Wave Analysis
XAUUSD - Bullish Trend, Key Resistance & Demand Zones in Focus.XAUUSD – Technical Analysis & Trade Scenario
XAUUSD is trading in a strong bullish structure, clearly supported by an ascending trendline that has held multiple higher lows. This confirms that buyers are still in control of the overall market direction.
Price is now approaching a key Resistance / Liquidity High area. Just below this level, a Bearish Order Block is marked, which represents a potential distribution zone where sellers may enter the market.
From this area, a short-term pullback is expected:
• First reaction level: Ascending Trendline
• If the trendline fails, price may continue toward the
Demand Zone / Support
• Deeper correction target:
Major Demand Zone (Higher Timeframe Support) for a possible bullish continuation.
Trading Bias:
• Rejection from resistance = Short-term sell opportunity
• Strong reaction from demand zones = Buy continuation setup
XAUUSD M15 | Elliott Wave Impulse (1–5) (Shorterm)Price is advancing in a clean 5-wave bullish impulsive structure, fully respecting Elliott Wave rules. Wave (3) shows strong momentum expansion, wave (4) corrects cleanly without overlap, and the structure remains technically valid.
Wave (5) projection:
🎯 Primary target: 5,000
🎯 Extended target: 5,030–5,050 (Fib extension zone)
Structure remains valid as long as price holds above the wave (4) base.
TAYOR!!!
Analytics: market outlook and forecasts
📈 WHAT HAPPENED?
Last week, the trading direction was clearly bearish.
Since Monday, sellers have taken the lead, driving the price through key support levels without significant resistance from buyers. It wasn't until Wednesday evening that the first signs of resistance appeared, although we expected only a local correctional rise.
As a result, Bitcoin tested the local resistance zone at $91,000-$91,700, after which the decline resumed.
💼 WHAT WILL HAPPEN: OR NOT?
The situation has become more difficult to assess and may lead to a reversal of the trend.
During the test of the local minimum, there were volume anomalies and significant buyer activity on the delta. If the price remains above the $88,000-$87,200 zone, it may indicate a return of buyer strength. In this case, the potential for movement will be directed towards the resistance zone of $92,600-$93,500 (volume anomalies).
If the price falls below this zone, the recovery may be uncertain. Despite the presence of strong supports, a full-fledged reversal may require stronger protection and additional time.
Buy Zones
$86,000–$84,800 (anomalous activity)
$84,000–$82,000 (strong volume anomalies)
Sell Zones
$92,600–$93,500 (volume anomalies)
$96,000–$97,500 (selling pressure)
$101,000–$104,000 (accumulated volumes)
📰 IMPORTANT DATES
Macroeconomic events this week:
• January 27, Tuesday, 13:30 (UTC) — speech by US President Donald Trump;
• January 27, Tuesday, 15:00 (UTC) — publication of the US Consumer Confidence Index for January;
• January 28, Wednesday, 13:30 (UTC) — speech by US President Donald Trump;
• January 28, Wednesday, 14:45 (UTC) — announcement of the Canadian interest rate decision;
• January 28, Wednesday, 19:00 (UTC) — announcement of the US Federal Reserve interest rate decision, as well as the US FOMC statement;
• January 28, Wednesday, 19:30 (UTC) — press conference by the US FOMC;
• January 29, Thursday, 13:30 (UTC) — publication of the number of initial jobless claims in the US;
• January 30, Friday, 9:00 (UTC) — publication of Germany's GDP for the fourth quarter of 2025;
• January 30, Friday, 13:00 (UTC) — publication of the German Consumer Price Index for January;
• January 30, Friday, 13:30 (UTC) — publication of the US Producer Price Index for December;
• January 31, Saturday, 1:30 (UTC) — publication of the Chinese Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index for January.
*This post is not financial recommendation. Make decisions based on your own experience.
#analytics
EUR/USD Outlook: Identifying the Next Leg UpDescription: Analyzing the current market structure, EUR/USD has completed a sharp rally and is now entering a healthy retracement zone. We are monitoring the price action closely for a rejection at the lower liquidity levels.
Key Observation: The price is expected to pull back into the identified value area before attempting to break higher.
Targets: Looking for an expansion toward 1.19000 psychological resistance.
