AUDJPY Above Dynamic Support | Bulls in Control🎄 I’d like to wish everyone a Happy New Year in advance, hoping the new year brings discipline, consistency, and plenty of green pips 💚📈
📌 Fundamental Outlook | Japanese Yen Weakness 🇯🇵
From a fundamental perspective, the Japanese Yen remains under pressure.
The Bank of Japan’s ultra-loose monetary policy, wide interest rate differentials versus currencies like the Australian Dollar, and the BOJ’s reluctance to tighten aggressively continue to weaken the JPY.
This keeps JPY as one of the weakest currencies in the market, supporting bullish JPY-crosses such as AUDJPY.
📊 Technical Analysis | AUDJPY – 1H Timeframe
🔹 Price is still trading above the rising dynamic support trendline
🔹 This trendline has acted as a strong and reliable support multiple times
🔹 Overall market structure remains Higher Highs & Higher Lows, confirming an uptrend
📈 Primary Scenario (Bullish):
As long as price holds above the dynamic support and the marked demand zone,
any pullback or correction can be considered a
👉 potential buy-the-dip opportunity.
🚀 A clean breakout and consolidation above the highlighted resistance zone could open the door for
further bullish continuation toward higher targets, as illustrated on the chart.
⚠️ Key Note
The bullish structure remains intact for now.
Only a confirmed break below the dynamic support would invalidate this bullish scenario.
❗️ Disclaimer
❗️ This analysis reflects personal opinion only and is not financial advice
❗️ Always apply proper risk management and trade according to your own strategy
📊 What’s your view?
🔘 Bullish continuation toward higher levels 🚀
🔘 Deeper correction before continuation ⏳
👇 Share your thoughts in the comments — happy to hear your perspective!
🏷️ Tags
#AUDJPY #Forex #TechnicalAnalysis #PriceAction
#TrendTrading #JPY #BuyTheDip
#SupportResistance #TradingView #SmartMoney
💚📈
Trade safe and stay profitable!
Harmonic Patterns
Could we see a rise from here?ER/NZD has reacted off the pivot which is an overlap resistance, and could rise to the 1st resistance, which has been identified as a pullback resistance.
Pivot: 2.02997
1st Support: 2.02259
1st Resistance: 2.04407
Disclaimer:
The opinions given above constitute general market commentary and do not constitute the opinion or advice of IC Markets or any form of personal or investment advice.
Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, are intended to be informative only, and are not advice, a recommendation, research, a record of our trading prices, an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. The information provided does not involve any specific investment objectives, financial situation, or needs of any specific person who may receive it. Please be aware that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance and/or results. Past performance or forward-looking scenarios based upon the reasonable beliefs of the third-party provider are not a guarantee of future performance. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. IC Markets makes no representation or warranty and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, nor any loss arising from any investment based on a recommendation, forecast, or any information supplied by any third party
Potential bullish rise?CAD/CHF has reacted off the pivot and could rise to the 1st resistance.
Pivot: 0.57802
1st Support: 0.57621
1st Resistance: 0.58186
Disclaimer:
The opinions given above constitute general market commentary and do not constitute the opinion or advice of IC Markets or any form of personal or investment advice.
Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, are intended to be informative only, and are not advice, a recommendation, research, a record of our trading prices, an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. The information provided does not involve any specific investment objectives, financial situation, or needs of any specific person who may receive it. Please be aware that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance and/or results. Past performance or forward-looking scenarios based upon the reasonable beliefs of the third-party provider are not a guarantee of future performance. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. IC Markets makes no representation or warranty and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, nor any loss arising from any investment based on a recommendation, forecast, or any information supplied by any third party
Bullish bounce off?AUD/JPY has bounced off the pivot, which is a pullback support, and could rise to the 1st resistance, which aligns with the 127.2% Fibonacci extension.
Pivot: 104.26
1st Support: 103.43
1st Resistance: 105.48
Disclaimer:
The opinions given above constitute general market commentary and do not constitute the opinion or advice of IC Markets or any form of personal or investment advice.
Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, are intended to be informative only, and are not advice, a recommendation, research, a record of our trading prices, an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. The information provided does not involve any specific investment objectives, financial situation, or needs of any specific person who may receive it. Please be aware that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance and/or results. Past performance or forward-looking scenarios based upon the reasonable beliefs of the third-party provider are not a guarantee of future performance. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. IC Markets makes no representation or warranty and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, nor any loss arising from any investment based on a recommendation, forecast, or any information supplied by any third party
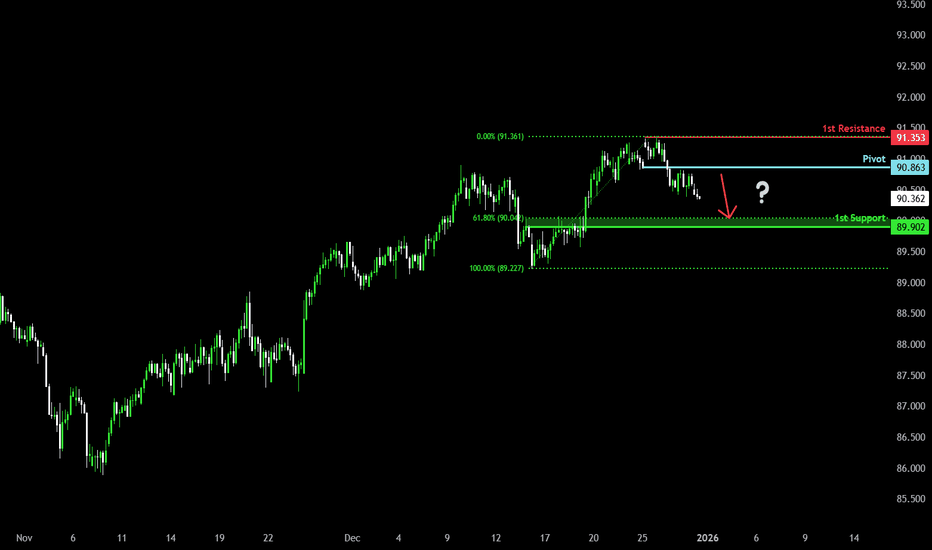
Bearish drop off?NZD/JPY has rejected off the pivot and could potentially drop to the 1st support.
Pivot: 90.86
1st Support: 89.90
1st Resistance: 91.35
Disclaimer:
The opinions given above constitute general market commentary and do not constitute the opinion or advice of IC Markets or any form of personal or investment advice.
Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, are intended to be informative only, and are not advice, a recommendation, research, a record of our trading prices, an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. The information provided does not involve any specific investment objectives, financial situation, or needs of any specific person who may receive it. Please be aware that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance and/or results. Past performance or forward-looking scenarios based upon the reasonable beliefs of the third-party provider are not a guarantee of future performance. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. IC Markets makes no representation or warranty and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, nor any loss arising from any investment based on a recommendation, forecast, or any information supplied by any third party
Gold: weak recovery and range-bound consolidation.Today marks the last trading day of 2025. Gold is overall in a phase of low-range consolidation and recovery following the sharp plunge. The short-term trend is dominated by bearish momentum, while oversold conditions have triggered a mild technical rebound. Year-end liquidity shrinkage has amplified price volatility, with the core trading range at 4320–4400, and the market is mainly characterized by weak recovery and range-bound consolidation.
Core Support Levels
4300 (key psychological round number + previous intraday low of 4303). A breakdown below this level will pave the way for a further pullback to 4280–4290 and open deeper downside potential.4310–4315 (20-day moving average). A firm hold here could extend the rebound, serving as a key reference for tentative long entries.
Secondary Support Level
4280–4290 (extreme pullback test level). A breakdown would unlock further downward room.
Core Resistance Levels
4380–4400 (5-day moving average pressure + key resistance zone for post-plunge rebounds). A breakout is extremely challenging, making this the core range for short entries.4450 (previous consolidation platform, acting as a strong resistance level against bullish counterattacks).
Secondary Resistance Levels
4430 (10-day moving average resistance level).4460 (crossover point of the 5-day and 10-day moving averages, facing significant technical selling pressure).
