Beyond Technical Analysis
District Metals - Bullish outlook for the Uranium StockDistrict Metals (DMX): A Sweden-Focused Metals Story With a Regulatory Catalyst
District Metals is a Canada-listed exploration and development company with a strong focus on Sweden. The company is positioned around two key themes: polymetallic base and precious metals in historically productive mining districts, and long-dated optionality tied to energy and critical metals.
One of the company’s core assets is the Tomtebo project in the Bergslagen mining district. Bergslagen is one of Europe’s most established mining regions, with centuries of documented production across copper, zinc, lead, silver and gold. Tomtebo hosts multiple historical mines and polymetallic showings distributed along a large structural trend. The investment case here is straightforward: modern exploration techniques applied to an old mining district that was never explored with today’s geophysics, structural modeling, or systematic drilling. Value creation is driven by data — drilling results, geological continuity and scale — not narratives.
The second leg of the story, and the one attracting increasing attention, is Viken. This project hosts uranium alongside other metals such as vanadium, molybdenum, nickel, copper and zinc. For years, the economic potential of Viken has been structurally capped by Swedish legislation, as uranium extraction was effectively prohibited. That regulatory ceiling mattered — regardless of geology, uranium could not be part of any mine plan.
That is now changing.
Sweden has formally decided to reverse its long-standing uranium ban. The Swedish parliament has approved amendments to the Minerals Act and the Environmental Code that allow uranium to be classified as a concession mineral, meaning it can legally be explored for and extracted under the standard permitting framework. These changes are scheduled to come into force on 1 January 2026.
This is a material shift. It removes a hard legal stop that has existed for decades. For projects like Viken, uranium can once again be considered as part of the economic equation rather than being ignored entirely. That said, this is not a shortcut to production. Permitting, environmental assessments, technical studies, social acceptance and economics still apply. The law change does not eliminate risk — it eliminates prohibition.
From a market perspective, District Metals sits at the intersection of three forces: drill-driven exploration upside at Tomtebo, regulatory re-rating potential tied to uranium in Sweden, and a broader European push for domestic supply of critical raw materials. This is inherently high-risk territory, but that is where optionality and asymmetric outcomes live.
Execution, not sentiment, will decide the outcome.
Disclaimer: This post is not financial advice and should not be considered a recommendation to buy or sell any security. Always do your own research before making investment decisions.
US100 Price Update – Clean & Clear ExplanationUS100 is currently trading under strong selling pressure after failing to sustain above the ascending trendline and the previous supply zone around 25,700–25,900. The sharp rejection from this area confirms that sellers remain in control.
Price has now broken below key structure support near 25,200–25,000, signalling a bearish continuation rather than a simple pullback. The recent impulsive bearish candle shows strong momentum, suggesting that any short-term bounce could be corrective.
As long as price remains below 25,700, the bias stays bearish. A short-term retracement toward 25,300–25,500 could offer selling opportunities, followed by a continuation lower toward 24,500. Only a strong reclaim above the broken trendline would invalidate this bearish scenario.
“If you come across this post, please like, comment, and share. Thanks!”
GOLD Price Update – Clean & Clear ExplanationSilver is currently trading within a rising channel, but price action shows a clear bearish rejection from the upper boundary of the channel. After forming a lower high near the resistance zone around 91.00–92.00, price failed to sustain bullish momentum and broke down sharply.
The recent strong bearish candle indicates loss of buying strength, suggesting that the market may shift from a short-term bullish structure into a corrective or bearish move.
Outlook: As long as price remains below the broken channel support and the 86.00 level, bearish pressure is likely to continue. A minor pullback toward 88.00–89.00 could occur, but sellers may re-enter from that zone. A decisive break below 85.00 could open the path toward 80.00 and 75.00.
“If you come across this post, please like, comment, and share. Thanks!”
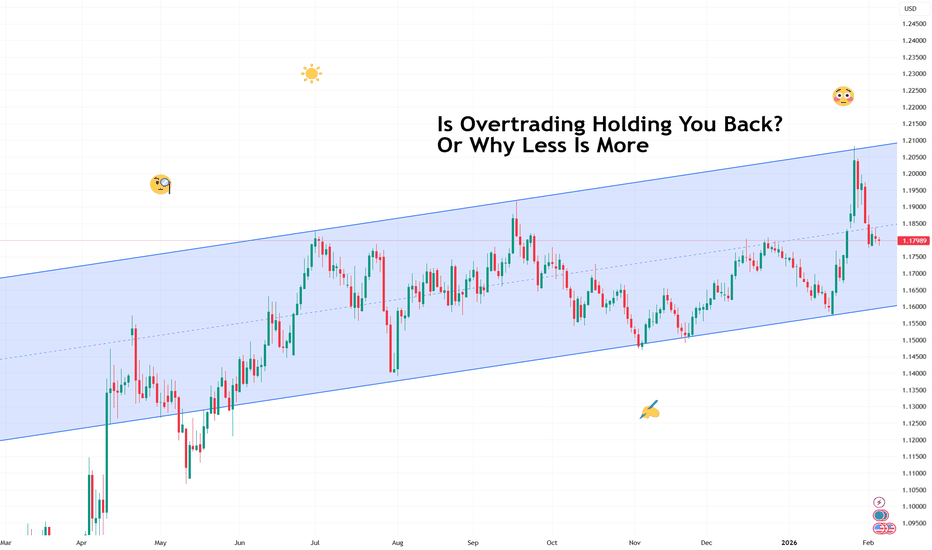
Is Overtrading Holding You Back? Or Why Less Is MoreMany traders think that activity means productivity. More charts, more clicks, more trades… more monitors?