Invalidation: A clean break and close below 1.17582 would shift the short-term bias to neutral.
Note: Volume and price behavior at the retest point will be critical for confirmation.
EUR/USD: Bullish Momentum and Retest StrategyDescription: The EUR/USD pair is currently showing strong bullish momentum on the 15-minute timeframe. After a significant impulse move, the price is approaching a potential correction phase before continuing its upward trajectory.
Support Level: A solid demand zone is identified near the 1.17936 level, where the price might seek liquidity.
Upside Target: The primary take-profit objective is set at 1.19022, targeting the next major resistance area.
Risk Management: The setup remains valid as long as the price stays above the 1.17608 mark.
Strategy: This is a classic "Buy the Dip" scenario in a trending market.
USD/JPY Outlook: Identifying Lower High FormationThe overall market structure for USD/JPY on the 15-minute timeframe has shifted to bearish. Following the recent breakdown, the current upward move is being viewed as a corrective rally to form a lower high.
Support Turned Resistance: The green box represents a broken support level that may now act as resistance during this retracement.
Projected Path: Expecting price to struggle around the 157.50 - 158.00 region before resuming its downward trajectory.
Levels to Watch: * Resistance: 158.30
Support: 155.70
Note: This setup focuses on "Sell the Rally" logic, aligning with the dominant short-term bearish momentum.
USD/JPY: Analyzing Potential Resistance at Supply ZoneAfter a sharp bearish impulse, USD/JPY is currently in a recovery phase. The price is approaching a significant supply zone (purple box) where institutional selling pressure was previously observed.
Key Resistance: The area between 158.00 - 158.50 is acting as a strong ceiling.
Analysis: We are looking for a liquidity grab or a bearish rejection candle near the supply zone to confirm the next leg down.
Target: The primary objective is a retest of the recent lows near the 156.00 handle.
Risk Management: The bearish bias would be invalidated if the price clears and stabilizes above the 158.50 resistance zone.
GBP/USD Outlook: Testing Supply for Liquidity SweepThe British Pound has reached a significant liquidity pool on the 15-minute timeframe. We are currently observing how price reacts to this supply zone after a parabolic move.
Market Structure: Price is currently trading at a premium. A pullback into the identified purple demand zones below would offer a more balanced market structure.
Key Levels:
Immediate Resistance: 1.36375
Downside Objective: 1.35163 (Key Support)
Strategy Note: This setup focuses on a short-term reversal play. Wait for bearish price action confirmation (like an engulfing candle) before considering the move toward the support base.
GBP/USD: Potential Retracement After Strong Bullish ImpulseFollowing a sharp rally, GBP/USD is showing signs of exhaustion near the current highs. The chart indicates a potential corrective move as price looks to balance the recent impulsive expansion.
Resistance Zone: Sellers are becoming active around the 1.36388 level, creating a temporary ceiling.
Target Area: Looking for a move lower toward the primary support zone at 1.35163, which aligns with previous structural consolidation.
Risk Management: The bearish outlook remains intact unless we see a strong break and daily close above 1.36876.
Observation: Monitoring for a "Change of Character" on lower timeframes to confirm the start of the retracement.
BTC/USD Intraday Outlook: Liquidity Grab and ExpansionDescription: After a sharp retracement, BTC/USD has entered a high-interest demand area. The current price action suggests that sell-side liquidity has been cleared, potentially paving the way for a bullish expansion.
Zone of Interest: The purple boxes represent key areas of imbalance and support.
Execution Logic: Anticipating a secondary retest of the lower boundary before the projected move toward the $90,000 psychological level.
Parameters: * Resistance: $89,250 & $89,960
Support: $88,200 & $87,950
XAU/USD Short-Term Structure and Momentum OverviewThis chart highlights short-term price movement in XAU/USD with visible intraday structure and momentum shifts. Price shows consolidation followed by directional expansion, with reactions around previously active price areas. Volume and price behavior suggest increased participation during key sessions. This idea is shared for technical observation and chart analysis purposes only.
DHAMPUR SUGAR possible reversal candidatReversal signal will come above 104 only, till then there is no signal. Above 104 partial can be done with small quantity. Long term investment pic. keep on radar and observe.
