions May ShifDespite the strong financial report, from a technical perspective, we've reached a point where caution is essential, and market conditions should be monitored closely. Even though the financial performance is robust, there’s a possibility that the situation could shift unexpectedly, which might lead to market changes that challenge the strong financial outlook.
MSFT — Daily & Weekly Structure Check (20 Nov 2025)Context
Price failed to clear $554–$555, the 1:1 measured move from the May flag.
A bearish double top formed on the daily; the downswing was kicked off by an island reversal.
Daily Structure
Today price lost $493–$492 (valley/neckline), confirming the double-top breakdown.
Volume confirms: heavier on down days, lighter on bounces.
Price is below the 5-day MA; the 21-day MA is acting as dynamic resistance.
The 50-day and 100-day MAs have also been lost, reinforcing intermediate weakness.
Weekly Context
The major trend remains intact above the longer MA, but the 21-day MA is now broken, aligning the weekly picture with daily weakness.
Key Levels
Resistance: $493–$492 (now breakdown/neckline); $554–$555 (measured-move cap).
Supports on the path lower: intermediate help from the 50/100-day MAs; the 200-day sits beneath the gap.
Target on confirmation: $430–$429 (top of the FVG) via a 1:1 measured move from the double-top.
Scenarios
Bearish continuation (primary): A weekly close below $493–$492 keeps momentum pointed to $430–$429. Expect potential pauses at the 50/100-day MAs; failure there leaves the FVG magnet in play with the 200-day below.
Bullish repair (secondary): A swift reclaim of $493–$492 followed by acceptance back above the 21-day MA would neutralize the breakdown and defer the measured-move path.
Triggers
Downside trigger: Friday close < $493–$492 → activates the 1:1 toward $430–$429.
Upside repair trigger: Daily close back > $493–$492 and back over the 21-day MA → negates immediate breakdown risk.
Risk & Invalidation
Bearish view invalidates on sustained closes back above $493–$492 with the 21-day MA reclaimed as support.
Until then, trend-following bias favors lower highs / lower lows on the daily.
Summary
Rejection at $554–$555, a double-top breakdown through $493–$492, confirming volume, and loss of the 5/21/50/100-day MAs all align bearish in the intermediate term.
The weekly trend is still up overall, but breaking the 21-day brings it into agreement with the daily.
Watch $493–$492 into the weekly close; it’s the pivot between a measured-move drive to $430–$429 and a repair back into range.
MSFT at a Turning Point – Key Levels to Watch for Nov. 201-Hour Outlook
MSFT has been in a clean down-channel, but today's late-session recovery finally broke above the short-term lower trendline. Price is now pushing into a critical resistance zone around $502–$505, which has rejected multiple times this week.
Key levels from the 1-hour structure:
* First resistance: $498.50
* Main rejection zone: $502–$505
* Bull breakout confirmation: $510 → opens $513–$515
* Downside support: $490, then $485
Momentum is improving — MACD is curling up and the candle structure is shifting away from heavy sell pressure. But MSFT still needs to reclaim $502.50 with conviction before bulls gain control for tomorrow.
1-Hour Bias:
Cautiously bullish if above $498.50, but still inside a larger downtrend unless $502–$505 breaks.
15-Minute Outlook (For Traders)
Short-term price action shows MSFT breaking out of a wedge and retesting the breakout cleanly around $493–$494. Strong impulsive candles came in after the retest.
What matters for tomorrow:
* As long as MSFT holds above $493–$494, buyers can push into $498–$500.
* A clean move through $500 → $502.50 would trigger momentum traders.
* If MSFT rejects early at $498–$500, expect a pullback to $490–$492.
15-Min Trading Thoughts:
* Bull setup: Pullback to $494–$496 with bounce confirmation → targets $500 / $502.
* Bear setup: Rejection at $502–$505 → targets $492 then $488.
Momentum is stronger on the 15-min chart than the 1-hour, which means MSFT has room to squeeze early but may struggle at $502–$505 unless volume shows up.
How GEX Supports the Levels
From the GEX (Gamma Exposure) chart:
Bullish elements:
* Highest positive call interest sits above $510–$515, meaning if MSFT breaks $505, market makers hedge by buying → upward acceleration.
