$RKLB , SetupENTRY : CMP
TP1 : 95.25
TP2 : 110.17
TP3 : 148.48
SL : If you wish
My SL is never a SELL, just an alarm to stop adding money and wait for better dca
Follow, Boost, Thank You !!
⚠️ Financial Disclaimer:
This post is not financial advice. I am not your financial advisor, your life coach, or your legally responsible adult.
Always do your own research and never trade based solely on internet comedy.
Trendingstocks
$LDO , Leonardo Milan SetupENTRY : CMP
TP1 : 124.6
TP2 : 146.9
TP3 : Let it Roll !!!!
SL : If you wish
My SL is never a SELL, just an alarm to stop adding money and wait for better dca
Follow, Boost, Thank You !!
⚠️ Financial Disclaimer:
This post is not financial advice. I am not your financial advisor, your life coach, or your legally responsible adult.
Always do your own research and never trade based solely on internet comedy.
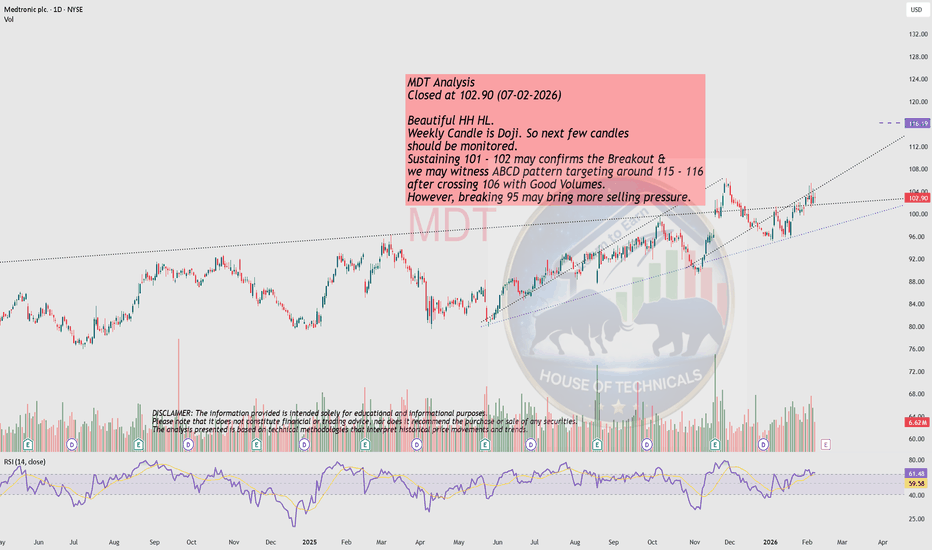
Beautiful HH HL. MDT Analysis
Closed at 102.90 (07-02-2026)
Beautiful HH HL.
Weekly Candle is Doji. So next few candles
should be monitored.
Sustaining 101 - 102 may confirms the Breakout &
we may witness ABCD pattern targeting around 115 - 116
after crossing 106 with Good Volumes.
However, breaking 95 may bring more selling pressure.
Navigating an Era of Uncertainty and TransformationRisks and Opportunities in the Global Market:
The global market today stands at a critical crossroads, shaped by rapid technological progress, shifting geopolitical alliances, economic realignments, and evolving consumer behavior. For governments, businesses, investors, and individuals, understanding the risks and opportunities embedded in this complex environment is essential for long-term sustainability and growth. While globalization has expanded access to markets, capital, and innovation, it has also amplified vulnerabilities. This dynamic interplay between risk and opportunity defines the modern global market and demands strategic foresight and adaptability.
Key Risks in the Global Market
One of the most significant risks facing the global market is geopolitical instability. Conflicts between nations, trade wars, sanctions, and regional tensions can disrupt supply chains, increase commodity price volatility, and weaken investor confidence. Events such as wars, territorial disputes, or diplomatic breakdowns often have ripple effects that extend far beyond national borders, impacting currencies, energy markets, and global trade flows. Businesses operating across multiple regions must continuously reassess political risk and regulatory uncertainty.
