XAUUSD – Pullback Only, Trend Not Broken YetGold is not reversing — this is a controlled pullback inside a broader bullish structure.
Price has rejected the upper zone and is now retracing to rebalance liquidity. As long as the key demand below holds, the bullish bias remains intact.
Key Technical View
Market is still respecting the rising structure.
Current drop is corrective, not a confirmed bearish CHoCH.
Strong demand cluster below aligns with trendline + prior imbalance → high reaction area.
Primary Plan – Trend BUY
Focus on BUY opportunities at discounted zones.
Wait for price reaction and structure confirmation — no chasing candles.
Upside Targets
TP1: 4,449
TP2: 4,477
TP3: 4,494
Risk Note
If price fails to hold the demand zone, step aside and reassess — patience > prediction.
➡️ Bias stays bullish until structure says otherwise.
Forextrading
XAUUSDXAUUSD is still in an uptrend. If the price can remain above $4420, further price growth is expected.
🔥Trading futures, forex, CFDs and stocks carries a risk of loss.
Please consider carefully whether such trading is suitable for you.
This content is not financial advice. Always conduct your own financial due diligence.
>>GooD Luck 😊
❤️ Like and subscribe to never miss a new idea!
NZDJPY: Bullish After Trap 🇳🇿🇯🇵
NZDJPY will likely bounce after a false violation
of the underlined intraday horizontal support.
Expect a pullback to 90.33 level.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
XAUUSD H3 – Liquidity in Control Near ATH
Gold is trading in a sensitive zone just below all-time highs, where liquidity, Fibonacci extensions, and trend structure are converging. Price action suggests a controlled rotation rather than a clean breakout, with clear reaction levels on both sides.
TECHNICAL STRUCTURE (H3)
Gold remains in a broader bullish structure, with higher lows supported by an ascending trendline.
The recent impulse confirmed bullish intent, but price is now stalling near premium liquidity, signalling potential short-term distribution.
Market behaviour shows buy-the-dip dynamics, while upside extensions are being tested selectively.
KEY LEVELS FROM THE CHART
Upper liquidity / extension zone:
Fibonacci 2.618 extension near the top band
This area represents profit-taking and sell-side liquidity, especially if price reaches it with weak momentum.
Sell reaction zone:
4412 – 4415 (Fibonacci 1.618 + prior ATH reaction)
A classic area for short-term rejection if price fails to break and hold above.
Buy-side focus:
4480
This level acts as a buy-on-pullback zone, aligned with trendline support and prior bullish structure.
Expected flow:
Price holds above 4480 → attempts to push toward ATH → potential extension into the 2.618 zone.
Failure to hold 4480 → rotation back toward lower structure for liquidity rebalance.
MARKET BEHAVIOUR & LIQUIDITY LOGIC
Current structure favours reaction-based trading, not chasing breakouts.
Liquidity above ATH is attractive, but the market may need multiple attempts or a deeper pullback before a sustained breakout.
As long as higher lows are respected, pullbacks remain corrective.
MACRO CONTEXT – DXY BACK ABOVE 99
The US Dollar Index (DXY) has climbed above 99 for the first time since December 10, gaining 0.14% on the day.
A firmer USD can slow gold’s upside momentum in the short term.
However, gold’s ability to hold structure despite a stronger dollar highlights underlying demand and strong positioning.
This divergence suggests gold is not purely trading off USD weakness, but also off liquidity, positioning, and risk hedging flows.
SUMMARY VIEW
Gold remains structurally bullish on H3
Short-term price action is driven by liquidity near ATH
4480 is the key level defining bullish continuation
Upside extensions may require consolidation or pullbacks before a clean break
In this environment, patience and level-based execution matter more than directional bias.
Gold Price Analysis: Why XAUUSD Holds Firm Above $4,400PEPPERSTONE:XAUUSD Why Gold Is Holding Firm Above $4,400 (9 January 2026)
🔍📈 Welcome back to Trade with DECRYPTERS
📊 MARKET OVERVIEW
On January 8, 2026, gold prices were volatile as commodity index rebalancing created early selling pressure, but the market later stabilized.
Spot gold dipped near $4,407 before recovering and closing around $4,477, posting a modest daily gain.
US gold futures settled slightly lower, reflecting cautious positioning ahead of key US economic data.
Investor focus remained on upcoming nonfarm payrolls for clues on Fed rate cuts.
🧩 KEY FUNDAMENTALS
🏦 Fed Policy
Rates at 3.50–3.75%
Expectations of 1–2 cuts in 2026 support gold via lower real yields.
💵 US Dollar & Yields
Firmer USD and stable to higher Treasury yields create short-term pressure.
Longer-term trend remains supportive for gold.
📉 Inflation
Cooling but still above target.
Sticky inflation keeps gold attractive as a hedge.
🏦 Central Bank Buying
Strong and ongoing buying from China, Poland, Brazil.
Provides a solid long-term price floor.
📈 Investor & ETF Flows
Expected to remain strong in 2026.
Reinforces upside momentum.
🌍 Geopolitical Risks
Elevated global tensions:
US–Venezuela
Middle East
Trade and debt risks
Driving sustained safe-haven demand.
🌐 GEO POLITICS
🇺🇸 US Venezuela Crisis
Maduro’s capture, oil control plans, and tanker seizures triggered strong safe-haven flows.
Highly bullish for gold.
🧊 Greenland Tensions
US threats and Denmark–NATO concerns raise transatlantic and Arctic risks.
Supportive for gold.
🔥 Middle East & Iran
Protests, Iran tensions, and Israel–Iran risks sustain regional instability.
🌍 Broader Global Risks
Russia–Ukraine
Gaza
US–China rivalry
Arctic competition
Add structural uncertainty.
⚖️ RISK ON / RISK OFF ANALYSIS
🔄 Risk On vs Risk Off
🟢 Risk On
Higher stocks
Firmer USD
Stable or higher yields
→ Pressure gold
🔴 Risk Off
Lower stocks and yields
Weaker USD
Higher volatility
→ Support gold
📊 US 10Y Yields
Around 4.17–4.18%
Stable near highs limits upside, but not bearish.
💵 USD DXY
Around 98.9
Mild short-term headwind.
📈 Equities (S&P 500)
Near record highs.