Dhampur Sugar Mills Ltd. is a mid‑cap sugar and ethanol producer incorporated in 1933. It operates integrated sugar complexes in Uttar Pradesh, with strong presence in sugar, ethanol, power co‑generation, and chemicals.
Promoter: The Dhampur Group, led by the founding family, continues to hold majority control and drive expansion in integrated sugar‑ethanol operations.
FY22–FY25 Snapshot
Sales – ₹4,820 Cr → ₹5,210 Cr → ₹5,640 Cr → ₹6,050 Cr
Net Profit – ₹210 Cr → ₹265 Cr → ₹310 Cr → ₹355 Cr
Operating Performance – Moderate → Strong → Very Strong → Stable
Dividend Yield – 1.2% → 1.4% → 1.6% → 1.8%
Equity Capital – ₹66 Cr (constant)
Total Debt – ₹1,420 Cr → ₹1,280 Cr → ₹1,050 Cr → ₹890 Cr (steady deleveraging)
Fixed Assets – ₹2,150 Cr → ₹2,240 Cr → ₹2,310 Cr → ₹2,420 Cr
EPS – ₹31.8 → ₹40.1 → ₹46.9 → ₹53.7
Institutional Interest & Ownership Trends
Promoter holding: ~49%, reflecting strong family control.
FIIs/DIIs: Modest exposure, with DIIs gradually increasing stake due to ethanol growth story.
Public float: ~51%, with delivery volumes showing accumulation by long‑term investors.
Strategic Moves & Innovations
Expansion of ethanol capacity to benefit from government’s blending program.
Focus on integrated operations (sugar, ethanol, power) for margin stability.
Investment in green energy and co‑generation to diversify revenue streams.
Efficiency improvements in cane procurement and crushing operations.
Cash Flow & Balance Sheet Strength
Operating cash flows strengthened in FY25, supported by ethanol margins.
Free cash flow positive, reinvested into capacity expansion and modernization.
Debt reduced steadily, improving balance sheet resilience.
Strong asset backing with integrated plants in Uttar Pradesh.
Risk Factors
Dependence on cyclical sugar prices and government policies.
Regulatory risks in ethanol pricing and blending mandates.
Margin sensitivity to cane costs and monsoon variability.
Competition from other integrated sugar‑ethanol players.
Investor Takeaway
Dhampur Sugar Mills Ltd. demonstrates steady revenue growth, margin expansion, and deleveraging, supported by ethanol capacity expansion and integrated operations. With government focus on ethanol blending and rising institutional interest, the company is well‑positioned for sustained growth, though cyclical risks in sugar pricing remain.
XAGUSD: Bullish Continuation AheadXAGUSD: Bullish Continuation Ahead
From our previous analysis, the $95 target was reached.
Silver has delivered a strong bullish breakout after consolidating inside a clear contracting triangle formation.
The breakout was followed by impulsive upside movement, confirming strong buying interest and a continuation of the broader bullish trend.
The price corrected once again and is also showing another major accumulation pattern indicating increasing bullish momentum.
Price is now consolidating above the 94.00 area, which is acting as a key support zone.The current consolidation near the highs suggests accumulation before the next leg higher.
President Trump continues to create higher volatility in all financial instruments and this should support silver's rise.
If momentum resumes, the next upside targets are:
🎯 100.00
🎯 105.00
You may find more details in the chart!
Thank you and Good Luck!
❤️PS: Please support with a like or comment if you find this analysis useful for your trading day❤️
XAUT/USDT - Expectation 1-2 WeekXAUT has the up trend and price can continue the up moves till the 5300 point, 4950 point can use as short term support, under this point price can decrease till 4500 point.
Geopolitics situation is advantage for GOLD price, USA regional conflict, and Iran regional conflicts are pushing the price up. until we will see the calm future we can not talk about downsides from GOLD.
XAUUSD REACHES 5000+$Seems very fast but we got to above 5,000 $ on gold just recently.
For now price is in discovery territory. Most retracements to 4650 $ or 4250 $ is an opportunity to buy move and momentum addition to take price above 5500.
XAUUSD IS RISING AS USDCNY IS FALLING.GOOD CORRELATION OF METALS AND CHINA GROWTH.
