Is Red Cat the Drone King America Has Been Waiting For?Red Cat Holdings (RCAT) stands at the epicenter of a transformative moment in defense technology. The December 2025 FCC ban on Chinese drone manufacturers DJI and Autel has effectively eliminated Red Cat's primary competition, creating a protected market for domestic producers. With Q3 fiscal 2025 revenue surging 646% year-over-year and a balance sheet fortified with over $212 million in cash, Red Cat has positioned itself as the primary beneficiary of America's pivot toward sovereign defense supply chains. The company's "Blue UAS" certification and inclusion on NATO's procurement catalog provide immediate access to both domestic and allied defense markets at a critical moment of global rearmament.
The company's technological architecture differentiates it from competitors through integrated systems spanning air, land, and sea domains. The "Arachnid" family, including the Black Widow quadcopter, Edge 130 hybrid VTOL, and FANG strike drone, creates a closed-loop ecosystem enhanced by partnerships with Palantir for GPS-denied navigation and Doodle Labs for anti-jamming communications. Red Cat's Visual SLAM technology enables autonomous operation in contested electromagnetic environments, directly addressing Pentagon requirements under the Replicator initiative for "attritable mass" autonomous systems. The recent partnership with Apium Swarm Robotics advances one-to-many drone control, multiplying the combat effectiveness of individual operators.
Strategic acquisitions of FlightWave and Teal Drones have rapidly expanded Red Cat's capabilities while maintaining strict supply chain sovereignty. The company's selection as a finalist for the Army's Short Range Reconnaissance Tranche 2 program validates its tactical systems for infantry deployment. With NATO allies ramping up defense spending and the Ukraine conflict demonstrating voracious demand for small unmanned systems, Red Cat faces a multi-year secular tailwind. The convergence of regulatory protection, technological differentiation, financial strength, and geopolitical necessity positions Red Cat not merely as a defense contractor but as a cornerstone of America's robotic warfare infrastructure for the coming decade.
Supplychain
Is the World Sleepwalking Into a Platinum Catastrophe?The global economy is currently entering a precarious era defined by resource nationalism, where the BRICS+ alliance has effectively consolidated control over critical minerals, including the vast majority of primary platinum production. As geopolitical fragmentation deepens, the West faces a severe strategic vulnerability, as it relies heavily on adversaries like Russia and China for the metals essential to its green transition. This dependency is compounded by the weaponization of trade, with export controls on other strategic minerals already signaling that platinum—a metal critical for hydrogen fuel cells and electrolysis—could be the next target in a looming "commodities cartel" strategy.
Simultaneously, the market is grappling with a severe and structural supply deficit, projected to reach a critical 850,000 ounces by 2025. This shortfall is driven by the collapse of primary production in South Africa, where a crumbling energy infrastructure, labor instability, and logistical failures are strangling output. The situation is exacerbated by a "recycling cliff," as economic pressures reduce the scrapping of old vehicles, drying up secondary supply lines just as above-ground inventories are being rapidly depleted.
Despite these supply shocks, demand is poised for a tsunami driven by the hydrogen economy, where platinum is the indispensable catalyst for Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolyzers and heavy-duty fuel cell vehicles. While investors historically viewed platinum through the narrowing lens of internal combustion engines, resilient demand from hybrid vehicles and strict Euro 7 emissions regulations ensures that automotive usage remains robust. Furthermore, the hydrogen sector is projected to grow at a staggering 32% CAGR through 2030, creating entirely new structural demand that the current supply chain cannot meet.
Ultimately, the article argues that platinum is drastically mispriced, trading at a deep discount despite its strategic imperative and monetary value as a hard asset. The convergence of supply destruction, geopolitical leverage, and exponential green demand signals the arrival of a "Platinum Supercycle". With cyber warfare posing an additional invisible risk to mining infrastructure and China aggressively securing patent dominance in hydrogen technology, the window to acquire this undervalued asset is closing, positioning platinum as the potential "apex trade" of the coming decade.
Is Europe's Industrial Crown Jewel Being Quietly Dismantled?Volkswagen Group, once the symbol of German engineering dominance and post-war European recovery, is experiencing what can only be described as a structural dismantling rather than a cyclical downturn. The company faces a perfect storm of challenges: geopolitical vulnerability exposed by the Nexperia semiconductor crisis, where China demonstrated escalation of dominance over critical supply chains, catastrophic labor cost disadvantages ($3,307 per vehicle in Germany versus $597 in China), and a complete failure of its CARIAD software division that consumed €12 billion with little to show for it. The result is unprecedented: 35,000 German job cuts by 2030, the first factory closures in 87 years, and Golf production moving to Mexico.
The technological surrender is perhaps most revealing. VW is investing $5.8 billion in American startup Rivian and $700 million in Chinese EV maker XPeng—not as strategic partnerships, but as desperate attempts to acquire the software and platform capabilities it failed to develop internally. The company that once provided technology to Chinese joint ventures now buys entire vehicle platforms from a Chinese startup founded in 2014. Meanwhile, its profit engine has collapsed: Porsche's operating profit plummeted 99% to just €40 million in Q3 2024, while VW's China market share eroded from 17% to under 13%, with only 4% share in the critical EV segment.