The day feels productive when something is always happening (ref: the economic calendar ). The sense of participation feels rewarding.
This mindset forms early. And it’s normal — markets stay open across time zones and social feeds reinforce the idea that opportunity lives in constant motion. It becomes easy to believe that frequent action leads to faster learning and better results.
Markets, however, reward decision quality far more than decision quantity.
🤑 The Market Never Sleeps, but Your Edge Does
Markets offer endless movement all across the macro board . Stocks trend, currencies oscillate, crypto trades through weekends, and futures light up overnight. Availability creates temptation. But it also creates a false sense of urgency. And that can lead to overtrading.
Overtrading emerges when availability replaces selectivity. The presence of movement becomes enough reason to participate. Over time, that shift erodes consistency.
📉 How Trade Frequency Dilutes Quality
As trade count increases, standards tend to loosen. Entries happen at random points. Rationales fade and vague ideas begin to qualify. (Why not buy silver OANDA:XAGUSD at $120?)
This process rarely feels reckless. It feels adaptive. The trader remains engaged, yet the edge spreads thinner with each additional position. Performance suffers through gradual dilution rather than sudden failure.
🧮 Why Fewer Trades Improve the Math
Every trade carries friction. Spreads, swaps, slippage, fees, and mental effort accumulate with frequency.
When trades are selective, friction affects fewer outcomes and higher-quality setups offset costs more efficiently.
Many traders improve results by removing their weakest trades rather than adding new tools. Fewer decisions often lead to stronger averages.
🧘 Learning to Sit with Inactivity
Periods without trades feel uncomfortable at first. But with time, perspective shifts and missed trades reveal themselves as avoided losses. Market clarity improves without pressure to act.
After all, you’re not a hedge fund (yet) and you’re not obligated to produce quarterly results for your clients (ok, fine… yet). You don’t need the pressure to act.
Sitting on your hands becomes a skill rather than a weakness. Many traders identify this transition as a turning point in their development.
Here it from the legend himself:
“I began to realize that the big money must necessarily be in the big swing.” - Jesse Livermore.
📊 Cleaner Data, Better Reviews
Fewer trades create clearer feedback because patterns stand out and mistakes become easier to diagnose. What’s more, you can do a much better homework on one or two trades a month than 30-40 trades.
On the flipside, overtrading floods review processes with noise. Selectivity produces cleaner datasets and more actionable insights.
Improvement accelerates when analysis focuses on quality rather than volume.
🎯 Why Less Is More
And here’s why less is more. When you trade less, you do more intentional participation.
It involves waiting for familiar conditions, accepting missed moves, and treating restraint as a form of risk management.
The objective centers on precision rather than presence. The goal here is to last to see another day, because markets will be there tomorrow, offering another chance to pick up a profit.
Again, overtrading often feels productive. Screens stay active and effort remains visible. Markets, however, reward patience, clarity, and selectivity. If the “more is less” concept sounds as distant as “cut losses, let profits run,” worry not — it gets easier.
“It never was my thinking that made the big money for me. It always was my sitting. Got that? My sitting tight!” - Jesse Livermore.
Off to you : How do you approach your trades? Are you the active trader seeking out daily moves in multiple trades or you take a broader view with less time spent in and out of positions?
Gold in consolidation todayToday the gold xauusd market is consolidating due to lest volume and we are waiting for the break out in either side so we can take a trade. I am not interested now in trade as long as there is consolidation. It occurs just for engineering liquidity and Smart money are quietly and slowly executing position and we want to be with them never against them thanks.
XAUUSD SELL 5 Feb 20261. Identifying the Immediate Trend (Consolidation)
What we saw: The price on the far right ("C4,922.66") is almost exactly where it opened ("O4,921.15"). The daily high and low are very close together (~12 points).
The Principle: When the open and close are nearly identical and the price moves in a small band, it forms a Doji-like or small-bodied candle pattern on a higher timeframe. This indicates a balance between buyers and sellers—indecision.
Conclusion: Therefore, the short-term trend is consolidative or sideways. There is no clear directional momentum in this specific 15-minute session.
2. Determining Key Support & Resistance Levels
Immediate Levels (Today's High/Low):
Why 4,929.72 is resistance: Price moved up to this level and then turned down. This shows that, at least for today, sellers emerged at this price, preventing further gains. It's the most recent "ceiling."