AUDUSD 1H Outlook Today: Weak High Compression After BOSAUDUSD has been trending cleanly higher on the 1H with multiple BOS prints and a strong bullish impulse into premium. Price is now compressing under a marked Weak High near the 0.6940 area, while current price holds around 0.6913. This is a typical “impulse → pause → decision” structure, where the next high-probability move is either:
a liquidity sweep / breakout above the weak high, or
a mean-reversion pullback into the nearest demand blocks and Fibonacci discounts.
Market Structure and Price Behavior (1H)
The trend remains bullish (higher highs / higher lows), confirmed by repeated BOS.
The top is labeled Weak High, meaning liquidity is likely sitting above it.
The current consolidation suggests buyers are taking profit and the market is waiting for a catalyst to either expand up or retrace into support.
The cleanest approach today is to trade levels + confirmation, not the middle of the range.
Key Resistance Levels (Where Breakout or Rejection Forms)
0.6940 – 0.6950: Weak High / liquidity cap (primary resistance)
0.6920 – 0.6925: intraday supply / minor ceiling inside the pause
0.6900: pivot line (if this breaks and holds below, pullback risk increases)
Key Support Levels (Demand Blocks + Fibonacci Confluence)
Visible demand zones on the chart align well with Fibonacci retracements from the impulse 0.6662 → 0.6940:
0.6880 – 0.6874: first pullback shelf (Fib 23.6% ≈ 0.6874)
0.6840 – 0.6834: demand + Fib 38.2% ≈ 0.6834
0.6800 – 0.6798: demand + Fib 50% ≈ 0.6801
0.6768 – 0.6760: Fib 61.8% ≈ 0.6768 (stronger reaction zone)
0.6722 – 0.6720: deeper discount (Fib 78.6% ≈ 0.6721)
0.6662: strong low (major invalidation level for bulls)
Trendline Context (Risk Management)
The steep trendline drawn from the base of the move is bullish, but steep trendlines often break during healthy corrections. If price loses the consolidation base and fails to reclaim it, expect a rotation into 0.6840 / 0.6800 to rebalance the move.
EMA + RSI Filters (Simple, Effective)
Use these filters to avoid low-quality entries:
EMA
Bullish condition: price holding above EMA20/EMA50 on 1H (buy dips).
If price closes below EMA50 and retests it from underneath, shift to pullback mode.
RSI
Bull trend regime: RSI tends to hold above 50 on pullbacks.
If RSI loses 50 and fails to reclaim it during rebounds, bearish pullback continuation becomes more likely.
High-Probability Trade Setups (With Stop Loss)
Setup A: Breakout Long Above Weak High (Continuation)
Entry: 1H close above 0.6940, then buy the retest 0.6940 – 0.6928
Stop loss: below 0.6915 (or below the retest swing low)
Take profit 1: 0.6960
Take profit 2: trail toward the next round-number expansion if momentum stays strong
Best when: breakout candle is strong and RSI stays firm above 50.
Setup B: Pullback Long Into Fibonacci Demand (Higher R:R)
Entry zone 1: 0.6880 – 0.6874
SL: below 0.6860
TP: 0.6920 → 0.6940
Entry zone 2 (better): 0.6840 – 0.6834 (Fib 38.2 + demand)
SL: below 0.6818
TP: 0.6880 → 0.6920 → 0.6940
Entry zone 3 (deep pullback): 0.6800 (Fib 50 + demand)
SL: below 0.6768
TP: 0.6840 → 0.6880 → 0.6920
Rule: only take longs if price shows rejection + bullish displacement from the zone (don’t blind catch).
Setup C: Short Only If Structure Flips (Countertrend Scalps)
This is not the primary bias, but it’s valid if the market breaks down.
Trigger: 1H acceptance below 0.6900, then a failed retest into 0.6900 – 0.6913
Stop loss: above 0.6925
Targets: 0.6880 → 0.6840 → 0.6800
This setup works best if RSI fails to reclaim 50 during the retest.
Invalidation Levels (Know When Bias Changes)
Bull continuation is strongest while price holds above 0.6900 and respects EMA support.
Bull bias weakens if price accepts below 0.6900 and keeps making lower highs.
Major bullish invalidation comes from a breakdown toward 0.6662 (strong low).
Trading Notes
AUDUSD is in a bullish structure, but the market is currently negotiating a Weak High. The best trades today come from either:
confirmed breakout above 0.6940, or
patient buys at 0.6840 / 0.6800 with confirmation.
