Unlocking Currency DerivativesStrategies, Instruments, and Risk Management in the Global FX Market
Currency derivatives are powerful financial instruments that allow traders, investors, and corporations to manage foreign exchange (FX) risk, speculate on currency movements, and enhance portfolio efficiency. As global trade, capital flows, and cross-border investments continue to expand, understanding and effectively using currency derivatives has become essential. Unlocking currency derivatives means not only knowing what these instruments are, but also mastering how, why, and when to use them.
Below is a detailed, structured explanation of currency derivatives, their types, uses, strategies, risks, and relevance in modern financial markets.
1. Understanding Currency Derivatives
Currency derivatives are financial contracts whose value is derived from an underlying currency pair (e.g., USD/INR, EUR/USD).
They allow participants to lock in future exchange rates or profit from changes in currency prices.
These instruments are widely used in international trade, investment hedging, and speculative trading.
Currency derivatives trade both on exchanges (standardized contracts) and over-the-counter (OTC) markets (customized contracts).
2. Why Currency Derivatives Matter
Exchange rates are influenced by interest rates, inflation, geopolitics, trade balances, and central bank policies.
Sudden currency fluctuations can significantly impact profits, costs, and asset values.
Currency derivatives help manage uncertainty by transferring risk from those who want to avoid it to those willing to take it.
They provide transparency, liquidity, and price discovery in global FX markets.
3. Major Types of Currency Derivatives
Currency Forwards
Customized OTC contracts to buy or sell a currency at a predetermined rate on a future date.
Widely used by corporates to hedge import/export exposure.
Currency Futures
Exchange-traded, standardized versions of forwards.
Offer transparency, daily mark-to-market settlement, and lower counterparty risk.
Currency Options
Give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specific rate before or on expiry.
Useful for asymmetric risk protection.
Currency Swaps
Agreements to exchange principal and interest payments in different currencies.
Commonly used by banks, governments, and large institutions.
4. Participants in the Currency Derivatives Market
Hedgers
Corporations, exporters, importers, and investors protecting against adverse currency movements.
Speculators
Traders seeking to profit from anticipated currency fluctuations.
Arbitrageurs
Participants exploiting price inefficiencies across markets.
Institutional Players
Banks, hedge funds, asset managers, and central banks providing liquidity and depth.
5. Hedging with Currency Derivatives
Currency derivatives allow businesses to stabilize cash flows and protect profit margins.
Importers hedge against currency appreciation, while exporters hedge against depreciation.
Options provide flexible hedging by allowing participation in favorable moves while limiting downside risk.
Effective hedging improves financial planning, budgeting, and investor confidence.
6. Speculative Trading Strategies
Directional Trading
Taking long or short positions based on macroeconomic or technical analysis.
Carry Trade
Borrowing in a low-interest currency and investing in a high-interest currency.
Volatility Trading
Using options strategies such as straddles and strangles to profit from large price movements.
Range Trading
Benefiting from stable currency movements using option selling strategies.
7. Role of Interest Rates and Central Banks
Interest rate differentials are a major driver of currency prices.
Central bank actions, such as rate hikes, quantitative easing, and forward guidance, directly impact FX markets.
Currency derivatives allow traders to position themselves ahead of policy announcements.
Understanding monetary policy cycles is critical to unlocking consistent returns.
8. Risk Management in Currency Derivatives
Currency derivatives involve leverage, which can magnify gains and losses.
Key risks include market risk, liquidity risk, counterparty risk, and regulatory risk.
Stop-loss strategies, position sizing, and diversification are essential risk controls.
Margin requirements and mark-to-market settlements demand disciplined capital management.
9. Regulatory Framework and Market Integrity
Exchange-traded currency derivatives are regulated to ensure transparency and reduce systemic risk.
OTC markets have evolved with central clearing and reporting requirements.
In countries like India, regulators such as SEBI and RBI oversee currency derivative markets.
Compliance enhances investor protection and market stability.
10. Currency Derivatives in Portfolio Diversification
Currency exposure can be both a risk and an opportunity.
Currency derivatives help investors diversify beyond equities and commodities.
They provide low correlation benefits during global market stress.
Professional portfolios often use currency overlays to optimize returns.