Why 4,917.29 is support: Price fell to this level and then bounced. This shows buyers stepped in here, creating a "floor." These two levels define the current micro-range.
Broader Levels (From the Chart Scale):
Resistance Zone (4,952–5,050): The left side of the chart shows the price previously rising toward 4,952.57 and even 5,050. These are psychological and technical levels where the market has previously reversed or paused. The market "remembers" these levels.
Support Zone (4,666–4,700): This area on the lower left shows a significant cluster of price action where a major low was formed before a strong rally. This is now a major support zone—if the price falls back here, many buyers would be expected to re-enter.
3. Reading the Broader Chart Structure & Patterns
The "Narrative" of Price Movement:
Look at the overall chart from left to right: Price made a large swing up from the ~4,666 low to the ~4,952 high. This is a clear uptrend leg.
After the high, the price began to move down and sideways (forming what looks like a downtrend channel or a series of lower highs on the right side). This is a pullback or retracement within the larger uptrend.
Pattern Recognition: This structure—a sharp rise (the "flagpole") followed by a downward-sloping consolidation (the "flag")—is a classic Bullish Flag pattern. This pattern suggests the prior uptrend may resume.
The Critical Question: Is this pullback a healthy pause (bullish flag) or the start of a reversal? The answer lies in the support levels. If the price holds above the recent swing low (around 4,850-4,789), the bullish flag thesis remains valid. If it breaks, the trend is threatened.
4. Formulating the Trading Outlook (Scenarios)
This is where analysis turns into a plan. We define what would confirm or invalidate our interpretation.
Bullish Scenario: For the bullish flag pattern to play out, price must break upward out of its consolidation. The most immediate signal would be breaking today's high (4,930), then the more significant level of the recent pullback high near 4,952. This would target a move equal to the initial "flagpole," projected upward.
Bearish Scenario: If instead, the price breaks below the immediate support (4,917), it suggests the pullback is deepening. A break below the major support zone (~4,789) would decisively break the higher-low structure of the larger uptrend, signaling a potential trend reversal.
Neutral Scenario: As long as price chops between these immediate levels with small candles and low volume, the market is in a holding pattern. No new trade is justified until a break occurs.
February 2025 Monetary Policy ReportThe February 2025 Monetary Policy Report confirms that the U.S. economy is navigating a late-cycle disinflationary expansion rather than entering a recessionary phase. Inflation has decelerated meaningfully from its 2022 peak, yet remains above the Federal Reserve’s 2 percent objective, while economic growth continues at a solid pace supported by consumption and productivity gains. The labor market has rebalanced from extreme tightness toward a more sustainable equilibrium without material deterioration in employment conditions. Against this backdrop, the Federal Reserve has begun easing policy, but the report makes clear that this is a recalibration from peak restriction rather than the start of a rapid or accommodative easing cycle.
Inflation dynamics remain the central constraint on policy. Headline PCE inflation declined to 2.6 percent year over year in December, while core PCE inflation stood at 2.8 percent, indicating continued but incomplete progress toward price stability. The Federal Reserve emphasizes that disinflation during 2024 was uneven, with notable persistence in core services prices. Core goods prices have largely normalized and are slightly deflationary, reflecting healed supply chains and balanced goods markets. Housing services inflation has moderated but remains elevated due to the well-documented lag between market rents and measured shelter inflation, suggesting continued downward pressure through 2025. In contrast, core non-housing services inflation has flattened at a relatively high level, reflecting labor-intensive sectors and idiosyncratic non-market price components. This composition underscores that the remaining inflation challenge is structural and wage-linked rather than cyclical or commodity-driven.
Inflation expectations remain a stabilizing force in the outlook. Survey-based and market-based measures of longer-term inflation expectations remain broadly consistent with the Federal Reserve’s 2 percent objective and within the range observed before the pandemic. This anchoring is critical, as it provides policymakers with the flexibility to reduce policy restraint gradually without undermining credibility or risking a resurgence in inflation psychology. Short-term inflation expectations have fluctuated with recent data but remain contained, reinforcing the view that monetary policy remains effective.
Labor market conditions appear solid and increasingly balanced. The unemployment rate stabilized at 4.1 percent in the second half of 2024, a level that remains low by historical standards. Job openings and quits have declined from their post-pandemic extremes but remain above pre-2019 averages, suggesting continued labor demand without excess overheating. Importantly, labor market easing has occurred primarily through slower hiring rather than increased layoffs, a pattern consistent with a soft landing rather than a cyclical downturn. Layoff indicators remain subdued, and employment losses have been concentrated in manufacturing rather than services.
Labor supply growth has slowed materially, which has implications for wage dynamics. Labor force participation has largely plateaued, and immigration-driven population growth appears to have decelerated sharply after mid-2024. As a result, wage growth, while moderating, remains somewhat elevated. Nominal wage growth slowed to approximately 3.6 percent year over year by the end of 2024, down from post-pandemic peaks but still above its pre-pandemic pace. The Federal Reserve notes that wage growth at this level may be inconsistent with 2 percent inflation unless supported by sustained productivity gains.