Trading Strategy:
Sell 4380 - 4400
SL 4415
TP 4430 - 4420 - 4410
Buy 4300 - 4310
SL 4285
TP 4350 - 4360 - 4370
Mitani Sangyo: Diversified Growth Meets MomentumMitani Sangyo Co., Ltd. (8285) has established a robust uptrend over the past year and we are currently observing a healthy consolidation phase following a period of consistent gains. As this Japanese conglomerate pulls back slightly from recent highs, it presents an interesting chart structure to watch for potential trend continuation.
Fundamentally, the company operates as a diversified powerhouse with segments spanning Chemicals, Information Systems, and Energy. Supported by reported 18.6% revenue growth, Mitani Sangyo is leveraging its multi-sector presence to capture opportunities in both domestic markets and the growing Southeast Asian region. This expansion strategy, coupled with a focus on high-value IT integration and renewable energy projects, has positioned the stock as a compelling mix of stability and growth. Investors are particularly noting its resilience amid broader sector reforms aimed at improving capital efficiency.
Technically, the chart confirms a powerful bullish stance, boasting a gain of over 72% . Price action remains stacked well above the 50-day , 100-day , and 200-day SMAs , signalling that the long-term trend is firmly intact. The recent pullback has cooled the RSI to 59.06 , offering a breather from overbought conditions without breaking market structure. While the MACD histogram is currently red and flattening indicating a pause in immediate buying pressure, the volume profile remains stable suggesting this is a routine correction rather than a reversal.
Mitani Sangyo might be one to watch.
--------------------------------------------
About Me: Global TradingView Moderator (English) and full-time trader. I focus on top-performing stocks worldwide, trading momentum and clean trend continuations after pullbacks. I use a trailing stop system customised for each stock to manage risk, lock in gains, and exit when the trend ends. Nothing I post is trading advice. I simply highlight interesting companies from around the world that may be worth a closer look. Please give this idea a BOOST if you found it interesting, and FOLLOW ME to discover more standout stocks and businesses from global markets.
--------------------------------------------
INJ/USDT Weekly: Last Major Demand Before Macro Structure FailsINJ/USDT on the Weekly (1W) timeframe is still trading inside a large ascending channel (macro uptrend) that has been in place since 2021. However, price is currently undergoing a deep corrective phase after the previous peak and is approaching a very critical historical demand area.
Price is trading well below the channel midline, indicating medium-term bearish pressure, yet the overall macro structure remains valid as long as the lower channel boundary and the major demand zone hold.
---
Pattern Explanation
1. Ascending Channel (Macro Structure)
Upper boundary: major distribution and repeated rejections (previous ATH area).
Channel midline: equilibrium zone.
Lower boundary: long-term accumulation area.
Price is now moving toward the lower boundary, which historically acts as a strong bullish reaction zone.
2. Weekly Distribution → Breakdown
A clear distribution range formed near the top (around 40–50 USDT).
Breakdown from this range created lower highs and lower lows, signaling a medium-term bearish trend.
3. Major Demand Zone (Yellow Block 2.65 – 1.85)
This area represents the base before the previous major bullish impulse.
Confluence with:
Lower boundary of the ascending channel
Historical accumulation zone
Psychological low-price area
This zone acts as the last major support before the macro structure is invalidated.
---
Key Levels
Support
2.65 – 1.85 → Major Weekly Demand Zone (yellow block)
3.80 – 4.20 → Minor support (already broken)
Resistance
6.80 – 7.50 → Breakdown resistance
12.00 – 14.00 → Mid-channel resistance
20.00+ → Major distribution zone
---
Bullish Scenario
Price holds and reacts strongly within the 2.65 – 1.85 demand zone.
Appearance of:
Weekly rejection candles
Bullish engulfing or long lower wicks
Market structure shifts from lower low → higher low.
Bullish Targets
6.80 – 7.50
12.00 – 14.00
20.00+ (if price returns toward mid–upper channel)
Bullish Conclusion:
The 2.65 – 1.85 zone may act as a long-term accumulation area if buyers successfully defend the lower channel.
---
Bearish Scenario
A confirmed weekly close below 1.85.
Breakdown of the ascending channel lower boundary.
Macro structure shifts from uptrend to downtrend.
Bearish Implications
Potential extended capitulation phase
Price may enter:
A prolonged sideways range
Or search for a new demand zone below the current structure
Bearish Conclusion:
Losing the 1.85 level would signal macro structural failure, significantly increasing downside risk.