Another major risk is macroeconomic volatility. Inflationary pressures, interest rate fluctuations, debt crises, and uneven economic recovery among countries create instability in global financial markets. Central banks’ monetary policy decisions—especially by major economies like the United States, the European Union, and China—can trigger capital flows that destabilize emerging markets. Currency depreciation, rising borrowing costs, and shrinking liquidity pose serious challenges for governments and corporations alike.
Supply chain disruptions have emerged as a critical vulnerability in the global market. The pandemic exposed how dependent global production systems are on a limited number of suppliers and geographies. Natural disasters, labor shortages, trade restrictions, and logistical bottlenecks can halt production and inflate costs. Overreliance on single-source suppliers increases exposure to shocks, making resilience a key concern for global enterprises.
Technological risk is another growing challenge. While digitalization enhances efficiency, it also increases exposure to cyberattacks, data breaches, and system failures. Cybersecurity threats can cripple financial institutions, disrupt trade platforms, and erode consumer trust. Additionally, rapid technological change can render existing business models obsolete, creating competitive pressure for firms unable to adapt quickly.
Environmental and climate-related risks are increasingly central to global market dynamics. Climate change has led to extreme weather events, resource scarcity, and regulatory shifts toward sustainability. Industries such as agriculture, energy, insurance, and manufacturing face rising costs and operational uncertainty. Failure to align with environmental standards and climate goals can result in regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and loss of market access.
Major Opportunities in the Global Market
Despite these risks, the global market also presents vast and evolving opportunities. One of the most powerful drivers of opportunity is technological innovation. Advances in artificial intelligence, automation, blockchain, biotechnology, and renewable energy are transforming industries and creating entirely new markets. Companies that invest in innovation can achieve higher productivity, reduced costs, and stronger competitive advantages.
Emerging markets represent another significant opportunity. Countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are experiencing rising incomes, urbanization, and digital adoption. These regions offer large consumer bases, growing demand for infrastructure, healthcare, education, and financial services. For global investors and corporations, emerging markets provide higher growth potential compared to mature economies, albeit with higher risk.
The transition toward a green and sustainable economy is opening new avenues for growth. Renewable energy, electric vehicles, sustainable agriculture, and green finance are gaining momentum as governments and corporations commit to net-zero targets. Companies that align their strategies with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles can attract long-term investment, reduce regulatory risk, and build stronger brand trust.
Digital globalization has also expanded opportunities beyond traditional trade. E-commerce, digital services, remote work, and cross-border data flows allow even small firms to access international markets. Technology-enabled platforms reduce entry barriers and enable businesses to scale globally with relatively low capital investment. This democratization of global trade fosters entrepreneurship and innovation.
Another important opportunity lies in financial market integration and diversification. Global capital markets allow investors to diversify portfolios across geographies and asset classes, reducing dependence on domestic economic cycles. Access to international funding enables companies to raise capital more efficiently and pursue global expansion strategies.
Balancing Risk and Opportunity
Successfully navigating the global market requires a balanced and strategic approach. Risk management is no longer about avoidance but about anticipation, diversification, and resilience. Businesses must diversify supply chains, hedge financial exposures, invest in cybersecurity, and remain agile in response to policy and market changes. Governments play a crucial role by promoting stable regulatory frameworks, fostering innovation, and strengthening international cooperation.
At the same time, capturing opportunities demands long-term vision and adaptability. Organizations that understand global trends, invest in human capital, embrace sustainability, and leverage technology are better positioned to thrive. Strategic partnerships, localization strategies, and data-driven decision-making can help firms mitigate risks while unlocking new growth avenues.
Conclusion
The global market is characterized by uncertainty, complexity, and constant change. Risks such as geopolitical tensions, economic volatility, climate challenges, and technological disruption pose serious threats, but they also coexist with unprecedented opportunities driven by innovation, emerging markets, sustainability, and digital transformation. Those who can accurately assess these forces and respond with agility and foresight will not only survive but prosper. In this evolving landscape, the ability to turn risk into opportunity is the defining factor of success in the global market.