11. Technology and the Evolution of FX Derivatives
Electronic trading platforms have increased accessibility and execution speed.
Algorithmic and high-frequency trading play a growing role in FX derivatives.
Advanced analytics, AI models, and real-time data improve decision-making.
Retail participation has increased due to lower entry barriers.
12. Challenges and Common Mistakes
Overleveraging due to low margin requirements.
Trading without understanding macroeconomic drivers.
Ignoring implied volatility and time decay in options.
Lack of a clear risk management framework.
13. Strategic Mindset for Mastery
Successful currency derivative trading requires patience, discipline, and continuous learning.
Combining macroeconomic insights with technical analysis enhances accuracy.
Keeping a trading journal helps refine strategies.
Long-term consistency matters more than short-term profits.
14. Future Outlook of Currency Derivatives
Globalization and cross-border investments will continue to drive demand.
Emerging market currencies will see increased derivative participation.
Regulatory clarity and technological innovation will expand market depth.
Currency derivatives will remain a cornerstone of global financial risk management.
Conclusion
Unlocking currency derivatives is about transforming complexity into opportunity. These instruments empower market participants to hedge risk, speculate intelligently, and navigate global financial uncertainty with confidence. When used with proper knowledge, discipline, and risk control, currency derivatives become not just tools of protection, but engines of strategic growth in the modern financial ecosystem.
Harmonic Patterns
BTC | 4HCRYPTOCAP:BTC — 4H Zoom-In | Bottoming Structure
Respecting the broader BTC Monthly outlook, price has been supported by a highly validated convergent Q-Structure at the apex ➤ $80,619 . Given that this level remains unchallenged, the ongoing consolidation phase since November 21 can reasonably be interpreted as a bottoming formation.
All wave structures identified on this timeframe—including a Leading Diagonal as Minor Wave 1, a deep retracement ending in an Expanding Diagonal ⓒ, and the current consolidation in a Double Three (Flat | Zigzag | Triangle)—while respecting the interactive function of the illustrated Q-Structures—have collectively formed an integrated structure indicating the development of a significant bottom, marking the extreme point of Primary Wave ⓸ within the impulsive Wave III sequence of BTC’s second Cycle.
🔖 This potential reversal has been projected since Nov. 15 during the BTC decline.
🔖 This outlook is derived from insights within my Quantum Models framework.
GER30 H4 | Bullish Momentum To Extend FurtherBased on the H4 chart analysis, we could see the price fall to our buy entry at 24,474.21, which is a pullback support that 23.6% Fibonacci retracement.
Our stop loss is set at 24,195.24, which is a pullback support that aligns with the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement.
Our take profit is set at 24,786.98, which is a swing high resistance that is slightly below the 161.8% Fibonacci extension.
High Risk Investment Warning
Stratos Markets Limited (
US2000 H4 | Falling Towards Key SupportThe price is falling towards our buy entry level at 2,479.37, which is an overlap support that aligns with the 38.2% Fibonacci retracement.
Our Stop loss is set at 2,449.15, which aligns with the 50% Fibonacci retracement.
Our take profit is set at 2,538.48, which is a pullback resistance.
High Risk Investment Warning
Stratos Markets Limited (
How Overconfidence Destroys Profitable TradersHow Overconfidence Destroys Profitable Traders
Understanding Overconfidence in Trading
Welcome everyone to another article.
One of the most dangerous stages a trader can walk into is not fear… but overconfidence. (EGO)
Overconfidence in trading is essentially ego.
However, there is still an important difference:
- Confidence is a real belief built on proof, statistics, and discipline.
- Overconfidence is an inflated belief in your ability beyond the proof. This is driven by ego.
Many traders do not fail because they do not know enough.
They fail because at some point, they believe they know enough or know “everything.”
What Overconfidence appears as in Trading:
A trader builds a system. ( yay! )
They go on a clean winning streak maybe 10, 12, even 15 profitable trades in a row.
At this point, the trader begins to think and assume:
“ I’ve cracked the code. ”
- Risk gets increased .
- Position sizes get bigger .
- Rules start to bend .
Confidence continues grow until it crosses a dangerous path where belief is no longer supported by data, statistics and proof.
Reality eventually steps in.