---
Conclusion
INJ/USDT is currently at a macro decision zone.
The 2.65 – 1.85 demand area is not just a regular support—it is the foundation of the long-term bullish structure.
Strong reaction = potential major reversal
Breakdown = macro trend shift
Waiting for weekly price action confirmation is strongly recommended.
---
#INJ #INJUSDT #CryptoAnalysis #WeeklyChart #AscendingChannel #DemandZone #SupportResistance #PriceAction #MarketStructure #AltcoinAnalysis
Grupo Cibest S.A.: Regional Banking Strength Meets MomentumGrupo Cibest S.A. (CIB) has been in a strong uptrend over the last year and we are currently seeing a minor retracement after consistent gains, which makes this an interesting chart to watch for a possible entry if the trend resumes. As a comprehensive financial institution, CIB provides banking, leasing, and asset management services across Colombia and Central America, actively targeting both SMEs and large corporate clients to drive financial inclusion.
Fundamentally, the company is riding a wave of regional economic recovery. With reported 20.6% revenue growth and favorable earnings revisions, CIB has attracted attention for its rare blend of deep value and high momentum. The stock currently holds high marks for financial strength, supported by a strategic shift toward digital banking infrastructure. Analysts point to attractive valuation metrics, specifically lower P/E ratios compared to industry peers as a key driver for sustained investor interest in this emerging market player.
Technically, the chart displays a powerful uptrend, boasting a gain of over 137% . The price action remains stacked well above the 50-day , 100-day , and 200-day SMAs , indicating strong structural support. The recent consolidation has cooled the RSI to 56.07 , moving it out of overbought territory into a neutral zone suitable for potential reentry. While the MACD histogram is flattening, indicating a pause in immediate momentum, the lower volume during this pullback suggests a lack of heavy selling pressure.
CIB might be one to possibly keep an eye on.
--------------------------------------
About Me: Global TradingView Moderator (English) and full-time trader. I focus on top-performing stocks worldwide, trading momentum and clean trend continuations after pullbacks. I use a trailing stop system customised for each stock to manage risk, lock in gains, and exit when the trend ends. Nothing I post is trading advice. I simply highlight interesting companies from around the world that may be worth a closer look. Give this idea a BOOST if you found it interesting, and FOLLOW ME to discover more standout stocks and businesses from global markets.
--------------------------------------
$BTC China just unveiled ~$9B in consumer subsidies funded via ultra-long sovereign bonds.
That tells me governments are finding new ways to fund stimulus without relying on speculative liquidity.
If capital is being absorbed by bonds + real consumption, CRYPTOCAP:BTC loses urgency as a liquidity outlet.
Short–mid term pressure makes sense.
2025 Performance Review: Why Capital Rotated Into Metals 2025 Investment Landscape — Capital Chose Stability Over Speculation
The data in the image clearly shows a decisive shift in capital allocation during 2025. Precious metals significantly outperformed traditional risk assets. Gold delivered a +67.3% return, while Silver (+155%) and Platinum (+137.1%) posted exceptional gains. In contrast, the S&P 500 rose a modest +17.7%, and Bitcoin declined by −9.3%. This divergence reflects a year dominated by macro uncertainty rather than growth-driven risk appetite.
Why Metals Outperformed in 2025
Gold’s strong appreciation was driven by a combination of persistent inflation pressure, declining real yields, and rising geopolitical risk. Central banks globally continued to diversify reserves away from fiat currencies, reinforcing structural demand for gold. Silver and platinum benefited not only from monetary hedging flows but also from industrial demand tied to energy transition and supply constraints. Metals, unlike equities or crypto, offered both capital preservation and asymmetric upside.
Risk Assets Lagged — A Market Defined by Caution
The S&P 500’s gains were largely multiple driven rather than earnings-led, making returns vulnerable to tightening liquidity conditions. Bitcoin, despite prior cycle optimism, struggled as speculative capital rotated out amid regulatory pressure, reduced liquidity, and lower risk tolerance. The underperformance of BTC relative to metals highlights a clear preference for tangible, inflation-protective assets in this phase of the cycle.
