#SXP/USDT looking extremely bullish#SXP
The price is moving within a descending channel on the hourly timeframe. It has reached the lower boundary and is heading towards a breakout, with a retest of the upper boundary expected.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is showing a downward trend, approaching the lower boundary, and an upward bounce is anticipated.
There is a key support zone in green at 0.0440. The price has bounced from this level several times and is expected to bounce again.
The RSI is showing a trend towards consolidation above the 100-period moving average, which we are approaching, supporting the upward move.
Entry Price: 0.0449
Target 1: 0.0468
Target 2: 0.0492
Target 3: 0.0520
Stop Loss: Below the green support zone.
Remember this simple thing: Money management.
For any questions, please leave a comment.
Thank you.
Wave Analysis
Gold Pullback or Extension? Smart Money Sets the Trap Near HighsXAUUSD | Daily Smart Money Plan – H1
Gold keeps its bullish structure intact after a strong impulsive leg, but the current price action shows hesitation just below the recent highs. After a clean BOS and aggressive expansion, price is now trading in premium, where buy-side liquidity has already been delivered. The chart suggests Smart Money is no longer chasing higher prices, but managing positions through rotation.
Macro backdrop today remains hot:
Markets are digesting fresh volatility around U.S. data expectations, shifting Fed rate-cut timing, and persistent geopolitical tension. These factors continue to support gold as a safe haven, but intraday execution shows rebalancing behavior, not blind continuation. Headlines may move price fast — liquidity decides where it settles.
Rather than exploding higher, price pulled back from the highs and left a clear imbalance (FVG) below, signaling unfinished business before any sustained continuation.
Market Structure & Liquidity Context
Higher-timeframe bias remains bullish
Strong bullish BOS confirms trend strength
Short-term pullback forms after liquidity delivery at highs
Clear H1 imbalance + buy zone below current price
Market logic favors premium → discount → continuation
➡️ News creates volatility, but Smart Money seeks efficiency
Key Trading Scenarios
🔴 Sell Reaction at Premium (Short-term rotation)
Zone: 5,265 – 5,275
SL: Above 5,300
Confluence:
Buy-side liquidity already tapped
Momentum slows near highs
Rejection here favors a dip into imbalance before continuation
🟢 Buy Reaction at Discount (Primary Long Setup)
Zone: 5,170 – 5,168
SL: 5,160
Confluence:
H1 imbalance mitigation
Prior structure support
Ideal Smart Money reload zone after pullback
🟢 Continuation Target
Upside Objective: 5,300 – 5,310
Next external liquidity pool
Target only valid after discount reaction + confirmation
Invalidation
Strong H1 acceptance above 5,300 without mitigation
Would signal direct continuation, skipping deeper rebalance
Expectation & Bias
This is not a FOMO breakout environment
Liquidity comes before direction
Rejection = rotation
Acceptance = continuation
Execution > Prediction
💬 Will gold respect the H1 imbalance near 5,170 before attacking 5,300 — or will Smart Money surprise with direct acceptance at the highs?
GBP/JPY continues to consolidate; prime support is located at 20The sell-off from the 214.86 swing high has stalled.
We are now seeing a period of consolidation. This could be seen as a Wyckoff zone. That would suggest that the next move is a spike to the downside to grab liquidity.
Resistance is located at 211.71. We have a gap open at 212.51.
Support is located at 208.36. This would also be the completion of a bullish Gartley pattern
Single currency analysis suggests selling JPY. There is no immediate bias for GBP.
Conclusion: the immediate bias is hard to ascertain. I would look for the gap open at 212.51 to attract sellers, and bespoke support at 208.36 to attract buyers (we are mid-range)
EUR/USD scope for a medium-term top to be in place at 1.2083EUR/USD continued to move to the upside from the 1.1578 swing low.
We have a 261.8% extension level up 1.2081. Yesterday's high trade was 1.2083.