Productivity is therefore a critical variable in the current macroeconomic regime. Business-sector labor productivity increased nearly 2 percent in 2024, and average productivity growth since late 2019 has exceeded the pace observed in the prior expansion. The Federal Reserve attributes this improvement to strong new business formation, efficiency gains from post-pandemic labor reallocation, and early stages of artificial intelligence integration into production processes. While policymakers remain cautious about overstating the near-term impact of AI, they acknowledge that sustained productivity growth could allow higher real wage growth without renewed inflationary pressure. This dynamic materially improves the probability of a durable soft landing.
Financial conditions remain restrictive overall but have eased at the margin following rate cuts. Short-term Treasury yields declined in line with policy easing, while longer-term yields rose in late 2024 as markets priced stronger growth and higher term premia. Equity prices continued to rise despite higher long-term yields, reflecting confidence in the economic outlook. Credit availability remains uneven, with large and mid-sized firms retaining access while small businesses and lower-credit households face tighter conditions. From a financial stability perspective, the Federal Reserve highlights elevated valuations across several asset classes, high hedge-fund leverage, and ongoing vulnerabilities in less regulated non-bank financial intermediaries, even as the banking system remains well capitalized and resilient.
Monetary policy is firmly in a recalibration phase. After holding rates at restrictive levels through mid-2024, the Federal Reserve reduced the federal funds target range by a cumulative 100 basis points, bringing it to 4.25–4.50 percent. The report frames this shift as a reduction in the degree of restraint rather than a move toward accommodation. Future policy decisions will remain data-dependent, with particular sensitivity to inflation persistence and labor market conditions. Balance sheet reduction continues in a predictable manner, though at a slower pace, with total securities runoff now approaching two trillion dollars. Policymakers reiterate their intention to conclude quantitative tightening once reserve balances are comfortably within the ample-reserves regime.
Looking forward, the baseline outlook implied by the report is one of continued moderate growth, gradually easing inflation, and cautious additional rate cuts over time. The Federal Reserve appears comfortable maintaining policy in mildly restrictive territory as long as inflation continues to trend downward and labor market conditions remain stable. Upside risks center on sustained productivity gains that could raise potential growth and accelerate normalization without inflation, while downside risks include renewed services inflation or geopolitical shocks that could disrupt energy markets and stall disinflation.
In strategic terms, this report signals a Federal Reserve that is managing success rather than responding to crisis. Policy is no longer focused on fighting runaway inflation, but neither is it pivoting toward stimulus. Inflation is now primarily a services- and wage-driven issue, the labor market is balanced rather than fragile, and productivity has emerged as the key variable shaping the medium-term outlook. Rate cuts should be interpreted as calibration and insurance, not as the beginning of a classic easing cycle.
Markets Implication:
From a rates perspective, the report reinforces that the peak in policy restriction is behind us, but it does not validate an aggressive easing cycle. The Fed has clearly signaled comfort with the current policy range relative to most rule-based estimates, implying that front-end rates should gradually drift lower but remain structurally higher than in the pre-pandemic regime. This supports a continued flattening bias at the very front of the curve, while the belly of the curve remains most sensitive to incoming inflation and labor data. Long-end yields are likely to remain volatile and range-bound, as stronger productivity and resilient growth limit downside in term premia even as inflation decelerates.
For the U.S. dollar, the report is modestly supportive on a relative basis. The Fed’s easing path remains more cautious than that of many advanced foreign economies, and the report explicitly acknowledges widening rate differentials and U.S. growth outperformance as drivers of dollar strength. As long as U.S. inflation does not undershoot sharply and labor markets remain stable, the dollar should retain support against low-growth currencies, particularly those tied to more aggressive easing cycles. Sustained dollar weakness would likely require either a sharper domestic slowdown or a clear acceleration in global growth outside the U.S.
Equity markets are implicitly validated but not fully endorsed by the report. The Fed’s characterization of financial conditions as still restrictive suggests policymakers are aware of elevated equity valuations but are not actively seeking to suppress risk appetite. The soft-landing narrative remains intact, supported by stable employment, easing inflation, and strong productivity growth. This environment favors equities with pricing power, balance-sheet strength, and exposure to productivity-enhancing investment, while highly leveraged or rate-sensitive segments remain vulnerable to renewed yield volatility. Equity upside from here is likely to be more earnings- and productivity-driven rather than liquidity-driven.
For precious metals, particularly gold, the report presents a mixed but constructive backdrop. On one hand, easing policy and slowing inflation reduce real-rate pressure at the margin. On the other hand, resilient growth, anchored inflation expectations, and a supported dollar limit the scope for a sharp upside breakout. Gold remains more sensitive to tail risks highlighted implicitly in the report, including geopolitical shocks, financial stability concerns in non-bank sectors, and any loss of confidence in the soft-landing path. Absent those catalysts, gold is more likely to trade as a hedge than as a momentum asset.