Key Investment Lesson from 2025
Markets rewarded discipline, macro awareness, and defensive positioning. Capital flowed toward assets with intrinsic value, limited supply, and global monetary relevance. Gold acted as both a hedge and a performance asset not merely a safe haven, but a core portfolio driver.
Strategic Outlook for 2026 — Positioning with Structure, Not Emotion
Heading into 2026, the priority is balance and selectivity. Precious metals particularly gold should remain a foundational allocation, especially during periods of monetary easing or geopolitical stress. Tactical exposure to equities should focus on sectors aligned with real assets and cash flow resilience. High-volatility assets like crypto require strict risk control and confirmation from broader liquidity conditions before meaningful allocation.
Conclusion
2025 was a year where markets clearly signaled what they value in uncertain environments: protection, scarcity, and macro alignment. Traders who respected structure and capital flow thrived. As 2026 begins, the edge will belong to those who continue to follow capital not narratives.
Gold Spot / USD – 4H TimeframeGold Spot / USD – 4H Timeframe
Market Structure
Gold was trading within a well-defined bullish 4H structure, supported by the primary red trendline.
Price has now decisively broken and closed below this primary trendline, confirming a loss of bullish structure.
Current Price Behavior
The pullback toward the broken trendline failed to reclaim structure, indicating weak bullish participation.
The horizontal support zone (yellow) has been tested and violated, removing short-term demand.
Price action remains corrective with lower highs, not impulsive to the upside.
Technical Expectation
Following a confirmed primary trendline break, the market typically seeks the next dynamic structural support.
The second (lower) red trendline represents the most probable downside target.
This level aligns with structural symmetry and acts as the next decision zone for continuation or stabilization.
Key Notes
This move is currently classified as a corrective decline, not a confirmed trend reversal.
Bullish continuation is only valid after a clear reaction or reclaim at the second trendline.
No premature buying; no chasing momentum.
Conclusion
With the primary bullish structure broken, price is technically favored to rotate lower toward the secondary trendline, where the next directional bias will be determined.
— Avo.Trades
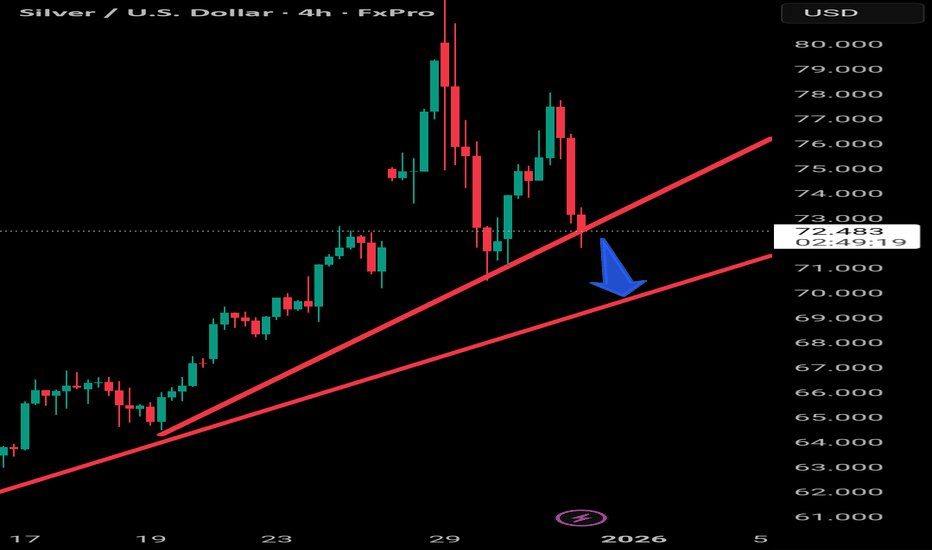
Silver / USD – 4H TimeframeSilver / USD – 4H Timeframe
Structure read (by your rules):
Market was in a strong bullish structure, riding the main red trendline perfectly.
Price broke below the first red trendline with strong bearish momentum.
That break already tells us: bulls lost control, momentum shifted.
What matters now:
After the first trendline break, price is not reclaiming structure.
Instead, it’s respecting the breakdown and failing to get back above the broken line.
This opens the door for a controlled bearish continuation, not a crash — a technical pullback.