We have a supply zone located at 1.2051
To the downside, we have a gap open from Jan 25 1.1828. Further support is located at 1.1795
It should be noted that the last break higher can be seen as a fifth wave (Elliott Wave), Wyckoff liquidity grab (on the weekly chart)
Conclusion: although there is scope for some volatility over the Fed interest rate decision and press conference this evening, there is now scope for a medium-term top to be in place. Prime resistance is located at 1.2051
Dow Jones (US30) holds within a large expanding wedge pattern; tWe continue to see a prolonged period of consolidation. This is the third week in succession that price action has stayed broadly within the week Jan 5 range (48,352-49,673).
This limited movement has resulted in an Expanding Wedge pattern being posted on the intraday chart. Trendline resistance is located at 50,396. Trend line support is located at 48,397.
On the upside, we also have the 50K Big Figure. These large, round numbers often attract price action.
Conclusion: the immediate bias is hard to ascertain. The next intraday move will be driven by the Fed's interest rate decision and press conference. With the long-term bias skewed to the downside, the preferred stance would be to sell into gains.
US Crude Oil (WTI) sits mid-range; rallies to be sold and dips tWe have seen continued upward momentum from the $58.92 swing low. This has resulted in a break of structure from the $62.20 high trade posted on Jan 14.
On the upside, we have a confluence zone at $64.65. This is the trend of higher highs and bespoke resistance.
Support is located at $60.32. This level has been pivotal
Conclusion: we sit mid-range. Look for rallies to be sold at $64.65 and dips to be bought at $60.32
Paramount Skydance (PSKY)P/E (Forward 2026),~12.3x,CHEAP ✅. Significantly below Netflix levels (~33x).
Forward P/E,~11.5x - 12.5x, Market is cautious due to debt for WBD acquisition.
Free Cash Flow,~$1.5 billion (adj.),MODERATURE ⚠️. Expected $800 million negative impact from transaction costs.
Debt/Equity,~0.31 (31%),GOOD ✅. Debt is surprisingly low after restructuring.
Revenue Growth,~47.7% (est. 2026),PHENOMENAL ✅
PEG,~0.25 - 0.40,ULTRA UNDERVALUED ✅. Based on expected growth, it is very cheap.
Cash on Hand,~$9.0+ billion,EXCELLENT ✅. Ready for big acquisitions.
FCF Margin,~5% - 7%, Low due to huge content investments ($1.5 billion extra).
Quick Ratio,~1.10, GOOD ✅. Stable liquidity.
Inst. Ownership,~65% - 75%, Strong support from large funds.
Current Ratio,~1.25, GOOD ✅. Stable balance sheet.
Analyst DCF,$23.54, OVER-VALUED ✅. According to Simply Wall St, the stock is 50% undervalued.
Wall St Target,$14.00 - $14.57, Potential growth of about 20-25% from a price of ~$11.60.
Short-Term Investment Outlook – COMEX Gold WITH TARGET USD 5778TVC:GOLD Short-Term Investment Outlook – COMEX Gold
By Arun Nagalingam
Elliott Wave Analyst | 25 Years of Trading Experience
Date: 28 January 2025
Time: 10:55 AM
Current Price: USD 5,259 per ounce
COMEX Gold is currently trading at USD 5,259 per ounce and remains in a strongly bullish short-term trend. The prevailing price action indicates sustained upside momentum, with an initial upside target of USD 5,778.
In the event of a corrective pullback, the metal is expected to find strong support in the range of USD 5,088 – USD 4,983. Any such decline is likely to be corrective in nature and may offer a buying opportunity rather than signaling a trend reversal.
Technical Perspective – Elliott Wave Analysis:
On the daily chart, Gold is positioned within an upward impulse wave structure, currently unfolding in the 3rd wave, which typically consists of five sub-waves. This wave configuration suggests that any correction should remain limited, with the broader trend continuing to favor the upside.
Based on the Elliott Wave structure, the overall upside potential is projected toward USD 5,778 and USD 6,155 in the coming weeks.