Crash: Global Impact on Economies, Markets, and Society1. Financial Markets: Contagion and Volatility
The most immediate global impact of a crash is seen in financial markets. Stock markets across continents react almost simultaneously due to high-frequency trading, global funds, and interconnected banking systems. A crash in one major market—such as the US, China, or Europe—often triggers panic selling worldwide. Indices fall sharply, volatility spikes, and liquidity dries up.
Global investors rush toward safe-haven assets like gold, US Treasuries, the Swiss franc, or the Japanese yen. Emerging markets face disproportionate damage as foreign institutional investors pull out capital, leading to sharp declines in equities, bonds, and currencies. Market confidence erodes, and even fundamentally strong companies see steep valuation corrections.
2. Banking and Financial System Stress
A global crash places enormous stress on the banking and financial system. Rising loan defaults, falling asset values, and liquidity shortages threaten financial stability. Banks become risk-averse, tightening lending norms, which restricts credit flow to businesses and consumers.
International banks with cross-border exposure suffer contagion effects. A crisis in one country’s banking system can quickly spread through global interbank markets. Central banks are often forced to intervene aggressively through rate cuts, liquidity injections, and emergency lending facilities to prevent systemic collapse.
3. Impact on Global Trade and Supply Chains
Global crashes significantly disrupt international trade. Demand contraction in major economies reduces imports, hurting export-driven nations. Manufacturing slows as orders decline, inventories pile up, and capacity utilization drops.
Modern supply chains are deeply globalized. A crash causes breakdowns due to bankruptcies, financing issues, logistics disruptions, and currency instability. Developing economies that rely heavily on commodity exports—such as oil, metals, or agricultural products—face sharp revenue declines as global prices fall.
4. Currency Markets and Capital Flows
Currency volatility intensifies during a global crash. Risk-off sentiment leads to capital flight from emerging and frontier markets into developed safe-haven currencies. This causes sharp depreciation in weaker currencies, increasing inflationary pressures through higher import costs.
Countries with large external debt denominated in foreign currencies face severe challenges, as debt servicing becomes more expensive. Balance-of-payments crises may emerge, forcing governments to seek IMF assistance or impose capital controls.
5. Economic Growth and Recession Risks
A global crash often results in synchronized economic slowdowns or recessions. Consumer confidence declines, discretionary spending falls, and corporate investment plans are postponed or canceled. Rising unemployment further weakens demand, creating a negative feedback loop.
Developed economies may experience slow recoveries due to high debt levels and aging populations, while developing economies face sharper growth contractions due to limited fiscal buffers. Global GDP growth can fall sharply, sometimes turning negative during severe crises.
6. Government Finances and Policy Challenges
Governments worldwide face mounting fiscal pressure during a crash. Tax revenues decline while spending on social welfare, unemployment benefits, and economic stimulus increases. Fiscal deficits widen, and public debt rises rapidly.
Policymakers are forced to choose between austerity and stimulus. While stimulus is necessary to revive growth, excessive borrowing raises concerns about debt sustainability, credit ratings, and long-term inflation risks. Coordination among global institutions like the IMF, World Bank, and G20 becomes critical.
7. Inflation, Deflation, and Cost-of-Living Effects
The inflationary impact of a global crash depends on its nature. Demand-driven crashes often lead to deflationary pressures as consumption and investment fall. Conversely, supply-side shocks—such as energy crises or geopolitical conflicts—can cause stagflation, combining low growth with high inflation.
For ordinary citizens, the cost-of-living impact is severe. Job losses, wage stagnation, rising food and energy prices, and reduced social security strain households, especially in lower-income and developing countries.
8. Corporate Sector and Business Failures
Businesses across sectors are affected by a global crash. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are particularly vulnerable due to limited access to capital and lower cash reserves. Bankruptcy rates increase, mergers and acquisitions rise, and weaker players exit the market.
Multinational corporations face declining revenues, foreign exchange losses, and geopolitical risks. Cost-cutting measures, layoffs, and restructuring become widespread. Innovation and long-term investment often suffer as companies prioritize survival over growth.