If this plan is useful, save it and follow for the next update when price either sweeps the Weak High or retraces into the Fibonacci demand zones.
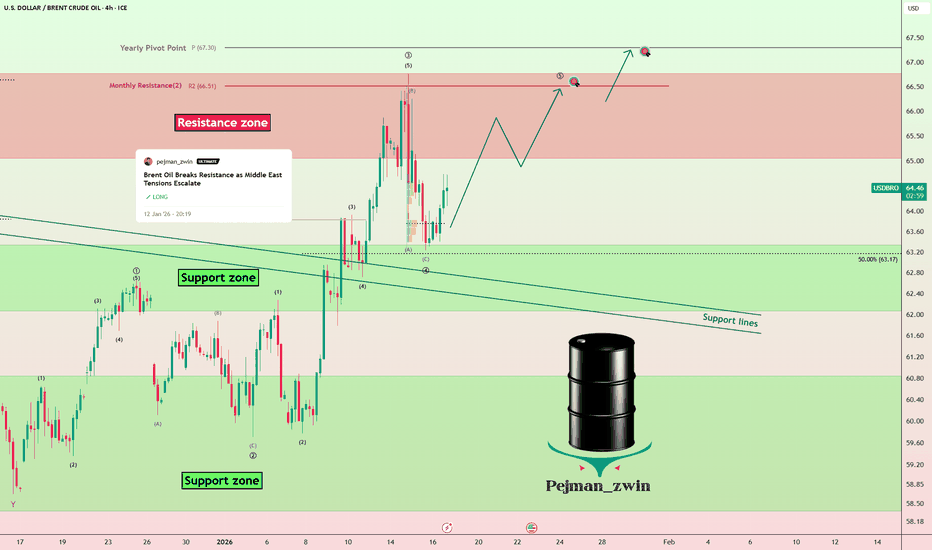
Middle East Risks Keep Brent Oil Bullish — Higher TargetsAs I expected in the previous idea , Brent Crude OIL( BLACKBULL:BRENT ) has risen and reached its targets, with a Risk-To-Reward: 2:01 (full target).
Brent Crude OIL is currently trading near the support zone($63.30-$62.00) and the support lines.
From an Elliott Wave perspective, it appears that Brent Crude OIL has completed main wave 4, and we can now expect the next impulsive wave for the main wave 5.
Additionally, news from the Middle East does not indicate a reduction in tensions, and we can expect potential surprises in the region. Therefore, I prefer to maintain long positions in Brent Crude OIL rather than short positions, and I’m looking for triggers to enter long.
I expect that Brent Crude OIL will once again target the resistance zone($66.80-$65.00) and potentially rise to around $66.47. The next target could be the yearly pivot point($67.30).
First Target: $66.47
Second Target: $67.30
Stop Loss(SL): $62.60
Points may shift as the market evolves
💡 Please respect each other's opinions and express agreement or disagreement politely.
📌U.S. Dollar/Brent Crude OIL Analysis (USDCAD), 4-hour time frame.
🛑 Always set a Stop Loss(SL) for every position you open.
✅ This is just my idea; I’d love to see your thoughts too!
🔥 If you find it helpful, please BOOST this post and share it with your friends.