Disclaimer:
This analysis is provided for educational and informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial or investment advice. Trading in commodities and financial markets involves substantial risk, including the potential loss of capital. Investors should conduct their own research and consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any trading or investment decisions.
Gold/Silver Ratio (Monthly): ABC Correction in Progress — C-WaveThe Gold/Silver ratio on the monthly timeframe appears to be unfolding as a large ABC corrective structure, with Wave C currently in progress and potentially extending.
Wave A completed with a sharp decline.
Wave B retraced deeply but failed near long-term channel resistance and Fibonacci confluence.
The recent impulsive selloff suggests C-wave continuation, not just noise.
Key Level to Watch:
43.15 — prior major swing low and structural inflection zone.
Holding above this level may allow stabilization or a complex pause.
A decisive monthly close below 43.15 would strongly favor a C-wave extension, opening lower extension zones.
This is a ratio chart, so moves reflect relative performance between gold and silver, not outright price direction.
Structure will be reassessed as new data develops.
Not financial advice.
Gold XAUUSD has hit our biggest TP I have been in gold trading for about years and have taught many students this skill. I have turned in this trade $1100 to $45000 results are in my social media with proof. Visit my bio and see the results. I have looked at weekly chart of USD it was very week and I took a nice buy trade in gold and holed it just for 1 day the result is in your screen.
S&P 500 (SPX) Breakout to Record High Confirms Bullish MomentumThe S&P 500 (SPX) has advanced to a new all-time high, confirming that the bullish sequence from the November 21, 2025 low remains intact. This breakout favors more upside in the near term. The rally from that low is unfolding in a clear five-wave structure, consistent with Elliott Wave analysis. Wave ((i)) ended at 6986.33, marking the first leg of strength. The pullback in wave ((ii)) developed as a zigzag correction. Within this phase, wave (a) ended at 6885.74, wave (b) rallied to 6979.34, and wave (c) declined to 6788.03. This completed wave ((ii)) at a higher degree.
From there, the index resumed higher in wave ((iii)). Wave (i) advanced to 6934.75, while wave (ii) pulled back to 6895.5. Momentum carried wave (iii) to 6988.82. A short-term pullback in wave (iv) is expected, but buyers should return for one more push higher to complete wave (v) of ((iii)). Afterward, the index should correct in wave ((iv)), addressing the cycle from the January 21, 2026 low before resuming its broader rally.
Near term, as long as the pivot at 6788.03 holds, pullbacks are likely to remain corrective. Buyers are expected to appear in three, seven, or eleven swings, supporting further upside. This structure highlights market resilience and suggests that the path of least resistance continues to point higher.
XAUUSD 15m Bullish Structure ✅ BEST BUY ZONE (High Probability)
From structure, the clean entry zone is:
🎯 Buy Zone: 5035 – 5050
(near Wave (2) retracement support)
This aligns with:
✔ Previous structure support
✔ Typical 50–61.8% pullback area