Risk-on bias diverts flows from gold.
📉 Volatility (VIX)
Around 15
Low volatility caps gold rallies.
🟡 Gold Price
Around $4,460–$4,465
Holding $4,400–$4,500 range after ~66% 2025 surge.
🧠 Key Dynamic
Mixed risk-on / risk-off signals pressure gold.
Geopolitics keep a risk-off premium intact.
🛡️ Structural Support
Expected Fed cuts + central bank buying reduce downside risk.
📰 KEY INSIGHTS FROM CREDIBLE SOURCES
🛢️ Venezuela Oil Control:
US actions and long-term involvement plans increase geopolitical and energy uncertainty, supportive for gold.
💡 Oil Extraction Claims:
Statements about extracting massive oil value raise inflation and supply risk concerns.
🏦 Mortgage Bond Purchases:
Large-scale bond buying resembles QE, fueling inflation and debasement fears.
🧊 Greenland Focus:
Arctic control proposals heighten global tensions and policy unpredictability.
🔥 Middle East & Iran Tensions:
Warnings and unrest elevate regional risk.
🏛️ Fed Influence:
Political involvement in Fed leadership adds uncertainty around rates and inflation.
📊 Market Reaction:
Bullion and oil bids during equity and bond weakness highlight gold’s defensive role.
✅ CONCLUSION
Gold remains structurally supported despite short-term volatility driven by a risk-on market backdrop and firmer yields.
Expected Fed rate cuts, cooling but sticky inflation, and sustained central bank buying continue to limit downside risks.
Elevated geopolitical tensions — from Venezuela and the Middle East to Greenland and broader global rivalries — preserve a strong safe-haven premium.
While stronger equities and a firmer dollar cap immediate upside, gold’s ability to hold the $4,400–$4,500 range signals underlying strength.
🙌 SUPPORT THE ANALYSIS
👍 Like
💬 Comment your key levels
📈 Share your charts
🚀 Let’s grow together
Best Regards,
M. Moiz Khattak
Founder
🟡 TRADE WITH DECRYPTERS 📊
Shaping the Future of Responsible FinanceSustainable and ESG Investing:
Sustainable investing, often referred to as ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing, represents a transformative shift in how capital is allocated in global financial markets. Unlike traditional investment approaches that focus primarily on financial returns, ESG investing integrates non-financial factors—such as environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance—into investment decision-making. This approach recognizes that long-term value creation depends not only on profits but also on how companies interact with the environment, society, and their stakeholders.
Understanding ESG Investing
ESG investing is built on three core pillars. The Environmental component examines how a company impacts the natural world. This includes factors such as carbon emissions, energy efficiency, waste management, water usage, and commitment to renewable energy. Companies that actively manage environmental risks and contribute to climate solutions are often viewed as better positioned for long-term sustainability.
The Social dimension focuses on how a company manages relationships with employees, customers, suppliers, and communities. Issues such as labor practices, workplace diversity and inclusion, human rights, product safety, and community engagement fall under this category. Strong social performance can enhance brand reputation, employee productivity, and customer loyalty.
The Governance pillar evaluates the quality of a company’s leadership and decision-making structures. This includes board independence, executive compensation, shareholder rights, transparency, and ethical business practices. Good governance reduces the risk of fraud, mismanagement, and regulatory penalties, thereby protecting investor interests.
Evolution of Sustainable Investing
Sustainable investing is not a new concept, but its scope and influence have expanded significantly in recent decades. Initially, it began with ethical or socially responsible investing (SRI), where investors excluded certain industries such as tobacco, alcohol, or weapons based on moral considerations. Over time, the approach evolved from exclusionary screening to a more comprehensive integration of ESG factors into financial analysis.
Today, ESG investing is increasingly data-driven and systematic. Institutional investors, asset managers, pension funds, and even retail investors now consider ESG metrics alongside traditional financial indicators. Global initiatives, such as the United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment (UN PRI), have further accelerated adoption by encouraging investors to incorporate ESG considerations into their investment processes.
Why ESG Investing Matters
One of the key drivers of ESG investing is the growing recognition that ESG risks are financial risks. Climate change, for example, poses significant threats to businesses through extreme weather events, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer preferences. Companies that fail to adapt to these challenges may face higher costs, disrupted operations, and declining valuations.
Similarly, poor social practices—such as unsafe working conditions or discriminatory policies—can lead to legal liabilities, reputational damage, and employee unrest. Weak governance structures can result in corporate scandals, financial misreporting, and loss of investor confidence. By identifying and managing these risks early, ESG investing aims to enhance long-term risk-adjusted returns.
Moreover, ESG investing aligns capital with broader societal goals. It supports the transition to a low-carbon economy, promotes social equity, and encourages responsible corporate behavior. In this sense, ESG investing serves as a bridge between financial markets and sustainable development.
ESG and Financial Performance
A common misconception is that sustainable investing requires sacrificing returns. However, numerous studies suggest that companies with strong ESG performance often demonstrate competitive or even superior financial outcomes over the long term. Effective ESG practices can lead to operational efficiencies, innovation, better risk management, and stronger stakeholder relationships.
For instance, companies investing in energy efficiency and renewable resources may reduce operating costs and regulatory risks. Firms with inclusive workplace cultures may benefit from higher employee engagement and innovation. Strong governance can improve strategic decision-making and capital allocation. While short-term market fluctuations may still occur, ESG-focused companies are often better equipped to navigate long-term challenges.
ESG Investing Strategies
Investors can adopt ESG investing through various strategies. Negative or exclusionary screening involves avoiding companies or sectors that do not meet certain ESG criteria. Positive screening focuses on selecting companies with strong ESG performance relative to their peers. ESG integration incorporates ESG factors directly into financial analysis and valuation models.
Another approach is thematic investing, which targets specific sustainability themes such as clean energy, water conservation, healthcare access, or gender diversity. Impact investing goes a step further by aiming to generate measurable social or environmental impact alongside financial returns, often in areas such as education, affordable housing, or renewable infrastructure.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its rapid growth, ESG investing faces several challenges. One major issue is the lack of standardized ESG reporting. Different rating agencies may assign varying ESG scores to the same company due to differences in methodologies and data sources. This inconsistency can make it difficult for investors to compare companies accurately.