High-probability scenario:
Price is likely to fall toward the second (lower) red trendline.
That second trendline acts as:
Dynamic support
Retest zone of the overall bullish structure
Decision area for continuation vs deeper correction
Key takeaway (tell it like it is): This is not random selling.
This is a classic 4H trendline sequence:
Strong uptrend → first trendline break → corrective move → test of the next structure line.
No buys make sense before price reacts at the second trendline.
No rushing shorts after the move already started — patience pays.
Let the market come to structure.
Structure always speaks first.
Newmont Corporation: Mining Momentum and Market StrengthNewmont Corporation (NEM) has been performing well over the last year. Nice and steady gains with a recent pullback that could be a good watch for an entry. As the world's largest gold producer, Newmont operates a diverse portfolio of Tier 1 assets across the Americas, Africa, and Australia. Beyond its primary focus on gold, the company is a significant producer of copper, silver, and zinc, positioning it as a cornerstone of the global materials sector.
The fundamental narrative is driven by Newmont’s strategic scale and a 20% revenue growth profile. Global economic uncertainty and persistent inflation have bolstered the appeal of safe-haven assets, providing a favorable backdrop for gold miners. Newmont’s robust profit margins and disciplined capital allocation supported by extensive exploration projects offer investors a stable foundation. While the broader market shows year-end caution, Newmont’s ability to generate cash flow from its low-cost mining operations remains a primary catalyst for long-term interest.
Technically, the chart reflects a powerhouse performance with a 166.09% year-to-date gain. Price action is firmly bullish, trading at $101.86 , well above the 50-day SMA ($90.53) and the 200-day SMA ($69.90) . A recent consolidation in the $100-$103 range has cooled the RSI to 59.86 , moving it out of overbought territory. Although current volume is roughly 6.02M , which is slightly below the 30-day average, the MACD remains in positive territory, suggesting the structural uptrend is intact despite the minor pause.
Newmont might be one to possibly keep an eye on especially while the Gold price continues to run.
---------------------
About Me: Global TradingView Moderator (English) and full-time trader. I focus on top-performing stocks worldwide , trading momentum and clean trend continuations after pullbacks. I use a trailing stop system customised for each stock to manage risk, lock in gains, and exit when the trend ends. Nothing I post is trading advice. I simply highlight interesting companies from around the world that may be worth a closer look. Give this idea a BOOST if you found it interesting, and FOLLOW ME to discover more standout stocks and businesses from around the world.
---------------------
Happy New Year 2026 TRADERSAs we close the chapter on 2025, it’s worth acknowledging what this year truly tested — not just strategies, but discipline, patience, and emotional control. The market offered moments of clarity and long stretches of uncertainty, sharp trends followed by brutal consolidations, and powerful macro moves that rewarded preparation while punishing impulse. Every win came from respecting structure, and every loss carried a lesson for those willing to learn from it.
To all traders who stayed committed to the process managing risk, protecting capital, and waiting for high-probability setups this year has strengthened you more than any single trade ever could. Progress in trading is built quietly, over time, through consistency and self-control.
As we step into 2026, may your decisions be calm, your risk disciplined, and your confidence grounded in experience rather than emotion. May you trade with clarity, adapt quickly, and continue evolving with the market. Wishing every trader health, resilience, and a year ahead filled with focus, growth, and sustainable profitability.
HAPPY NEW YEAR 2026
USDOLLAR H1 | Bullish BreakoutBased on the H1 chart analysis, we can see that the price has bounced off our buy entry, which is a pullback support.
Our stop-loss is set at 12.694, which corresponds to a pullback support that aligns with the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement.
Our take profit is set at 12.730, which aligns with the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement as a pullback resistance.
High Risk Investment Warning
Stratos Markets Limited (
EURUSD H1 | Bearish Drop OffThe rice has reacted off our sell entry level at 1.1756, which is a pullback resistance.
Our stop loss is set at 1.1777, which is a pullback resistance.
Our take profit is set at 1.1736, which is a pullback support that aligns with the 78.6% Fibonacci retracement.
High Risk Investment Warning
Stratos Markets Limited (
Falling towards key support?NZD/CAD is falling towards the pivot, which acts as an overlap support and could bounce to the 1st resistance.