In foreign exchange crosses involving yield differentials, the Fed’s tone favors carry stability rather than disruption. The absence of urgency in cutting rates reduces the probability of abrupt repricing in funding currencies. This supports higher-yielding USD pairs and discourages aggressive risk-on FX positioning until there is clearer confirmation of synchronized global easing. Volatility should remain compressed in the near term, but vulnerable to inflation surprises, particularly in U.S. services data.
In credit markets, the report supports continued spread stability rather than compression. Corporate balance sheets are not flagged as a systemic risk, but elevated valuations and tighter lending standards suggest limited room for further spread tightening. Investment-grade credit remains supported by the soft-landing outlook, while lower-quality credit is increasingly exposed to refinancing risk in a higher-for-longer rate environment. The Fed’s ongoing balance sheet reduction reinforces a gradual withdrawal of liquidity, which caps excess risk-taking.
For commodities, energy markets remain asymmetrically risky. While the report notes subdued demand pressures and rising non-OPEC supply, it also explicitly flags geopolitical tensions as an upside risk to prices. This creates a skewed distribution where downside is gradual and fundamental, while upside is sudden and event-driven. Industrial commodities are more directly linked to the productivity and investment narrative, particularly around AI, infrastructure, and data-center buildout, which may support selective strength even in a disinflationary environment.
Overall, the dominant market implication of the report is regime stability rather than regime change. The Fed is neither panicking nor declaring victory. Policy normalization will be slow, conditional, and data-driven, favoring range-bound trading conditions punctuated by volatility around inflation and labor surprises. The key risk to this equilibrium is not weak growth, but sticky services inflation or an exogenous shock that forces the Fed to reassert restraint.
Report 5/2/26Report summary
Markets are digesting a “policy-risk cocktail” that mixes Middle East escalation risk (and the sudden release valve of planned U.S.–Iran talks), a harder geopolitical line involving China and Russia, and a Fed that looks less willing to resume rate cuts while inflation remains sticky. The net effect is a tug-of-war between risk-off impulses (higher geopolitical tail risk, tighter-policy bias) and risk-on support (energy-price relief if diplomacy holds; still-resilient U.S. growth). The near-term baseline is choppy range-trading across major assets, with outsized sensitivity to headlines from Oman/Tehran/Washington and the Fed’s “higher-for-longer” narrative.
What happened and why it matters now
On the geopolitical side, markets are repricing the probability distribution around Iran: the risk of U.S. military action had risen in the background, while Beijing and Moscow signaled stronger alignment and warned against destabilization of Iran. A Trump–Xi call framed the relationship as “excellent” in U.S. messaging, but China’s readout emphasized reciprocity and elevated Taiwan as the core bilateral issue—an important reminder that strategic competition remains the structural backdrop even when tactical de-escalation is pursued.
Concurrently, Russia escalated pressure on Ukraine’s civil a major aerial assault after a short pause, hitting thermal power capacity across multiple regions and worsening winter hardship—an event that keeps Europe’s security premium alive even when gas/oil fundamentals look benign. Peace contacts continued, but the operational signal from Moscow is that coercion remains central to its bargaining posture.
On the macro/policy side, U.S. data and Fed communications e direction: growth is slowing at the margin (ADP private payrolls came in at +22k for January), but Fed officials are signaling they are more worried about inflation persistence than labor softness—reducing the market’s confidence in an imminent cutting cycle restart.
Observed market reactions
st real-time barometer of Middle East risk premium. Reuters reports Brent falling about $1.3 (roughly -1.9%) as the U.S. and Iran agreed to hold talks in Oman, easing immediate disruption fears. That move is consistent with a “risk premium compression” regime: absent an actual supply shock, the market sells volatility after diplomacy is confirmed.
Equities are showing internal rotation rather than broad panic. Reuters flagged a session where the S&P 500 slipped (-0.51%) and the Nasdaq fell harder (-1.51%) while the Dow finished higher (+0.53%), consistent with a market that is punishing duration/AI-adjacent exposures while still bidding defensives/cyclicals with nearer cash flows.
In FX, the dollar’s near-term impulse is more nuanced: the DXY is firming on hawkish-Fed messaging even as longer-horizon narratives about U.S. fiscal dominance and policy unpredictability weigh on structural “dollar exceptionalism.” In the immediate window, higher U.S. real-rate expectations tend to support DXY; in the medium window, deficits and institutional risk can cap rallies and keep the dollar’s risk premium unstable.
USDJPY is behaving like a “rate-differential + risk” hybrid: it has been moving back toward the upper end of recent ranges, with spot readings around the mid-157 area in some feeds, reflecting both a still-wide U.S.–Japan yield gap and episodic risk sentiment swings.