9. Social and Political Consequences
Beyond economics, global crashes have profound social and political implications. Rising inequality, unemployment, and financial stress can lead to social unrest, protests, and political instability. Trust in institutions, governments, and financial systems may erode.
Populism and protectionism often gain momentum as citizens blame globalization and international institutions for economic hardship. Trade barriers, economic nationalism, and geopolitical tensions may increase, further slowing global recovery.
10. Long-Term Structural Shifts
Every major global crash leaves behind lasting structural changes. Regulatory frameworks are strengthened, risk management practices evolve, and new economic models emerge. The 2008 financial crisis reshaped banking regulations, while the pandemic accelerated digitalization and remote work.
Investors reassess risk, diversify globally, and place greater emphasis on resilience, sustainability, and asset allocation. Governments rethink supply chain dependencies, energy security, and industrial policies.
11. Lessons and the Path Forward
The global impact of a crash highlights the importance of preparedness, coordination, and resilience. Early warning systems, strong financial regulation, prudent fiscal management, and diversified economies can reduce vulnerability. International cooperation is crucial, as no country can insulate itself entirely from global shocks.
While crashes are painful, they also serve as catalysts for reform and innovation. Economies that adapt quickly, protect vulnerable populations, and invest in long-term growth drivers often emerge stronger over time.
Conclusion
A global crash is not just a market event—it is a comprehensive economic, social, and political shock that reshapes the world. Its impact travels through financial systems, trade networks, governments, and households, leaving few untouched. Understanding these global consequences is essential for investors, policymakers, and citizens alike, as resilience in an interconnected world depends on foresight, cooperation, and the ability to learn from crises.
Infosys Holding Strong at Powerful Support – Big Move AheadThis is the weekly chart of Infosys (INFY).
INFY is currently trading within an ascending parallel channel, with a strong support zone in the ₹1300–₹1400 range.
The stock has shown a bounce from this level, offering traders and investors a favorable opportunity to accumulate.
If this support sustains, the next potential upside targets are around ₹1750–₹1800, with the upper boundary of the channel positioned near ₹2100–₹2200.
Thank you.
Thermax : Stage 1 Breakout (1-3 Months)#Thermax #stage1nreakout #ascendingtrianglepattern #patternbreakout #trendingstock #swingTrading
Thermax : Swing Trading
>> Stage 1 Breakout + Retest done
>> Ascending Triangle @ bottom of Downtrend
>> Trending setup in stock
>> Good strength & Recent Volume Buildup
>> Low Risk High Reward Trade
Swing Traders can lock profit at 10% and keep trailing
Pls Boost, comment & Follow for more Analysis
Disc : Charts Shared are for Learning Purpose & not a Trade recommendation. Pls consult a SEBI Registered Advisor before taking position in it
ELGIEQUIP : Breakout Soon#ELGIEQUIP #breakoutstock #swingtrade #trendingstock
ELGIEQUIP : Swing Trade
>> Breakout candidate
>> Trending changing happening
>> Good strength & Volume
>> Risk Reward Favorable
Swing Traders can lock profit at 10% and keep trailing
Pls Boost, Comment & Follow for more analysis
Disc : Charts shared are for Learning purpose not a Trade Recommendation, Take postions only after consulting your Financial Advisor or a SEBI Registered Advisor.
TATVA : Chart Pattern Breakout (Swing Pick)#TATVA #chartpatternbreakout #breakoutstock #flagbreakout
TATVA : Swing Trade
>> Chart Pattern Breakout
>> Flag & Pole Breakout Visible
>> Trending stock
>> Good Strength in stock
>> Volumes Driedup, Expansion imminent
>> Good Upside Potential
Swing Traders can lock profit at 10% and keep trailing
Disc : Stock charts shared are for Learning purpose and not a Trade recommendation.