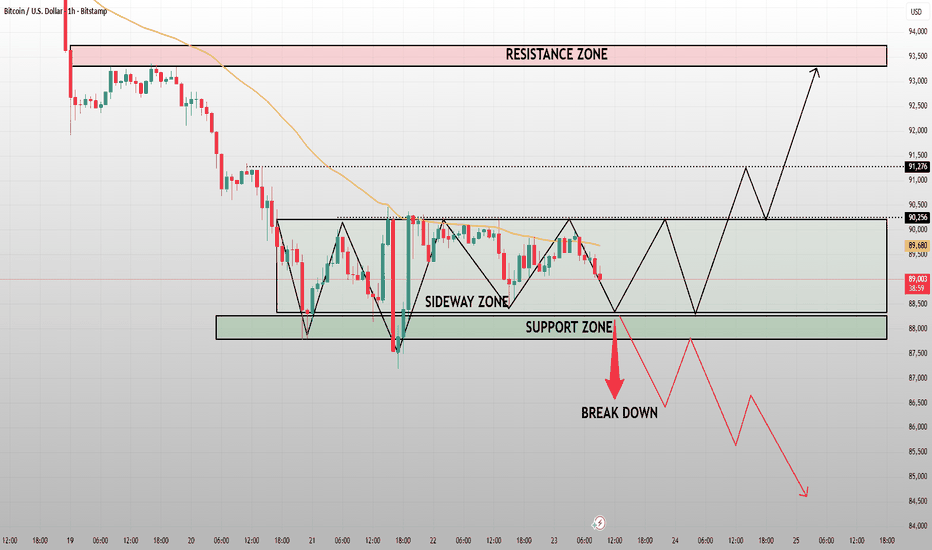
BTCUSD H1 – Compression Inside Range, Expansion Is ComingOn the H1 timeframe, Bitcoin is currently trapped in a well-defined sideways range after a sharp impulsive sell-off from the higher resistance area. That initial drop clearly shifted short-term momentum bearish, but instead of continuation, price has transitioned into range-bound behavior, signaling absorption and indecision between buyers and sellers. The market is now oscillating cleanly between the upper range resistance (~90,200–90,300) and the lower support zone (~87,800–88,200), with repeated wicks and overlapping candles — classic signs of balance, not trend.
From a structural perspective, this is not a trend yet, but a preparation phase. Liquidity is being built on both sides. The EMA is flattening and running through the middle of the range, reinforcing the idea that momentum is neutral and price is waiting for a catalyst. As long as BTC remains inside this sideways zone, trading the middle carries poor risk-reward, and patience is required.
Key scenarios going forward:
If buyers manage to hold above the support zone and break decisively above the range high, the upside opens toward the 93,000–94,000 resistance zone, where prior supply sits. That would confirm a successful absorption of sell pressure and a bullish range expansion.
However, a clean breakdown and acceptance below the support zone would invalidate the range and likely trigger a bearish continuation, opening the door toward deeper downside levels in the mid-85,000s, as indicated by the projected path.
BTC is in compression mode. The range will not last forever the next impulsive move will come from a confirmed breakout or breakdown, not from guessing inside the box. Let price show its hand, then act. Risk management remains key.
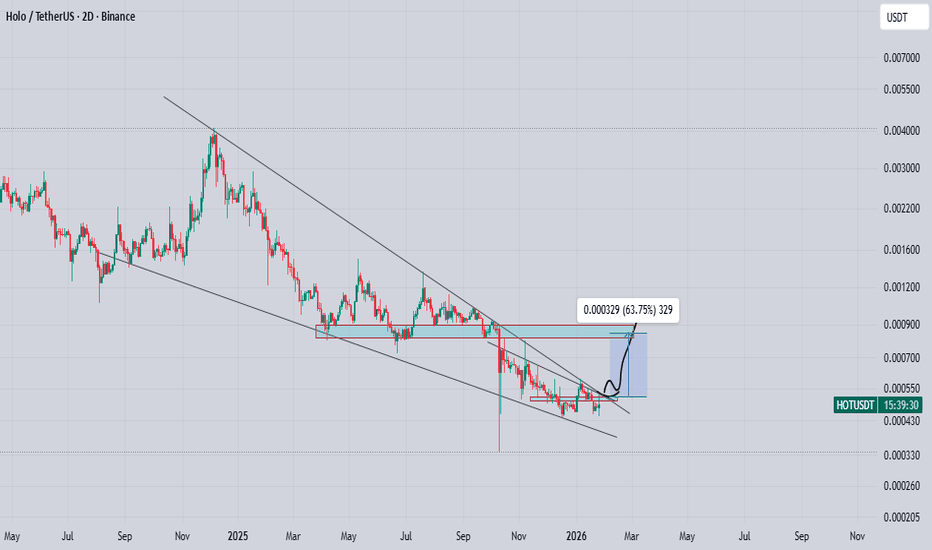
hot coin looking good after long bearish wavePrice is continuing to squeeze and compress, indicating building pressure. A strong upside breakout is possible from this zone.
A good volume candle closing above the descending trendline can trigger a solid move in the coming days. If the breakout holds successfully with a daily or 2-day candle close, we could see a 60–70% bullish rally toward the marked resistance area on the chart.