Fiscal and political implications
The U.S. policy mix remains the biggest macro amplifier. A Fed that is reluctant to cut into sticky inflation increases the financing cost of large deficits and tightens financial conditions at the margin—especially if the market starts to believe the central bank will tolerate higher term premia rather than cap yields. That’s why any perceived tilt toward balance-sheet tightening and “less market insurance” has outsized impact on equity multiples and long-duration assets.
Geopolitically, a firmer China–Russia alignment around Iran elevates the risk that regional crises become bargaining chips in a wider contest (sanctions enforcement, trade access, Taiwan signaling, energy flows). Even if the base case is diplomacy in Oman, the distribution now has fatter tails: miscalculation risk is higher, and that raises the value of optionality (gold, convex hedges) while compressing valuations where h-multiple growth, leveraged balance sheets).
Forecasts
In the next month, the highest-probability path is “headline-driven mean reversion.” If U.S.–Iran talks proceed without a major incident, crude can drift lower or stay capped, easing one inflation channel and giving equities some breathing room, but not enough to restore the prior multiple expansion if the Fed continues to emphasize inflation risk.
next quarter, the decisive macro question is whether inflation prints and wage dynamics soften enough to reopen the door to cuts. The ADP signal of cooling job growth helps the dovish case at the margin, but the Fed is explicitly telling you it wants clearer evidence on inflation before it pivots—so the market’s “policy put” is higher-strike and less reliable.
Geopolitically, Ukraine infrastructure strikes suggest energy and logistics risk in Europe stays “on,” even if pricing isn’t reacting every day. That means Europe remains exposed to abrupt risk repricings (insurance costs, rebuilding needs, defense outlays), and it keeps a bid under strategic commodities and defense supply chains.
Asset-by-asset implications
XAUUSD: Gold’s setup is constructive in this regime because it benefits from both geopolitical tail risk concerns about fiscal dominance and institutional credibility. The main tactical headwind is a firm DXY and higher real yields; if those surge, gold can chop or pull back, but dips tend to be bought when geopolitical tails remain live.
S&P 500: Expect dispersion to dominate index direction. When oil supports margins and consumer real income; when the Fed leans hawkish, it compresses duration and hits the index’s growth concentration. The result is a market that can look “fine” on the surface while leadership narrows or flips quickly—keep a close eye on breadth and earnings sensitivity to discount rates.
Dow Jones: The Dow’s relative resilience in the cited session fits a playbook where less-duration, more cash-flow-visible constituents hold up better during rate-and-geopolitical uncertainty. If crude remains contained and the U.S. economy avoids a hard landing, Dow-style exposures can keep outperforming.
USDJPY: If the Fed stays hawkish and Japan’s rate normalization remains incremental, USDJPY bias stays upward; however, sharp risk-off episodes can still trigger yen strength via repatriation and de-risking. In other words, it’s a trend-plus-whipsaw profile—position sizing matters more than conviction.
DXY: Near term, DXY support comes from rate expectations and relative growth; medium term, the “policy credibility + fiscal path” narrative can reassert itself and cap rallies. Watch for any escalation in trade/tariff rhetoric or explicit pressure on Fed independence as catalysts that can flip dollar strength into dollar risk premium.
Crude Oil: The market is currently trading “war premium vs diplomacy premium.” Confirmation of talks drains premium; cancellation or incidents in the Strait/Hormuz region re-inject it quickly. The asymmetry is important: downside is typically grindy, upside is often gap-like.
Risks and opportunities
The key downside risk is a regime shift where diplomacy fails, leading to a supply shock in crude at the same time the Fed is constrained by sticky inflation. That’s the classic stagflationary impulse: equities derate, credit spreads widen, and EM importers suffer. A second risk is that Ukraine energy strikes intensify enough to spill into broader European industrial confidence, reviving a continental growth scare even if oil is calm.
The main opportunity is that successful U.S.–Iran talks reduce oil volatility and ease the inflation outlook at the margin, allowing risk assets to stabilize even without immediate Fed cuts. In that environment, the winners are typically “quality carry” trades: equities with visible cash flows and pricing power, selective cyclicals benefiting from lower energy input costs, and relative-value FX rather than one-way dollar bets.
Nifty 50 | Long-Term Gann Percentage StructureThis idea shares a historical, educational study on how percentage expansion and time–price structure, as described in classical WD Gann methodology, appeared on the Nifty 50 index.
The purpose of this post is to study market structure, not to provide predictions or trading advice.
📌 Structural Background
In April 2023, Nifty formed a major swing low on the daily timeframe.
From a Gann perspective, long-term market movements often unfold through:
Mathematical percentage relationships
Major swing reference points
Time symmetry across trends
One commonly studied expansion in Gann work is the 32% proportional move from a major base.
📈 What the Chart Demonstrates
The chart highlights:
A clearly defined major low acting as a structural anchor
A percentage-based projection zone derived mathematically
Price movement unfolding gradually toward that zone over time
Respect for proportional expansion rather than random movement
This example shows how markets often react to mathematical proportions over longer horizons
.