Do your own analysis or Consult a SEBI Registered Advisior for taking positions
ZAGGLE : Chart Pattern Breakout ( Swing Pick )#ZAGGLE #breakoutstock #flagbreakout #chartpatternbreakout #flagandpole
ZAGGLE : Swing Trade
>> Chart pattern Breakout
>> Flag and pole breakout visible
>> Trending stock
>> Low Risk , High Reward Trade
>> Good Strength & Decent Volumes Building up
Swing Traders can Lock Profit at 10% and keep trailing
Disclaimer : Stock Charts shared are for Learning Purpose and not a Trade Recommendation. Do your Own Analysis or Consult ur Financial advisor or a SEBI Registered Advisor
DSONIC Potential uptrend to 0.56 in short term/ Long term 0.7653 Reason for holding this stock :
DSONIC provided a sustain dividend around 6+ % annually
Technical analysis show it trading around the demand zone, I believe it was the opportunity for Buy
Continues growth on company profit since 2021
Short Term TP on 0.56 with 30% capital gain ( expected TP within 6 month )
Long Term TP on 0.765 with 77% capital gain ( Expected TP within 3 years )
7% per annual * 3 = 21%
77 % capital gain + 21% per annual = 98%
98% / 3 years = 32.67% per annual.
Record for holding
200 lots for short term
200 lots for Long Term
DLong
ready to breakThe chart for Bhartiya International (NSE) is a monthly timeframe chart. Let's break it down and analyze it step by step.
### General Observations:
1. Resistance Breakout:
The price had previously formed a resistance around the **₹638 level**, which was tested multiple times between **2016 and 2018**. However, in those attempts, the price failed to break out.
In **2024**, the price has decisively broken above this level. A breakout like this, especially on higher volume, suggests strong bullish momentum.
2. **Volume Analysis (Highlighted Circle)**
There is a noticeable increase in volume at the beginning of 2024, right before the breakout, which is often a confirmation of a strong trend reversal. The increased volume shows that institutional or significant investor participation is present, supporting the upward movement.
The subsequent monthly candles also show significant gains, supported by decent volume, which adds further confirmation to the bullish outlook.
### Candlestick Patterns:
1. **2024 Candles:**
The latest candle (September 2024) is a strong bullish candle with no upper wick, indicating that bulls dominated the session, closing near the high of the month.
Prior months in 2024 show a series of higher highs and higher lows, a classic uptrend pattern.
2. **Long-Term Trend:**
The stock was in a prolonged downtrend or consolidation from **2018 to 2020**, followed by a recovery in **2021**.
After some consolidation around the **₹337 level** (acting as previous resistance turned support), the stock began its upward movement starting around **late 2023**.
### Chart Patterns:
1. Cup and Handle Formation:
There seems to be a potential **Cup and Handle** formation spanning from **2016 to 2023**:
The price peaked in **2016** around **₹638**, followed by a prolonged correction down to **₹85** (forming the cup base) and eventually moving back up to the resistance level.
The **handle** was relatively short and formed in early **2024**, leading to a breakout.
This pattern is typically bullish and often leads to strong upward momentum post-breakout.
### Possible Targets:
**Target 1 (Near-term):**
After the breakout above ₹638, the next potential target can be projected using a Fibonacci extension or by measuring the height of the cup (from ₹85 to ₹638, i.e., approximately ₹553) and adding this to the breakout point.
This gives a near-term target around **₹1200**.
**Target 2 (Long-term):**
If the breakout sustains and the stock continues its uptrend, we could see much higher levels in the longer term. A next major psychological level would be around **₹1500** or higher.
### Support Levels (Stop-Loss):
**Immediate Support:**
₹638, the previous resistance, now acts as immediate support. If the price closes below this level on a monthly basis, it may signal weakness.
**Major Support:**
₹337 is a strong support level that previously acted as resistance. In case of a significant market correction, this level could be tested.
### Summary:
**Bullish Bias:** The stock has broken out of a long-term resistance supported by strong volume, indicating bullish momentum.
- **Target:** near-term target could be around ₹1200, with potential for even higher levels over the long term.
- **Stop-Loss:** A conservative stop-loss can be set just below ₹638, or for a larger safety margin, below ₹337.
This stock seems to be in the early stages of a breakout, and the chart is giving clear bullish signals. However, regular monitoring is required, especially for potential corrections or changes in market conditions.