* Light resistance around $500–$502, so price can push into that zone easily.
Bearish elements:
* Strong negative GEX / put support at $485, acting as the floor for the week.
* Heavy put walls between $480–$485, making breakdowns less likely unless market-wide selling hits.
GEX Summary:
* Break $505 → path to $510–$513 opens quickly.
* Lose $490 → hedging pressure drives it toward $485.
Option Trading Suggestions Based on GEX
For tomorrow's session:
Bullish Idea
If MSFT breaks and holds over $502.50:
* Consider 505C or 510C, same-week expiration.
* Safer choice: Next-week 510C (less decay).
Reason: GEX shows low resistance between $505 → $510.
Bearish Idea
If MSFT rejects $502–$505 early:
* Consider 495P or 490P.
* Conservative approach: next-week 490P.
Reason: Price tends to fade back into the $492–$488 pocket when the breakout fails.
Final Thoughts
MSFT is at a key pivot zone. Both 1-hour and 15-minute charts show recovery momentum, but the chart won’t turn fully bullish unless $502.50–$505 breaks. Expect volatility around that zone tomorrow.
Disclaimer
This analysis is for educational purposes only and is not financial advice. Always manage risk and trade with a plan.
$MSFT likely heading lower soon.Microsoft has received some downgrades recently, has a clear double top, and now a breakdown through the lower end of the range.
Not sure yet how deep this move runs, but (1), (3), and (5) remain the immediate downside targets.
I’ll be playing this tighter than usual given we’re entering seasonal bullishness. Not sure it shows up this year, but it’s something to stay aware of.
MSFT USMicrosoft is currently playing out a beautiful Batman pattern : having broken through the sloping trendline, retested, and also retested at 50 SMA.
However, yesterday, the market pulled the stock above the support level of 490-493, and traders may attempt a rebound after seeing a false breakout.
At the very least, going long in such a situation is very dangerous.
MSFT 1HR 11/18/2025Description of the Chart
This analysis is shared strictly for educational purposes and is not financial advice. It is intended to illustrate chart-reading techniques, structure mapping, and scenario planning.
The chart is a 1-hour price chart of Microsoft Corp. (MSFT) with technical analysis markings focused on an ABCD harmonic pattern, bearish momentum, and downside targets.
Main Pattern (ABCD Structure)
The chart shows an ABCD harmonic setup:
(A) – a swing high
(B) – a swing low
(C) – a lower high
(D) – a deeper low completing the harmonic pattern
You’ve labeled the full structure with orange lines showing the ABCD sequence.
Fibonacci Arc / Fib Levels
From point C, a rainbow-colored Fibonacci arc cluster is drawn downward toward the D area.
These levels overlap the price action around (D), marking potential retracement and continuation zones.
Entry Zone + Bearish Breakout
The chart marks an ENTRY point just after price hits (D).
There is a red rectangular zone labeled BEARISH BREAKOUT showing where price broke below support.
A 1st Target is indicated directly underneath this breakout zone.
Negative Pressure Zone
Above point (C), there is an orange dashed outline labeled:
“negative pressure”
This signifies bearish pressure preventing upward continuation likely indicating failing bullish momentum.
Targets Failed
To the right of point C, a dashed orange line says “TARGETS FAILED”, suggesting expected bullish continuation levels above were not reached.
EPS Levels / Resistance Lines
Labeled as EPS, possibly upcoming earnings or expected price zones.
Support Zone Around D
A red dashed support line runs across the chart near point (D).
Price breaks below this area, confirming the bearish structure.
Downside Targets
1ST Target
Marked in orange, located just beneath the bearish breakout area.
SECOND TARGET
A large orange box in the lower part of the chart, around the 400–420 USD region.
This is a deeper bearish target zone.
Other Elements
Current price is shown near 492.50.
RSI (Relative Strength Index) indicator box shows 36.98 RSI, indicating weakening momentum.
Summary
The chart shows a bearish ABCD harmonic pattern completing at (D).
After the completion, price breaks downward into a bearish breakout zone, triggering a short entry toward:
Target 1 (short-term)
Target 2 (major bearish zone around 400–420)**
Upward continuation levels (“EPS”) failed due to negative pressure around point (C).
NOT