Another concern is greenwashing, where companies exaggerate or misrepresent their sustainability efforts to attract ESG-focused capital. Without robust disclosure and verification, investors may struggle to distinguish genuine ESG leaders from those making superficial claims.
Additionally, ESG factors can be complex and subjective. Balancing financial performance with ethical considerations may involve trade-offs, and not all investors share the same values or priorities. These challenges highlight the need for better regulation, transparency, and investor education.
The Future of ESG Investing
The future of sustainable and ESG investing appears increasingly influential and mainstream. Governments and regulators worldwide are introducing stricter disclosure requirements related to climate risks and sustainability reporting. Advances in data analytics, artificial intelligence, and satellite monitoring are improving the quality and availability of ESG data.
Investor demand is also expected to grow, particularly among younger generations who prioritize sustainability and purpose-driven investing. As awareness of global challenges such as climate change, inequality, and resource scarcity increases, ESG considerations are likely to become an integral part of investment decision-making rather than a niche strategy.
Conclusion
Sustainable and ESG investing represents a fundamental shift in the philosophy of finance—from short-term profit maximization to long-term value creation that accounts for environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and strong governance. By integrating ESG factors into investment decisions, investors can better manage risks, identify opportunities, and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable global economy. As financial markets continue to evolve, ESG investing is poised to play a central role in shaping the future of responsible and resilient capitalism.
CHFJPYThe overall trend for CHFJPY remains upward, but the price is currently in an overbought condition, as indicated by the RSI indicator in the overbought zone. This may signal a potential price correction. We expect that if the price fails to break through $199, a short-term decline is possible. Consider selling in the red zone.
🔥Trading futures, forex, CFDs and stocks carries a risk of loss.
Please consider carefully whether such trading is suitable for you.
This content is not financial advice. Always conduct your own financial due diligence.
>>GooD Luck 😊
❤️ Like and subscribe to never miss a new idea!
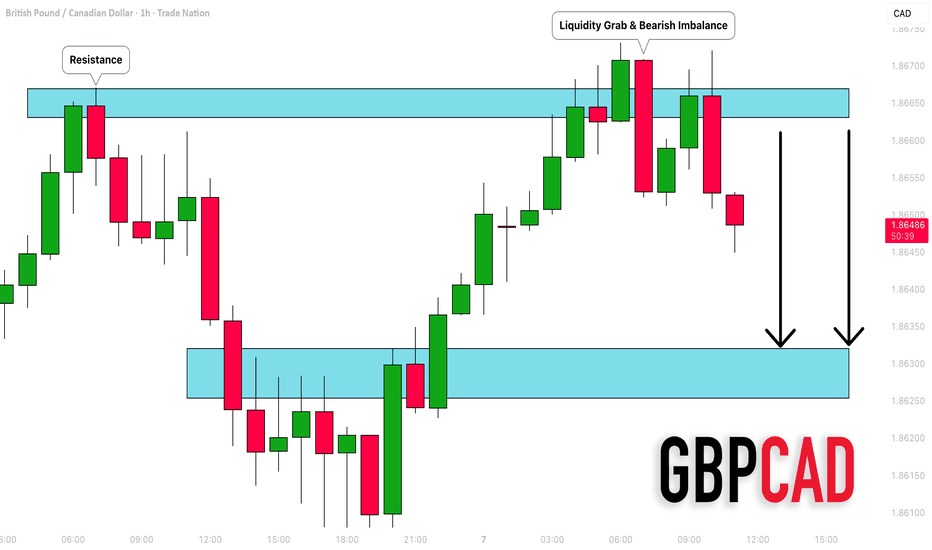
GBPCAD: Bearish Move After a Trap 🇬🇧🇨🇦
I took a short position on GBPCAD this morning
after the price made a false violation of the underlined resistance
and dropped, forming a selling imbalance candle.
I expect that the pair will drop more and reach 1.86323 level.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
XAUUSD (H2) – Liam View: Buy liquidity pullback.1) Macro snapshot (Venezuela headlines = faster repricing)
Since Maduro was reportedly detained, Venezuela’s market has reacted aggressively — your note highlights the IBC index surging +74.71% in just two sessions and +156% over 30 days, showing a rapid “repricing” of political risk and expectations. For gold, this kind of backdrop usually means bigger swings + liquidity sweeps: the market can flip between risk-on bursts and renewed safe-haven demand.
➡️ So the best play today is still level-based execution, not chasing candles.
2) Chart read (H2) – Uptrend intact, but it needs a clean pullback
From your H2 chart:
The broader structure is still bullish, but price is in a short-term pullback after the recent push up.
The key level is the 0.618 Buy Zone: 4414–4417 — a classic re-entry area (liquidity + fib confluence).
Above, we have Buyside Liquidity near the recent highs — that’s the magnet if buyers regain control.
3) Trade plan (clear Entry / SL / TP) ✅ Scenario A (priority): BUY the 0.618 pullback
Buy zone: 4414 – 4417 Stop loss (SL): below 4406 (or safer: below the most recent H2 swing low) Take profit (TP):
TP1: 4460–4470 (recent rebound high area)
TP2: sweep Buyside Liquidity (above the highs)
TP3: if the breakout holds, continue towards the upper resistance band on your chart
Logic: In a bullish structure, the 0.618 pullback is often the cleanest “re-buy” entry — especially when headlines trigger sharp dips and fast rebounds.
✅ Scenario B: Shallow pullback → buy only with confirmation
If price doesn’t reach 4414–4417 and only dips lightly:
Wait for a lower-TF confirmation (M15/H1 shift / rejection)
Take a smaller continuation buy and aim for a quick 8–12$ move
⚠️ Scenario C (scalp only): SELL after a buyside sweep and rejection
If price runs the highs (buyside liquidity sweep) and then prints a strong rejection:
You can sell scalp back into 4460–4445
SL: above the sweep high
Not a long-term bearish call while the rising structure is still valid.
4) Key note (headline week)
Venezuela headlines can keep volatility elevated, so:
Avoid entering mid-candle
Use zones + confirmation
Reduce size if spreads widen
If I had to pick one clean trade today: wait for the 0.618 buy zone (4414–4417), then buy for a push into buyside liquidity.