You will never again feel as confident as you did during your first major winning streak when it looked like the market finally made sense and success was “ figured out. ”
That feeling is exactly what traps traders.
Overconfidence WILL break Risk Management
Overconfidence destroys a trader by slowly dismantling their risk management, their system, their discipline, their psychology and their consistency.
It rarely happens all at once.
First:
- “ I’ll just risk a little more this time. ”
- “ This setup looks perfect. ”
- “ I’m on a winning streak. ”
Over time, the trader begins to:
• Ignore position sizing rules ( Too many LOTS or contracts )
• Move stop losses (Increases risk)
• Add to losing trades ( Does not accept the original loss )
• Trade larger to “maximize opportunity” (Stick to what you can afford to lose )
The trader thinks and believes the system will continue to work, because it worked before.
But markets do not reward belief, they reward discipline. (I have mentioned this many times in my previous posts.)
Once risk management breaks, even a profitable system becomes dangerous and can lead to zero profits, or even down to negatives.
Overconfidence Blocks Positive criticism and continuous Learning
There is no such thing and there will never be a 100% perfecto trading system/strategy.
Losses are part of the game.
Overconfident traders struggle when reality does not meet their expectations.
Instead of adapting to the market by adjusting their strategy they:
- Resist feedback (Or consider any feedback as hate/negative criticism)
- Ignore changing market conditions (Consolidation, flat lining, barcoding etc)
- Refuse to admit the system is underperforming (Bad performance & results)
- Believe the problem can’t be them (“It’s not the system, it’s the computer!”)
But Why…?
Well because… their mind keeps rewinding the dopamine high from when everything worked perfectly and the win rate was 99%
They only remember the wins, and “ GREEN ” $$$ %%% not the probability.
The exact moment a trader believes they “can’t be wrong,” learning comes to a halt.
And in trading, when learning stops, losses accelerate, revenge trading increase, risk management collapses, and consistency becomes scrambled.
Overconfidence changes Traders into > Gamblers
Overconfidence does not just cause losses it can also change behavior.
Frustration from unexpected losses turns into:
- Anger
- Impatience
- Forced trades
- Revenge trading
Rules get ignored.
Emotions take control.
The trader may still look like a trader, but they are acting like a gambler.
The most dangerous part?
They still believe they are right…
Example: How Overconfidence Destroyed a Profitable Trader
Let’s look at Bobby.
Bobby was a profitable trader. A very successful one in his 4th year of trading.
He discovered what he believed was a 99% win-rate system.
The first month was incredible.
The second month was just as good. Cash flowing in, heaps of green.
By the third month, losses started to appear.
Instead of falling back, taking a breather and reassessing , Bobby doubled down.
Continuing to trade the same system despite clear signs of underperformance.
He was no longer focusing on perfect executions and setups, he was chasing the high.
Losses turned into frustration .
Frustration turned into anger .
Anger turned into impatience .
Soon Bobby was:
• Forcing trades
• Revenge trading
• Ignoring risk management
Bobby refused to take responsibility.
“It was my internet.”
“My computer lagged.”
“My family distraccted me.”
The excuses piled up, but the account kept shrinking.
Bobby did not fail because of the system.
Bobby failed because ego stopped him from adapting to the market and adjusting his system.
Markets Will Always Humble Ego
Markets will humble traders in ways they never expect.
No matter how experienced you are, there is always something else to learn.
Trading is not a destination, it is a constant process of adaptation towards the market. Traders who believe they “know everything” will always be reminded by the market that They. Do. Not.
Overconfidence doesn’t end trading careers immediately.
But it slowly erodes them trade by trade turning it into mental torture.
Final Thoughts
Confidence is necessary to trade.. But Ego is fatal!
The very moment a trader believes they have cracked the code is often the moment their decline begins.
Stay humble.
Respect risk.
Let statistics, not emotion, guide your decisions.
Because in trading, the market doesn’t punish ignorance it punishes ego.
Chapter IV: Own Yourself The shop felt different that morning. Not quieter ... just still. Like the air knew something was about to change before anyone said a word.
The Apprentice stood at the doorway with a small backpack slung over his shoulder. His hands were steady, but his breath wasn’t. He looked around the shop the workbench where he’d first fumbled a wrench, the corner where he’d stared at charts until his eyes blurred, the mirror that had once shown him more truth than he wanted to see.