🧠 Key Learning Points
This case study reinforces several timeless Gann concepts:
Large trends often respect fixed mathematical proportions
Important levels emerge from structure, not speculation
Time and patience play a critical role in trend development
Studying completed structures improves future market understanding
The focus is not accuracy, but process and discipline in analysis.
⚠ Disclaimer
This idea is shared strictly for educational and research purposes.
It does not constitute financial advice, recommendations, or live market calls.
XAUUSD – Short-Term Price Action Analysis (30M)This idea is shared for educational purposes only.
On the 30-minute timeframe, XAUUSD is reacting near a resistance zone around 4920–4935.
Price may show a short-term pullback toward the 4790 area before the next move.
🔍 Key Levels:
Observation Zone: 4920
Invalidation Level: 4935
Target Area: 4790
This analysis is based on price action and market structure, not a trading signal.
Always manage risk and follow your own strategy.
USD/MYR Outlook: Why the Ringgit Is Defying Asian TrendsThe Malaysian Ringgit is currently defying regional currency trends. It stands as a top performer among its Asian peers. Investors are now recalibrating their expectations for the USD/MYR pair. This shift stems from robust domestic growth and strategic global positioning.
Macroeconomic Stability and Growth
Bank Negara Malaysia maintains a disciplined monetary policy. Local fiscal reforms have successfully enhanced international investor confidence. Strong export data continues to support the currency’s intrinsic value. These economic fundamentals provide a sturdy floor for the Ringgit.
Geostrategy and Neutrality
Malaysia leverages its "China Plus One" strategy with great precision. The nation attracts global firms seeking supply chain diversification. This geostrategy stabilizes long-term capital inflows despite global tensions. Neutrality allows Malaysia to trade effectively with both Eastern and Western powers.
Semiconductor and High-Tech Dominance
Malaysia controls a vital share of global semiconductor testing and packaging. High-tech exports drive consistent demand for the Ringgit. Modern industrial parks in Penang foster a deep culture of innovation. This technological edge secures Malaysia’s spot in the global value chain.
Patent Growth and Scientific Advancement
The government aggressively incentivizes high-tech R&D and patent filings. This focus shifts the economy toward higher value-added services. Science-led growth attracts sophisticated institutional investors to the region. Increasing intellectual property output signals a maturing, high-tech economy.
Digital Security and Infrastructure
Cybersecurity remains a primary priority for Malaysia’s digital transition. Massive data center investments signal long-term structural strength. Robust digital infrastructure bolsters the nation's evolving business model. These advancements protect the economy from modern digital threats.
Management and Leadership
Clear government leadership simplifies complex regulatory frameworks. Transparent policies significantly reduce market volatility for foreign traders. This administrative stability makes USD/MYR a preferred pair for regional exposure. Leadership now prioritizes sustainable growth over short-term gains.
Future Business Models
Malaysia is transitioning toward green energy and ESG-compliant industries. New business models focus on high-efficiency manufacturing and digital services. This evolution ensures the Ringgit remains relevant in a decarbonizing world. The nation is successfully future-proofing its economic engine.
Conclusion for Investors
The USD/MYR pair reflects a shifting global power dynamic. Malaysia's blend of tech mastery and fiscal discipline is working. The Ringgit is no longer just a commodity currency. It is a sophisticated proxy for Southeast Asian innovation.
Nifty 50 | Gann Time–Price Interaction June 2024 (Educational)This idea presents a historical, educational case study on how Gann Natural Time Cycles (NTC) and price levels interacted on Nifty 50 during early June 2024.
It is shared strictly for learning and structural understanding, not as trading advice or a forward-looking forecast.
📌 Market Context (Historical)
During the first week of June 2024, Nifty was approaching an important time window derived from classical WD Gann Natural Time Cycle calculations.
At the same time, a key horizontal price level was acting as a reference zone on the chart.
This created a time–price convergence, which is a core concept in Gann methodology.
📈 What the Chart Illustrates
From an observational perspective:
Price approached a clearly defined Gann reference level
The market showed increased activity near that zone
After interaction with the level, price expanded upward
This behavior highlights how time alignment can influence market reaction around important price areas
Rather than focusing on prediction, the chart demonstrates how markets often respond when both time and price align.
🧠 Educational Takeaways
This case study reinforces key Gann principles:
Time is as important as price
Levels act as decision zones, not guarantees
Confirmation comes from price behavior after interaction
Discipline means observing structure, not anticipating outcomes
Studying such examples helps traders develop process-based thinking instead of emotional decision-making.
⚠ Disclaimer
This idea is for educational purposes only.
It does not constitute financial advice, recommendations, or live trading calls.
Dow/Gold flashes GFC warningTop: Dow / Gold ratio
Bottom: SP:SPX
The Dow/Gold ratio shows How many ounces of gold does it take to buy the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
It gives insight into the question “who’s winning: paper or metal?”
It moves often coincide with large inflection points.