XAUUSD (H1) – Bullish channel intact, short pullback...Market context
On January 7, spot gold and silver both saw short-term selling pressure.
Spot gold slipped toward 4450–4455 USD/oz after a recent rally.
Spot silver dropped below 79 USD, reflecting broader short-term profit-taking across precious metals.
This pullback looks technical and corrective, rather than a reversal of the broader bullish trend. The macro backdrop remains supportive: geopolitical risks, long-term central bank demand, and expectations of easier monetary policy continue to underpin precious metals.
Technical view – H1 (Lana’s perspective)
Price is still respecting a rising price channel, showing healthy trend structure despite the current retracement.
Key observations from the chart:
The ascending channel remains valid; higher highs and higher lows are intact.
Price has reacted from the upper half of the channel, triggering short-term selling into sell-side liquidity.
The dotted midline and channel support are acting as dynamic reaction zones.
The recent drop appears to be a liquidity sweep / correction, not a breakdown.
This kind of pullback is common after strong impulsive legs and often provides better positioning for trend continuation.
Key levels to watch
Sell-side reaction (short-term pressure)
Near the channel midline and upper resistance, price may remain choppy.
Expect volatility while sell-side liquidity is being absorbed.
Buy-side interest zones
4458 – 4463: First reaction zone inside the channel.
4428 – 4400: Stronger support aligned with channel base and prior structure.
Acceptance above these zones favors bullish continuation.
Fundamental angle
Short-term weakness in gold and silver is driven mainly by profit-taking after recent highs.
Broader fundamentals remain constructive:
Ongoing geopolitical uncertainty
Strong central bank demand
USD valuation and global risk sentiment
These factors suggest that dips are more likely to be corrective opportunities, not trend-ending signals.
Lana’s trading mindset 💛
Avoid chasing price during pullbacks.
Respect the channel structure and wait for price to come into value.
Look for clear confirmation at support zones before engaging.
As long as the channel holds, the bullish bias remains valid.
This analysis reflects a personal technical view for educational purposes only. Always manage risk carefully.
XAUUSD Rejection From Resistance | Bearish Continuation SetupGold is currently trading below a well-defined resistance zone around 4,470–4,485, where price has faced multiple rejections. The structure suggests lower highs and weakening bullish momentum on the 15-minute timeframe.
As long as price remains below this resistance, the bias stays bearish. A rejection from this area opens the door for a move back into the support zone near 4,430, with a deeper continuation toward the final target around 4,395–4,400.
This setup is based on range rejection + resistance hold, offering a clear risk-to-reward opportunity for intraday traders.
Trade Plan:
Sell Zone: 4,465 – 4,485
Stop Loss: Above 4,490
Targets: 4,430 → 4,400
⚠️ Wait for confirmation and always manage risk properly.
Why Reserves Are Important1. Reserves as a Shield Against Economic Shocks
One of the primary reasons reserves are important is their ability to protect an economy from external and internal shocks. Global economies are exposed to unpredictable events such as financial crises, commodity price fluctuations, pandemics, wars, and sudden capital outflows. When such shocks occur, reserves allow governments and central banks to respond quickly without destabilizing the economy.
For example, during a balance of payments crisis, a country may face pressure on its currency due to high import bills or capital flight. Adequate foreign exchange reserves enable the central bank to intervene in the currency market, supply foreign currency, and stabilize the exchange rate. Without sufficient reserves, a country may be forced into sharp devaluation, leading to inflation, reduced purchasing power, and social unrest.
2. Ensuring Currency Stability and Confidence
Reserves are essential for maintaining confidence in a nation’s currency. Investors, traders, and international partners closely monitor the level of a country’s reserves to assess its ability to meet external obligations such as imports, debt repayments, and trade settlements. High reserves signal financial strength and credibility, while low reserves can trigger panic and speculative attacks on the currency.
Stable reserves help smooth excessive volatility in exchange rates. While most modern economies follow market-determined exchange rates, central banks often intervene to prevent extreme fluctuations that can harm exporters, importers, and overall economic planning. Thus, reserves act as a stabilizing force, supporting orderly functioning of foreign exchange markets.
3. Supporting International Trade and Payments
International trade relies heavily on trust and liquidity. Countries need foreign currency reserves to pay for essential imports such as crude oil, machinery, technology, fertilizers, and defense equipment. If reserves are insufficient, imports may be disrupted, leading to shortages, rising prices, and slowed economic growth.
Reserves ensure that trade commitments can be honored even during periods of low export earnings or global downturns. This is particularly important for developing and emerging economies, where export revenues may depend heavily on a few commodities or external demand conditions. By maintaining reserves, countries can continue trade smoothly and avoid economic disruptions.
4. Managing External Debt and Financial Obligations
Another key importance of reserves lies in managing external debt. Governments and corporations often borrow from international markets in foreign currencies. Repayment of this debt requires adequate foreign exchange availability. Strong reserve levels reassure lenders and credit rating agencies that the country can meet its debt obligations on time.
Adequate reserves reduce the risk of default and lower borrowing costs. Countries with weak reserve positions often face higher interest rates, stricter borrowing terms, or loss of access to global capital markets. Therefore, reserves directly contribute to financial credibility and long-term fiscal sustainability.
5. Crisis Management and Emergency Preparedness
Reserves are crucial during emergencies. Whether it is a global financial crisis, a natural disaster, a pandemic, or geopolitical tension, reserves provide immediate financial resources to respond effectively. Governments can use reserves to stabilize markets, support critical sectors, fund imports of essential goods, or provide economic stimulus.
For instance, during global crises, capital flows can reverse sharply, leading to liquidity shortages. Countries with strong reserves are better positioned to absorb such shocks without resorting to drastic measures like capital controls, import restrictions, or emergency bailouts. In this sense, reserves function like insurance—costly to build but invaluable in times of need.
6. Enhancing Investor Confidence and Economic Growth
Investor confidence is strongly linked to reserve adequacy. Foreign investors consider reserve levels when making decisions about direct investments, portfolio flows, and long-term projects. Healthy reserves indicate macroeconomic stability, disciplined policy management, and lower risk.