The Mentor stepped out from behind the bench, wiping grease from his palms.
“So,” he said softly, “you’re heading out.”
The Apprentice nodded. “I think it’s time.”
The Mechanic leaned against the tool chest, arms crossed. “You sure you’re ready? Out there, nobody’s gonna explain things twice.”
The Apprentice smirked. “You barely explained them once.”
The Mechanic grinned. “Fair.”
The Mentor approached, his expression somewhere between pride and worry.
“You’ve learned the tools that matter the ones that don’t rust. Mirrors, reflections, candlesticks, maps. But there’s one lesson you can’t learn here.”
The Apprentice waited.
“Owning yourself.”
The Mentor tapped his chest. “That’s the part you have to figure out on your own.”
The Apprentice frowned. “What does that mean?”
The Mechanic answered first.
“It means when you mess up — and you will — you don’t blame the tools, the market, the shop, or the teacher. You take responsibility. You fix it. You grow.”
The Mentor added, “And when you succeed, you don’t pretend it was luck. You own that too.”
The Apprentice looked down at his hands... the same hands that once trembled holding a wrench, the same hands that had hovered nervously over a chart. Now they felt capable.
“Where do I go?” he asked.
The Mentor smiled. “Anywhere. The map isn’t the chart. The map is you.”
The Mechanic reached into a drawer and tossed him a small, worn socket — the one the Apprentice had dropped on his first day.
“A reminder,” he said. “Mistakes are part of the job. What you do after them is what counts.”
The Apprentice caught it, feeling the weight of metal and memory.
He stepped toward the door, then paused.
“Will I see you again?”
The Mentor shrugged. “Maybe. Maybe not. But you’ll hear us. Every time you hesitate, every time you doubt, every time you’re about to do something reckless... we’ll be there.”
The Mechanic smirked. “Especially the reckless part.”
The Apprentice laughed, then turned and walked out into the sunlight.
The door closed behind him with a soft click.
For a long moment, the shop was still.
Then the Mentor exhaled.
“He’ll be alright.”
The Mechanic nodded. “He’s got the tools.”
And somewhere down the road, the Apprentice walked toward a future he didn’t fully understand... carrying the lessons of the shop, the weight of the socket, and the quiet confidence of someone finally ready to own himself.
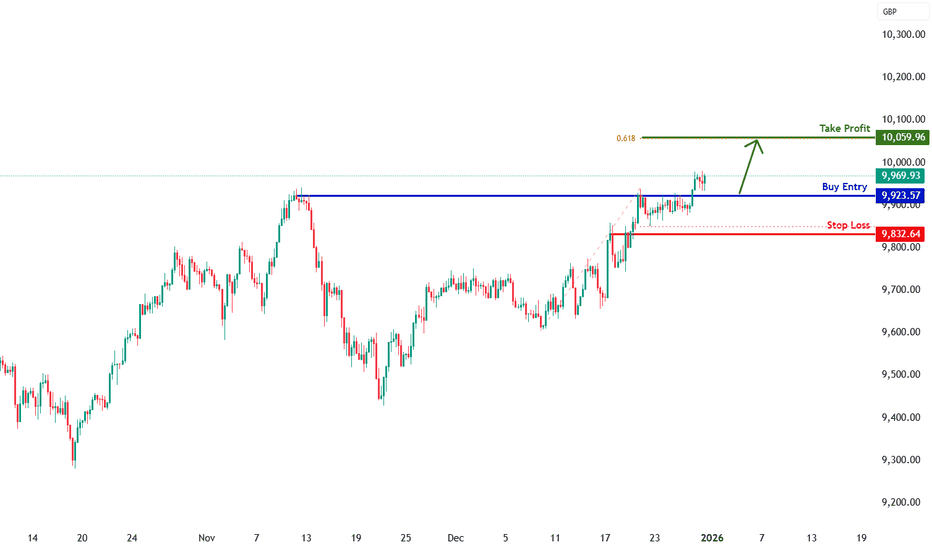
UK100 H4 | Bullish BreakoutThe price is falling towards our buy entry level at 9,923.57, which is an overlap support.
Our stop loss is set at 9,832.64, which is an overlap support.