Pivot: 0.79037
1st Support: 0.78682
1st Resistance: 0.79544
Disclaimer:
The opinions given above constitute general market commentary and do not constitute the opinion or advice of IC Markets or any form of personal or investment advice.
Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, are intended to be informative only, and are not advice, a recommendation, research, a record of our trading prices, an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. The information provided does not involve any specific investment objectives, financial situation, or needs of any specific person who may receive it. Please be aware that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance and/or results. Past performance or forward-looking scenarios based upon the reasonable beliefs of the third-party provider are not a guarantee of future performance. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. IC Markets makes no representation or warranty and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, nor any loss arising from any investment based on a recommendation, forecast, or any information supplied by any third party
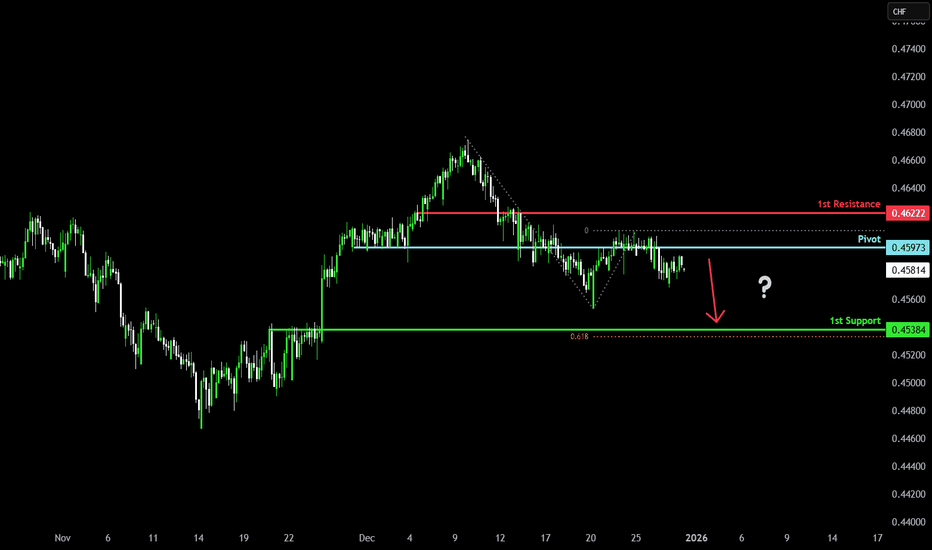
Bearish reversal?NZD/CHF has rejected off the pivot and could drop to the 1st support, which is a pullback support that aligns with the 61.8% Fibonacci projection.
Pivot: 0.45973
1st Support: 0.45384
1st Resistance: 0.46222
Disclaimer:
The opinions given above constitute general market commentary and do not constitute the opinion or advice of IC Markets or any form of personal or investment advice.
Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, are intended to be informative only, and are not advice, a recommendation, research, a record of our trading prices, an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. The information provided does not involve any specific investment objectives, financial situation, or needs of any specific person who may receive it. Please be aware that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance and/or results. Past performance or forward-looking scenarios based upon the reasonable beliefs of the third-party provider are not a guarantee of future performance. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. IC Markets makes no representation or warranty and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, nor any loss arising from any investment based on a recommendation, forecast, or any information supplied by any third party
BTC | 4HCRYPTOCAP:BTC — Quantum Model
4H Zoom-In | Trend Reversal
All wave structures identified on this timeframe—including an Ending Expanding Diagonal in Intermediate (C), a Leading Diagonal as Minor Wave 1, a deep retracement ending in an Expanding Diagonal ⓒ, and the current Flat consolidation—respecting the illustrated Q-Structures—have collectively formed an integrated structure indicating the formation of a bottom, marking the extreme low of Primary Wave ⓸.
The bullish outlook remains favoured, with expectations of a successful breakout above the resistance Q-Structure through the divergent zone toward the origin of the Ending Diagonal ⓒ at $93,558.29, which would strongly confirm the projected Primary-degree trend reversal.
🔖 This potential reversal has been projected since Nov. 15 during the BTC decline.
🔖 This outlook is derived from insights within my Quantum Models framework.