When investors feel confident, capital inflows increase, supporting economic growth, job creation, and technological advancement. On the other hand, declining reserves can trigger capital outflows, stock market volatility, and reduced investment. Thus, reserves indirectly contribute to sustainable economic development by creating a stable investment environment.
7. Supporting Monetary Policy Effectiveness
Reserves strengthen the effectiveness of monetary policy. Central banks rely on reserves to manage liquidity conditions and influence interest rates without causing excessive exchange rate volatility. For example, when tightening monetary policy, central banks may need to manage capital inflows that put upward pressure on the currency. Reserves allow them to intervene without losing policy independence.
In addition, reserves provide flexibility to implement counter-cyclical policies—tightening during booms and easing during downturns—without risking external instability. This policy space is especially valuable for emerging economies facing volatile global capital flows.
8. Strategic and Geopolitical Importance
Beyond economics, reserves have strategic and geopolitical significance. Countries with strong reserve positions have greater autonomy in decision-making and reduced dependence on external assistance. They are less vulnerable to external pressure from international institutions or foreign governments.
Gold and strategic commodity reserves also serve as long-term stores of value and symbols of national strength. In times of geopolitical uncertainty, reserves can act as a safeguard against sanctions, trade disruptions, or financial isolation.
9. Importance of Reserves at Micro Levels
The concept of reserves is not limited to governments. Businesses maintain cash reserves to manage operational risks, invest in opportunities, and survive downturns. Similarly, households keep savings as reserves to handle emergencies, job losses, or medical expenses. At every level, reserves provide security, flexibility, and peace of mind.
10. Balancing Reserves with Efficient Use
While reserves are essential, maintaining them involves costs, such as opportunity costs and management challenges. Excessive reserves may tie up resources that could otherwise be invested in growth-enhancing activities. Therefore, the goal is not merely to accumulate reserves but to maintain an optimal level that balances safety, liquidity, and efficiency.
Conclusion
Reserves are a cornerstone of economic stability and resilience. They protect against shocks, stabilize currencies, support trade and debt management, enhance investor confidence, and provide strategic independence. In a world characterized by uncertainty and rapid change, reserves act as a powerful buffer that allows economies to navigate challenges with confidence and control. Whether at the national, corporate, or household level, reserves represent preparedness, discipline, and long-term vision. Their importance cannot be overstated, as they form the foundation upon which sustainable growth and financial security are built.
GBPJPY: Classic Bullish Pattern 🇬🇧🇯🇵
GBPJPY violated a horizontal resistance of a narrow
accumulation range on a daily time frame.
It provides a strong bullish signal.
Expect a rise to 212.5 level.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
GBPUSD: BoS Trading 🇬🇧🇺🇸
I see a confirmed bullish break of structure on GBPUSD on a daily.
After a breakout, the market retest a broken structure and we see
a strong buying imbalance on an hourly time frame.
Expect more growth today.
Goal - 1.3575
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
XAUUSDHello Traders! 👋
What are your thoughts on GOLD?
After a strong bullish rally, Gold has entered a range-bound consolidation phase between clearly defined support and resistance zones.
At the moment, price is trading within the range, and positions taken in the middle of the range carry elevated risk, as price can reverse sharply from either side and trigger stop losses.
Trading Plan:
In the short term, the preferred strategy is to wait for a confirmed breakout from the range:
1–Bullish scenario: A clean break above the resistance zone, followed by a pullback and continuation to the upside
2–Bearish scenario: A confirmed breakdown below the support zone, followed by a pullback and continuation to the downside
Please Don’t forget to like and share your thoughts in the comments! ❤️
USDCHFUSDCHF: If the price can remain above 0.79259, there is a possibility of an upward price movement. Consider buying in the red zone.
🔥Trading futures, forex, CFDs and stocks carries a risk of loss.
Please consider carefully whether such trading is suitable for you.
This content is not financial advice. Always conduct your own financial due diligence.
>>GooD Luck 😊
❤️ Like and subscribe to never miss a new idea!
ETHEREUM POI BREAKOUT SETUP – SMART MONEY TARGETING HIGHER LEVELEthereum is currently trading in a well-defined bullish market structure, respecting higher highs and higher lows while approaching a key resistance zone. The price has already shown strong impulsive buying pressure from the support zone, confirming that smart money accumulation is in control.
The presence of Equal Highs (EQH) earlier in the structure indicates a liquidity grab, which was followed by a strong expansion move. This behavior often signals institutional participation, preparing the market for continuation rather than reversal.
At the current level, Ethereum is consolidating just below resistance, forming a healthy pause. A clean breakout and hold above this resistance zone would open the path toward higher premium levels, where momentum traders are likely to step in aggressively.
If a short-term pullback occurs, the last low remains a critical bullish defense level. As long as price holds above this level, the bullish bias remains intact and dips are expected to be buying opportunities, not weakness.
This setup represents a classic smart money continuation model — liquidity taken, structure respected, and expansion loading.
Smart Money Selling Below Major Resistance on GBPUSDGBP/USD is currently trading within a critical zone on the 1-hour timeframe after a clear buy-side liquidity sweep above previous highs. The market has already collected liquidity from the upside, which is often a sign of smart money distribution rather than continuation. Price reaction near the marked resistance zone confirms the presence of strong selling pressure.
Following the liquidity grab, the market delivered a clear Break of Structure (BOS) to the downside, indicating a potential shift in short-term momentum. Price is now consolidating below resistance, suggesting a classic distribution phase where institutions may be building short positions.
As long as price remains below the resistance zone and fails to reclaim previous highs, the bearish bias remains valid. The equal highs and sell-side liquidity resting below current price make downside targets more attractive. A continuation move could drive price toward the nearest sell-side liquidity and the higher timeframe support zone.
Traders should wait for confirmation such as bearish candle formations or a break-and-retest structure before entering positions. Risk management remains essential, as invalidation of this setup would occur on a sustained move above the resistance zone.
XAUUSD Bullish Structure | Liquidity Grab → BOS → Premium TargetGold (XAUUSD) is currently unfolding a high-probability Smart Money Concept (SMC) bullish setup on the 1H timeframe, clearly showing how institutional flow is driving price action. The market initially engineered a sell-side liquidity sweep, trapping weak sellers below equal lows before delivering a strong impulsive move to the upside. This liquidity grab from the discount zone highlights the presence of smart money accumulation at lower prices.