Our take profit is set at 10,059.96, which aligns with the 61.8% Fibonacci projection.
High Risk Investment Warning
Stratos Markets Limited (
JPN225 H4 | Bullish Bounce OffThe price has bounced off our buy entry level at 50,261.74, which is an overlap support.
Our stop loss is set at 49,846.21, which is an overlap support.
Our take profit is set at 51,425.25, which is a pullback resistance.
High Risk Investment Warning
Stratos Markets Limited (
Could we see a reversal from here?KIWI (NZD/USD) is reacting off the pivot, which has been identified as an overlap support that aligns with the 38.2% Fibonacci retracement and could bounce to the 1st resistance, which is also an overlap resistance.
Pivot: 0.5744
1st Support: 0.5713
1st Resistance: 0.5792
Disclaimer:
The opinions given above constitute general market commentary and do not constitute the opinion or advice of IC Markets or any form of personal or investment advice.
Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, are intended to be informative only, and are not advice, a recommendation, research, a record of our trading prices, an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. The information provided does not involve any specific investment objectives, financial situation, or needs of any specific person who may receive it. Please be aware that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance and/or results. Past performance or forward-looking scenarios based upon the reasonable beliefs of the third-party provider are not a guarantee of future performance. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. IC Markets makes no representation or warranty and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, nor any loss arising from any investment based on a recommendation, forecast, or any information supplied by any third party
Bearish drop?Aussie (AUD/USD) has reacted off the pivot and could drop to the 1st support, which aligns with the 100% Fibonacci projection.
Pivot: 0.6685
1st Support: 0.6633
1st Resistance: 0.6721
Disclaimer:
The opinions given above constitute general market commentary and do not constitute the opinion or advice of IC Markets or any form of personal or investment advice.
Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, are intended to be informative only, and are not advice, a recommendation, research, a record of our trading prices, an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. The information provided does not involve any specific investment objectives, financial situation, or needs of any specific person who may receive it. Please be aware that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance and/or results. Past performance or forward-looking scenarios based upon the reasonable beliefs of the third-party provider are not a guarantee of future performance. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. IC Markets makes no representation or warranty and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, nor any loss arising from any investment based on a recommendation, forecast, or any information supplied by any third party
AXISBANK – Inverse Harmonic completion → Bearish (Jan Option)On the daily chart, AXISBANK has completed an inverse harmonic structure (X-A-B-C-D) and price reacted sharply from the D-point PRZ (Potential Reversal Zone). The rally into D looks like the “final leg” of the pattern and we’re now seeing rejection + loss of bullish follow-through — which keeps the bearish reversal thesis active.
Why this looks bearish (chart confluence)
Harmonic completion at D (PRZ): Pattern completes near a key retracement/extension cluster (your harmonic ratios marked on chart).
Supply zone + rejection: The PRZ aligns with a strong overhead supply region where price struggled to sustain.
Breakdown trigger level identified: The 1246.5 zone is the key “line in the sand” for confirmation (break & hold below / breakdown + retest).
Downside magnet zones: 1123.85 is a major horizontal support area and also aligns with the rising trendline support projection (confluence target).
Trade Plan (as per chart)
✅ Entry trigger (wait for confirmation)
Entry: Below 1246.5 (preferably daily close below, or breakdown → pullback retest → rejection for cleaner entry)
🛑 Invalidation
SL: 1262.1 (keep it strict — if price reclaims and holds above, the breakdown thesis weakens)
🎯 Targets
Primary Target: 1123.85
(Optional trade management) Consider partial booking near psychological / minor supports on the way down (to reduce risk), then trail for the main target.
How I’ll manage it (practical execution)
If price breaks 1246.5 impulsively, I prefer not chasing. I’ll wait for a pullback to 1246–1250 and look for rejection.
If we get a weak bounce but price stays below 1262, the structure still favors sellers.
Once price starts moving in favor, reduce risk quickly (trail SL / partials), because banking stocks can snap back fast.
Jan Options Idea (if you’re planning options)
Bias: Short setup = Put-side view
Prefer ATM/ITM puts for better delta (less decay pain than far OTM).
Conservative approach: Bear Put Spread (reduces premium + theta pressure), hold for the swing toward 1123 zone.