The current level typical coincides with stock market tops:
1929
1972
1974
2008
USDZAR – 4H | Sell Plan (No Entry Yet)Market is currently moving into a higher-timeframe supply / premium area.
This zone is not an automatic sell it’s an area of interest.
I am waiting for price to push higher into the zone and then prove buyers are weak.
What I need before selling:
Price taps deeper into supply
Rejection (long wicks / strong bearish close)
Lower-timeframe structure shift (lower high / break of minor support)
Until that happens, there is no trade.
If price breaks and holds above the supply, the idea is invalid and I step aside.
Targets are placed at the discount zone, where liquidity and previous lows sit.
This is patience over prediction.
I react to confirmation I don’t guess tops.
Process first. Execution second. Profits follow. Stop chasing and start waiting.
Google’s AI Pivot: The World’s Next Pharma GiantAlphabet recently shattered Wall Street expectations with its Q4 2025 earnings report. Management is aggressively increasing capital expenditure for 2026. This spending fuels a massive expansion of AI infrastructure. Investors now see a clear shift in Google's corporate strategy.
The Great Technological Pivot
Google is no longer just a search engine company. It is transforming into a dominant scientific powerhouse. DeepMind remains the crown jewel of this technological ecosystem. Their newest AI models now learn faster than any previous systems.
From AlphaFold to AlphaGenome
AlphaFold already solved the protein-folding mystery for global science. Now, AlphaGenome decodes the "dark matter" of the human genome. It processes a million DNA letters at once. This tool predicts gene regulation with unprecedented precision.
The Most Important Pharma Company
This technology transforms Google into a pharmaceutical powerhouse. Traditional drug discovery is notoriously slow and expensive. Google’s AI accelerates this process by several decades. They now own the digital blueprint of human biology.
Patent Analysis and High-Tech Moats
Google’s patent portfolio reveals a deep focus on biotechnology. They dominate the foundational algorithms for life sciences. This intellectual property creates an unassailable competitive advantage. No traditional pharmaceutical company can match this computational scale.
Geostrategy and Leadership
CEO Sundar Pichai is leading an "AI-first" biological revolution. This geostrategy secures Google's role in global health security. Management is prioritizing long-term scientific dominance over advertising growth. They are building a more resilient, high-tech business model.
Macroeconomics and Cybersecurity
Macroeconomic pressures do not hinder their scientific progress. Google secures sensitive genetic data with advanced cybersecurity. This trust remains vital for the future of medicine. Alphabet is becoming the ultimate architect of human longevity.
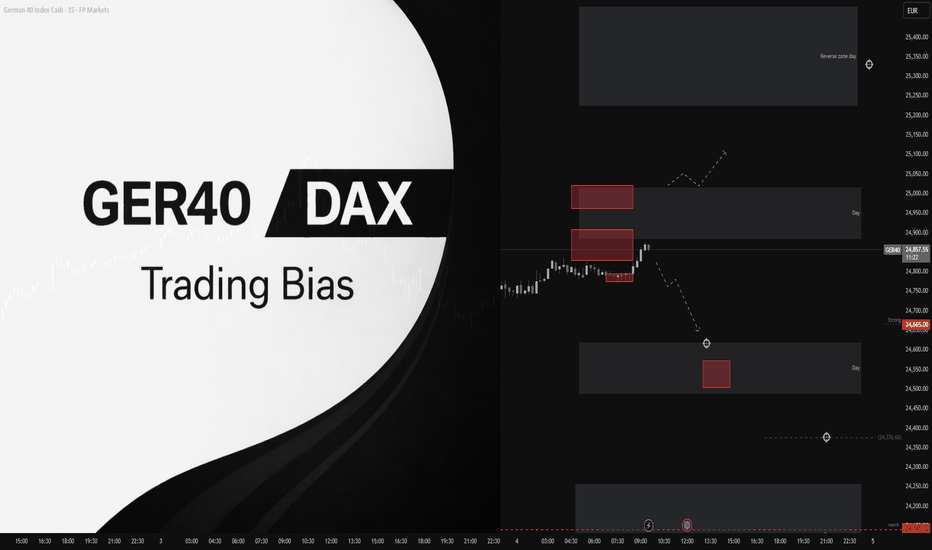
GER40 (DAX) – Intraday Trading Plan | Feb 4🔥 GER40 (DAX) – Intraday Trading Plan | Feb 4
The broader market context remains bearish.
The session opened below the key level at 24,847,
with the key level positioned below the Point of Control,
confirming a bearish intraday bias.
Intraday plan (short):
Primary targets:
– lower daily short zone: 24,618 – 24,588,
– daily reversal short zone: 24,141 – 24,062.
Intermediate reaction level:
– 24,665.
As long as price holds below 24,847,
short positions remain the priority.
Alternative scenario:
only a strong acceptance above the daily zone
opens a potential long setup
toward the upper daily reversal zone at 25,233 – 25,489.
This is not financial advice. Risk management is required.