Following the liquidity sweep, price respected the discount zone, formed a solid base, and then produced a clean Break of Structure (BOS), confirming a bullish shift in market structure. This BOS validates that buyers are now in control and that the previous bearish pressure has been absorbed. The strong bullish candles after BOS reflect momentum expansion, often seen at the start of continuation phases in Gold.
At present, price is advancing toward the premium zone, where the next logical objective lies. Above current price, buy-side liquidity is resting near the previous highs and within the marked resistance zone, making it a natural magnet for price. As long as the market continues to hold above the key support zone, the bullish bias remains intact and favors higher highs.
From a trading perspective, any healthy pullback into the discount or demand area may offer continuation buying opportunities, while aggressive entries can be managed after minor consolidations above structure. Risk remains clearly defined below the support zone, and a decisive breakdown beneath it would invalidate the bullish scenario.
ETFs and Index TradingThe Backbone of Modern Market Participation
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and index trading have transformed the way individuals, institutions, and professional traders participate in financial markets. What began as a passive investing concept has evolved into a highly sophisticated ecosystem that supports long-term investors, short-term traders, hedgers, and global asset allocators alike. Together, ETFs and index trading represent efficiency, diversification, transparency, and scalability—qualities that define modern financial markets.
1. Understanding ETFs and Index Trading
An Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is an investment vehicle that trades on stock exchanges like an equity but represents a basket of securities. Most ETFs are designed to track an index, such as the NIFTY 50, SENSEX, S&P 500, NASDAQ 100, Bank Nifty, or sectoral indices like IT, Pharma, or Energy.
Index trading, on the other hand, refers to trading instruments that derive their value from an index. These instruments include:
Index ETFs
Index futures
Index options
Index mutual funds
ETFs sit at the intersection of investing and trading: they provide index exposure while allowing intraday buying and selling, leverage (via derivatives), and strategic execution.
2. Evolution of ETFs and Index-Based Markets
Index investing gained prominence after academic research showed that most active fund managers underperform benchmarks over the long term. ETFs were introduced to solve three problems simultaneously:
High costs of active management
Lack of transparency in mutual funds
Limited flexibility in traditional index funds
Over time, ETFs expanded beyond plain vanilla indices into:
Smart beta ETFs
Factor-based ETFs (value, momentum, quality, low volatility)
Sectoral and thematic ETFs
Commodity and currency ETFs
Leveraged and inverse ETFs
This evolution made index trading not just a passive activity but an active strategic tool.
3. Why ETFs and Index Trading Are So Popular
a. Diversification
With a single trade, an investor gains exposure to dozens or hundreds of stocks. This reduces unsystematic risk and smooths portfolio volatility.
b. Cost Efficiency
ETFs typically have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds. Lower costs compound into significant long-term advantages.
c. Liquidity and Flexibility
ETFs trade throughout the market session. Traders can:
Enter and exit intraday
Use limit and market orders
Apply stop-loss strategies
Short sell (where permitted)
d. Transparency
ETF holdings are disclosed daily, unlike mutual funds which disclose periodically. This makes risk assessment clearer.
e. Tax Efficiency
ETFs often have lower portfolio turnover, resulting in fewer taxable events compared to active strategies.
4. Types of Index Trading Strategies
Index trading is not a single approach—it spans multiple styles depending on time horizon and objective.
a. Long-Term Index Investing
This strategy focuses on compounding wealth over years or decades by:
Regular SIPs into index ETFs
Buy-and-hold allocation
Rebalancing periodically
It benefits from economic growth, inflation protection, and corporate earnings expansion.
b. Swing and Positional Index Trading
Traders use technical analysis on index ETFs or futures to capture medium-term moves. Common tools include:
Support and resistance
Moving averages
Trend channels
Relative strength vs other indices
c. Intraday Index Trading
Highly liquid index ETFs and futures allow intraday trading based on:
Opening range breakouts
VWAP strategies
Market profile
Order flow and volume analysis
d. Options-Based Index Trading
Index options enable advanced strategies such as:
Covered calls on ETFs
Protective puts
Spreads (bull, bear, calendar)
Volatility-based trades
This adds income generation and risk management to index exposure.
5. ETFs as Trading Instruments
ETFs are not just passive vehicles; they are active trading tools.
a. Sector Rotation
Traders rotate capital between sector ETFs based on:
Economic cycles
Interest rate trends
Earnings momentum
For example, banking and capital goods may outperform in expansion phases, while FMCG and pharma may outperform during defensive phases.
b. Thematic and Tactical Bets
ETFs allow participation in themes such as:
Energy transition
Technology and AI
Infrastructure and manufacturing
ESG and sustainability
These themes can be traded tactically without stock-specific risk.
c. Hedging with ETFs
Portfolio risk can be hedged by:
Shorting index ETFs
Buying inverse ETFs
Using index futures against ETF holdings
This is especially useful during volatile or uncertain markets.
6. Index Trading and Market Efficiency
Index trading contributes significantly to market efficiency:
Improves liquidity across constituent stocks
Enhances price discovery
Reduces impact of individual stock manipulation
Stabilizes markets during large fund flows
Institutional investors use index futures and ETFs to deploy large capital quickly without disrupting individual stocks.
7. Risks and Limitations of ETFs and Index Trading
Despite their advantages, ETFs and index trading carry risks:
a. Market Risk
ETFs follow the index—if the index falls, the ETF falls. There is no downside protection unless hedged.
b. Tracking Error
ETFs may not perfectly replicate index returns due to:
Expense ratios
Cash holdings
Rebalancing inefficiencies
c. Overtrading
Easy liquidity can encourage excessive trading, increasing costs and emotional decision-making.
d. Concentration Risk
Some indices are heavily weighted toward a few large stocks, which can distort diversification benefits.
8. ETFs vs Individual Stock Trading
Aspect ETFs & Index Trading Individual Stocks
Risk Lower (diversified) Higher (stock-specific)
Time Required Less More
Volatility Moderate High
Research Depth Macro/sector Company-level
Consistency Higher Variable
For most participants, ETFs offer a more stable and scalable approach.