(This is based purely on the technical setup shown.)
Levels on chart:
Entry: 1246.5 | SL: 1262.1 | TG: 1123.85
I am not a SEBI-registered analyst. This idea is shared purely for educational and study purposes. Please do your own analysis or consult a certified financial advisor before taking any trades.
#AXISBANK #HarmonicPattern #BearishBat #TechnicalAnalysis #OptionsTrading #NSE #PriceAction #TradingView
Gold - The -50% correction is starting!🎯Gold ( OANDA:XAUUSD ) is starting a -50% correction:
🔎Analysis summary:
For the past 10 years, we have been witnessing an underlying bullrun on Gold. Just like we saw back in 2011, the 10 year bullrun was followed by a correction of -50%. Together with the retest of the ultimate resistance trendline, Gold is now clearly shifting bearish.
📝Levels to watch:
$4,500
SwingTraderPhil
SwingTrading.Simplified. | Investing.Simplified. | #LONGTERMVISION
Gold - This metal is collpasing very soon!😱Gold ( OANDA:XAUUSD ) is preparing a major dump:
🔎Analysis summary:
Gold has been rallying an incredible +175% over the course of the past couple of months. But at this exact moment, Gold is retesting the ultimate resistance trendline. Considering that Gold is totally overextended, we will see a harsh drop in the very near future on Gold.
📝Levels to watch:
$4,500
SwingTraderPhil
SwingTrading.Simplified. | Investing.Simplified. | #LONGTERMVISION
XAUUSD SELL SETUP ACTIVE📉 GOLD SELL | Precision Setup at Resistance 🔥
Gold is reacting from a strong supply / resistance zone, showing signs of buyer exhaustion. Market structure favors a short move as long as price stays below the invalidation level.
🔓 Entry: 4520- 4525
❌ Stop Loss: 4535 (structure break)
🎯 Target: 4496
⚠️ Wait for confirmation, manage risk strictly.
Clean setup. Calm execution. No emotions.
💡 Educational purpose only — not financial advice.
XAUUSD Buy Setup | Strong Support + Bullish Structure📌 Trade Plan:
🔓 Entry: 4455 - 4460
❌ Stop Loss: 4440
🎯 Target: 4480 NEXT Target 4500
Gold (XAUUSD) is showing bullish strength after holding a key demand zone, and price action suggests buyers are stepping in from support. A buy position is considered in the 4455–4460 zone with a well-defined stop loss below 4440 to manage risk. If bullish momentum continues, the first upside target is 4480, while the final target is placed near 4500, aligning with the next resistance area. Trade is based on structure, support validation, and controlled risk management.
GOLD BUY TODAY | Demand Zone Holding, Upside Targets Open🔓 Entry: 4380 – 4390
❌ Stop Loss: 4365
🎯 Target: 4430 Next Target: 4450
GOLD BUY (XAUUSD) Price is holding above a key demand zone with bullish price action and trend support intact. Looking for upside continuation as buyers remain in control. A sustained move higher can push price toward the next resistance levels. Trade is planned with clear risk management and favorable risk-reward, suitable for intraday to short-term continuation.
Potential bearish reversal?Fiber (EUR/USD) is reacting off the pivot and could reverse to the 1st support, which is a pullback support.
Pivot: 1.1749
1st Support: 1.1680
1st Resistance: 1.1806
Disclaimer:
The opinions given above constitute general market commentary and do not constitute the opinion or advice of IC Markets or any form of personal or investment advice.
Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, are intended to be informative only, and are not advice, a recommendation, research, a record of our trading prices, an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument and thus should not be treated as such. The information provided does not involve any specific investment objectives, financial situation, or needs of any specific person who may receive it. Please be aware that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance and/or results. Past performance or forward-looking scenarios based upon the reasonable beliefs of the third-party provider are not a guarantee of future performance. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. IC Markets makes no representation or warranty and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, nor any loss arising from any investment based on a recommendation, forecast, or any information supplied by any third party
[EURNZD] Long then Short approximately 200 pips round tripEarlier long setup with higher risk in progress. Second setup with confirmation and higher success rate is active, long targeting approximately 200 pips then short targeting approximately 200pips. Short setup will need to confirm in LTF for entry. Not trading advice.