✔ Liquidity sweep already done at C
🟢 XAUUSD 15m bullish structure confirmed
📉 ABC correction completed
📈 New impulse Wave (1) formed — waiting Wave (2) retracement
🎯 Buy zone: 5035–5050
🚀 Targets: 5120 → 5200
❌ Invalidation below 5000
#ElliottWave #Gold #XAUUSD #BuyTheDip
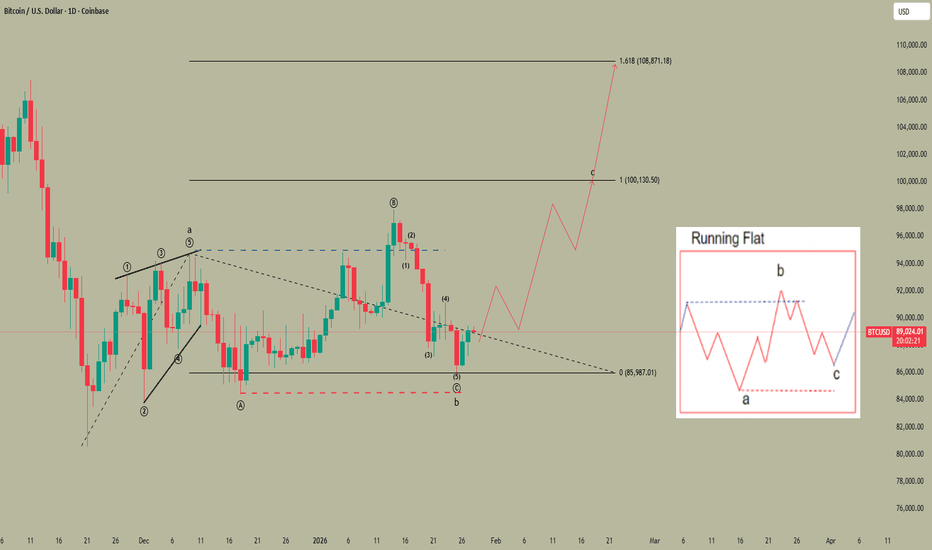
$BTC 4H – Wave Count ReviewCRYPTOCAP:BTC 4H – Wave Count Review 🧵
Quick look back at the idea:
Expected path:
Dip from 98k→ bounce ~91k (volume node) → retrace toward 95k → controlled dip to fattest volume cluster ~88k.
What happened:
No bounce, straight impulsive break lower, overshooting all the way to ~86k and violating the key 87.6k zone.
Simple information you can use right away: When price exhausts an expanding diagonal (clearly labeled on the chart), the resolution is frequently sharp and oversized—it skips intermediate supports and hunts the next major volume stack. Exactly what played out here.
The 87.6k violation lowers the immediate odds of new highs and introduces real structural ambiguity.
At the same time, the clean 97k → 86k drop creates fresh possibilities (more on that in the next full wave update).
Original post here: x.com
You buying this bounce, fading it, or sitting on hands? 👇
NG1! - Correction NeededFrom January 15 to January 26 of this year, a five-wave impulse was completed. We now expect a correction.
Potential targets:
6.360
5.741
5.204
4.677
The most probable range appears to be between 5.204 - 4.677 or lower, given that this is a commodity.
The exact correction structure will become clear as the move develops.
Estimated movement potential from current levels:
Approximately 4-30%
---
Please subscribe and leave a comment!
You’ll get new information faster than anyone else.
---
Jan 28, 2026 - XAUUSD GOLD Analysis and Potential Opportunity📊 Summary:
Pay close attention to the resistance at 5190. If price holds above 5190, there is little resistance overhead, and upside targets can be tracked in 5-point increments.
At the same time, watch the strength of support at 5159. If price breaks below 5159, bearish pressure will intensify, and the strategy shifts to selling rallies where resistance holds. If price holds above 5175, short-term long opportunities can be considered.
Trade carefully, manage risk well, and prioritize capital protection.
🔍 Key Levels to Watch:
• 5190 – Resistance
• 5159 – Key intraday support
• 5152 – Support
• 5133 – Support
• 5111 – Support
📈 Intraday Strategy:
SELL: If price breaks below 5159 → target 5152, with further downside toward 5144, 5140, 5133
BUY: If price holds above 5175 → target 5180, with further upside toward 5185, 5190, 5195
If you find this helpful or traded based on this plan, your likes, comments, and follows mean a lot and keep me motivated. Thanks for the support!
Disclaimer: This is my personal view, not financial advice. Always use proper risk control.
XAUUSD Update PRE FOMC January 2026 Today, we will face the first FOMC meeting of 2026.
Gold's market structure indicates that the price has already broken through 5100.
At key Fibonacci levels, the price will now face a resistance at 5500-5600 range.
Will the price be able to break through this level directly ?
Or will it require a correction/retracement first ?
Lets see the market reaction and stay safe and alert !
Have a great day !