9. Role of ETFs and Index Trading in Portfolio Construction
Modern portfolios increasingly use ETFs as core building blocks:
Core: Broad market index ETFs
Satellite: Sector, thematic, or factor ETFs
Tactical: Short-term index trades
Hedging: Inverse or options-based index exposure
This layered approach balances growth, stability, and flexibility.
10. The Future of ETFs and Index Trading
The future points toward:
Increased adoption of smart beta and factor ETFs
More active ETF strategies
Deeper integration with derivatives and algorithmic trading
Growth of global and cross-border ETFs
Expansion of ESG and thematic indices
As markets become more data-driven and cost-sensitive, ETFs and index trading will continue to dominate capital allocation.
Conclusion
ETFs and index trading represent the democratization of financial markets. They allow participants to access broad market returns, execute sophisticated strategies, manage risk efficiently, and reduce dependency on stock-picking skills. Whether one is a long-term investor focused on compounding or a short-term trader seeking liquidity and precision, ETFs and index trading provide a powerful, flexible, and future-ready framework.
In an era where consistency often outperforms complexity, ETFs and index trading stand as the foundation of disciplined, modern market participation.
Participants’ Market Coverage1. Types of Market Participants and Their Coverage
Financial markets are populated by a wide range of participants, broadly categorized into institutional investors, retail investors, intermediaries, proprietary traders, hedgers, and regulators. Each group covers markets differently.
Institutional investors—such as mutual funds, pension funds, insurance companies, sovereign wealth funds, and endowments—typically provide broad market coverage. They operate across equities, fixed income, commodities, real estate, and increasingly alternative assets like private equity and infrastructure. Their long-term mandates require diversified exposure across sectors and geographies, making them key providers of stable capital. Because of their size, institutional investors influence benchmark indices and play a central role in capital allocation.
Retail investors generally have narrower market coverage. Their participation is often concentrated in domestic equities, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), derivatives for speculation or hedging, and popular thematic investments. While individually small, their collective impact can be significant, especially during periods of heightened sentiment or technological access through online platforms.
Proprietary traders and hedge funds focus on selective but deep market coverage. Rather than covering all markets broadly, they specialize in specific strategies—such as arbitrage, macro trading, statistical strategies, or event-driven trades—across multiple instruments. Their coverage is opportunistic and dynamic, shifting rapidly as risk–reward conditions change.
2. Market Coverage Across Asset Classes
Participants’ market coverage varies significantly by asset class.
In equity markets, coverage is typically broad due to high liquidity, transparency, and accessibility. Large-cap stocks attract coverage from almost all participant types, while mid- and small-cap stocks may have thinner coverage, often dominated by domestic institutions and select funds. This uneven coverage can create pricing inefficiencies in less-followed stocks.
In fixed income markets, coverage is more fragmented. Government bonds enjoy deep participation from central banks, institutions, and foreign investors, while corporate bonds—especially lower-rated or illiquid issues—have limited coverage. This asymmetry affects liquidity and price stability.
Derivatives markets—including futures and options—are heavily covered by hedgers, speculators, and arbitrageurs. Coverage here is driven by leverage, risk management needs, and the ability to express views efficiently. Participants often focus on the most liquid contracts, leaving less popular maturities or underlyings with sparse participation.
In commodity and currency markets, coverage is global but concentrated among professional participants such as exporters, importers, banks, and macro funds. Retail participation exists but is relatively smaller compared to equities.
3. Geographic Market Coverage
Participants’ market coverage also differs by geography. Developed markets generally enjoy extensive coverage due to strong regulation, transparency, and liquidity. Emerging and frontier markets, while offering higher growth potential, often suffer from limited coverage because of political risk, currency volatility, and regulatory uncertainty.
Foreign institutional investors (FIIs) play a crucial role in extending market coverage to emerging economies. Their participation improves liquidity, governance standards, and global integration. However, reliance on foreign capital can also introduce volatility, as global risk-off events may trigger sudden withdrawals.
Domestic institutions help stabilize coverage by providing a local capital base that understands country-specific risks. Balanced participation between domestic and foreign players leads to healthier market development.
4. Time Horizon and Coverage
Market participants differ in their time horizons, which influences how they cover markets.
Long-term investors—such as pension funds and insurance companies—cover markets with a focus on fundamentals, valuation, and sustainability. Their steady participation dampens excessive volatility and supports long-term price discovery.
Short-term traders, including high-frequency traders (HFTs) and day traders, cover markets at a micro level. Their activity is concentrated in highly liquid instruments and contributes to tight bid–ask spreads and rapid price adjustments. However, their coverage is shallow in illiquid or less-followed markets.
The coexistence of multiple time horizons enhances overall market efficiency. When one group withdraws, another often fills the gap, maintaining functional coverage.
5. Role of Intermediaries in Market Coverage
Intermediaries such as stock exchanges, brokers, market makers, and clearing institutions are critical to participants’ market coverage. Market makers, in particular, ensure continuous two-way quotes, enabling participants to transact even during periods of stress. Without them, coverage would become fragmented and liquidity would evaporate quickly.
Technological advancements have expanded coverage by reducing transaction costs and improving access. Electronic trading platforms allow participants to cover multiple markets simultaneously, breaking down geographic and structural barriers.
6. Information, Research, and Coverage Quality
Market coverage is not only about participation volume but also about information depth. Analysts, rating agencies, data providers, and financial media enhance coverage by producing research and disseminating information. Well-covered markets tend to be more efficient, as prices reflect available information more quickly.
Conversely, markets or securities with poor research coverage may experience mispricing. While this increases risk, it also creates opportunities for skilled participants who can conduct independent analysis.
7. Regulatory Influence on Market Coverage
Regulation shapes participants’ market coverage by defining who can participate, how much risk they can take, and which instruments are permissible. Strong regulatory frameworks encourage broader participation by building trust and reducing systemic risk. Overregulation, however, may discourage participation and reduce coverage, particularly in innovative or niche markets.
Balanced regulation promotes inclusive coverage while safeguarding market integrity.
8. Implications of Participants’ Market Coverage
Participants’ market coverage has far-reaching implications. Broad and diversified coverage enhances liquidity, stabilizes prices, and improves capital formation. Narrow or uneven coverage can lead to volatility, liquidity gaps, and systemic vulnerabilities.
For investors, understanding coverage patterns helps in identifying risks and opportunities. Markets with limited coverage may offer higher returns but require careful risk management. For policymakers, fostering balanced participation supports economic growth and financial stability.
Conclusion
Participants’ market coverage is the backbone of financial market functioning. It reflects how different actors engage across assets, regions, and time horizons, shaping liquidity, efficiency, and resilience. A well-covered market benefits from diverse participation, robust information flow, and effective intermediation. As markets evolve through globalization and technology, understanding and adapting to changing coverage dynamics remains essential for all stakeholders in the financial ecosystem.
Gold 2026 Outlook: Central Banks, Weak USD, Geopolitical Risk🟡 Gold Outlook 2026
Central Bank Demand and Geopolitical Risks Drive Record Prices
(5 January 2026)
🔍📈 Welcome back to Trade with DECRYPTERS
📊 MARKET OVERVIEW
Gold opened 2026 positively but remained volatile on January 2 due to thin post-holiday trading. Prices rose early on a weaker dollar and Fed rate-cut expectations before easing on profit taking.
Spot gold closed near $4,330 after failing to hold above $4,400.
COMEX futures settled around similar levels.
Overall sentiment remains bullish, supported by strong central bank buying and rising geopolitical risks.
🔑 KEY FUNDAMENTALS
🚀 Strong Start to 2026
- Gold trading around $4,400–$4,410, up 1–2% YTD
- Follows a historic 60–70% rally in 2025, the strongest in decades
- 2026 analyst targets: $4,500–$5,500
1) JP Morgan: ~$5,055 (Q4 avg)
2) UBS: ~$5,000
3) Goldman Sachs: ~$4,900 (year-end)
🏦 Central Bank Demand — Strongly Bullish
- Structural buying for diversification and de-dollarization
- 2026 forecast: 750–900 tonnes vs 400–500 tonnes pre-2022
- Key buyers: China, Poland, India
- Support highlighted by the World Gold Council
💰 Interest Rates & Monetary Policy — Bullish
- Fed funds rate around 3.50–3.75% after 2025 cuts
- Markets pricing 1–2 more cuts in 2026
- Real yields around 1.9%, historically low and supportive for gold
💵 US Dollar Weakness — Bullish
- DXY around 98.5–98.8 after ~9% drop in 2025
- Pressure from rate differentials, deficits, and policy uncertainty
🌍 Geopolitical & Economic Risks — Strong Safe-Haven Demand
- Ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and Middle East tensions
- Venezuela escalation and trade-tariff uncertainty
- Severe risk-off scenarios could push gold 15–30% higher
📥 Investor Demand & ETFs — Supportive
- 2025 ETF inflows: $70–77B (700–850 tonnes)
- 2026 outlook: 250–275 tonnes (moderated but strong)
- Bar & coin demand remains robust at 1,200+ tonnes
🌐 GEO-POLITICS
🇺🇸 US–Venezuela Crisis — Strongly Bullish
- US forces captured Nicolás Maduro in Caracas (Jan 2–3)
- Donald Trump announced temporary US control
- Triggered immediate safe-haven buying; gold jumped above $4,450
🇷🇺 Russia–Ukraine War — Bullish
- Renewed strikes and stalled diplomacy
- Energy and supply risks continue to support gold demand
🔥 Middle East Tensions — Bullish
- Iran unrest and Gaza-related risks unresolved
- Escalation threats sustain gold’s haven appeal
📜 Trump Policies & Trade Risks — Net Bullish
- Tariff uncertainty and aggressive foreign policy raise volatility
- Investors favor gold amid policy-driven headline risk
⚖️ RISK-ON / RISK-OFF ANALYSIS
🟡 Gold Price
- Trading near $4,400–$4,410
- Holding strong after ~66% rally in 2025
- Structural demand keeps gold resilient despite risk-on conditions
📉 Yields & Rates
- US 10Y yield around 4.2%, real yields ~1.9%
- Higher yields pressure gold; lower yields support it
- Markets expect 1–2 Fed cuts in 2026 (mildly bullish)
💵 US Dollar (DXY)
- Near 98.6, down ~9% in 2025
- Move toward 95–97 could add 5–15% upside to gold
📊 Stocks & Volatility
- S&P 500 at record highs, VIX ~15 (risk-on mood)
- Normally caps gold, but decoupling due to central bank buying
- Gold regains strength quickly if volatility rises
🔄 Risk Scenarios
- Risk-On (60–70%)
Gold consolidates or dips to $4,000–$4,200, then resumes uptrend
- Risk-Off (20–30%)
Lower yields & weaker USD push gold $5,000+
- Downside (10–20%)
Strong growth & higher rates pull gold to $3,500–$4,000
📰 KEY INSIGHTS FROM CREDIBLE SOURCES
🟡 Gold Market
- Gold recently hit record highs near $4,500
- Increasingly compared with Bitcoin as a store of value
🇻🇪 Venezuela Crisis
- Trump announced US control over Venezuela’s oil assets
- Plans include extraction and sale of large oil volumes
- Heightened geopolitical risk supports gold
⚡ Energy & Trade Policy
- Aggressive US energy expansion plans
- Tariff threats on countries buying Russian oil (including India)
- Tariffs framed as national security and wealth tools
🏛️ Federal Reserve Pressure
- Trump publicly criticized Fed leadership
- Political pressure adds policy uncertainty, supporting gold
₿ Crypto Angle
- Bitcoin reserve discussions intensify
- Reinforces gold’s role amid fiscal and geopolitical instability
✨ CONCLUSION
Gold enters 2026 with a firmly bullish structure, driven by strong central bank demand, a weaker US dollar, and escalating geopolitical risks.
While risk-on conditions and stable yields may cause short-term consolidation, gold has clearly decoupled from traditional correlations.
Geopolitical tensions — especially Venezuela, global conflicts, and trade policy — continue to drive safe-haven flows. Downside appears limited, while sustained uncertainty keeps the path open toward $4,900–$5,500 in 2026.
🙌 Support the Analysis
👍 Like the post
💬 Comment your key levels
📈 Share your charts with the community
🚀 Let’s grow together
Best Regards
M. Moiz Khattak Founder
🟡 TRADE WITH DECRYPTERS 📊