This isn't just corporate restructuring—it's a fundamental transfer of power. VW's "In China, For China" strategy, which moves 3,000 engineers to Hefei and creates a separate technological ecosystem under Chinese jurisdiction, effectively places the company's intellectual property and future development under the control of a systemic rival. The patent analysis confirms the shift: while BYD has built a moat of 51,000 patents focused on battery and EV technology, much of VW's portfolio protects legacy internal combustion engines—stranded assets in an electric future. What we're witnessing is not Germany adapting to competition, but Europe losing control of its most important manufacturing sector, with the engineering and innovation increasingly done by Chinese hands, on Chinese soil, under Chinese rules.
Is Intel’s Apple Deal the Ultimate Pivot?Intel (NASDAQ: INTC) stock soared over 116% this year. Reports suggest Apple may use Intel’s foundry by 2027. We analyze the drivers behind this potential resurrection.
Geopolitics & Geostrategy: The Stability Premium
In a volatile world, Intel offers a "stability premium." TSMC’s concentration in Taiwan risks Western supply chains. The US government now holds a ~10% stake in Intel. This actively incentivizes domestic production to secure the grid. Apple chooses Intel to hedge against geopolitical friction. This move aligns with US strategic interests, treating Intel as a sovereign asset.
Management & Leadership: The Tan Effect
CEO Lip-Bu Tan drives a massive cultural shift. He replaced Pat Gelsinger’s engineering vision with operational discipline. Tan prioritizes customer listening, an area where Intel historically struggled. This pivot is paying off. Securing Apple proves Intel is shedding its "arrogant" legacy. It is becoming a true service-oriented foundry.
Technology & Innovation: The 18A-P Advantage
The deal relies on Intel’s **18A-P process technology**. Apple aims to use this for entry-level M-series chips. This validates Intel's aggressive manufacturing roadmap. Additionally, the Trump administration invested $150 million in xLight. This startup develops next-gen lithography lasers to aid chipmaking. It reinforces the ecosystem surrounding Intel’s manufacturing capabilities.
Business Models: The Foundry Pivot
Intel is transforming from a product company to a hybrid foundry. Analysts estimate the Apple deal could generate ~$1 billion annually. However, the "Apple Seal of Approval" is worth far more. It signals to giants like Qualcomm that Intel is ready. It also creates leverage against TSMC’s pricing power.
Final Verdict: The Apple rumors convert Intel into a legitimate turnaround play. US geopolitical interests align with the new leadership. Validated technology suggests Intel’s worst days are likely over.
Is Boeing's Defense Bet America's New Arsenal?Boeing's recent stock appreciation stems from a fundamental strategic pivot toward defense contracts, driven by intensifying global security tensions. The company has secured major wins, including the F-47 Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) fighter contract worth over $20 billion and a $4.7 billion deal to supply AH-64E Apache helicopters to Poland, Egypt, and Kuwait. These contracts position Boeing as central to U.S. military modernization efforts aimed at countering China's rapid expansion of stealth fighters like the J-20, which now rivals American fifth-generation aircraft production rates.
The F-47 program represents Boeing's redemption after losing the Joint Strike Fighter competition two decades ago. Through its Phantom Works division, Boeing developed and flight-tested full-scale prototypes in secret, validating designs through digital engineering methods that dramatically accelerated development timelines. The aircraft features advanced broadband stealth technology and will serve as a command node controlling autonomous drones in combat, fundamentally changing air warfare doctrine. Meanwhile, the modernized Apache helicopter has found renewed relevance in NATO's Eastern flank defense strategy and counter-drone operations, securing production lines through 2032.
However, risks remain in execution. The KC-46 tanker program continues facing technical challenges with its Remote Vision System, now delayed until 2027. The F-47's advanced variable-cycle engines are two years behind schedule due to supply chain constraints. Industrial espionage, including cases where secrets were sold to China, threatens technological advantages. Despite these challenges, Boeing's defense portfolio provides counter-cyclical revenue streams that hedge against commercial aviation volatility, creating long-term financial stability as global rearmament enters what analysts describe as a sustained "super-cycle" driven by great power competition.
Is the Age of the Human Warehouse Over?Symbotic is no longer just a vendor; it is becoming the operating system of the industrial economy. The robotics leader saw its shares surge nearly 40% Tuesday following a fiscal fourth-quarter report that shattered expectations. With revenue hitting $618 million and system deployments doubling, Wall Street is finally waking up to a new reality. Symbotic’s entry into the $93 billion healthcare logistics market signals a structural shift. The company is transitioning from a retail solution to a critical infrastructure provider, insulating the supply chain from human volatility.
Geopolitics & Geostrategy: The Automation of Sovereignty
Symbotic’s rise is a direct play on "supply chain sovereignty." As global trade routes fracture, nations are aggressively prioritizing domestic logistics resilience. Symbotic’s technology allows the U.S. economy to maintain high-velocity distribution without relying on a fragile, shrinking labor pool. By automating the "middle mile," the company reduces exposure to demographic decline and migration policy shifts. Logistics capacity is no longer just a business metric; it is now a national security asset.
Industry Trends: The Healthcare Alpha
The partnership with Medline Industries marks a pivotal diversification moment. Healthcare logistics demands a level of precision with zero tolerance for error that general retail does not. Winning a contract with a medical supply giant validates Symbotic’s AI as "clinical grade." This move aligns with the broader "Intelligent Supply Chain" trend of 2025. Resilience and redundancy now outweigh pure just-in-time efficiency. Symbotic is positioning itself as the backbone for mission-critical distribution.
Technology & Science: Density as a Deflationary Force
Symbotic’s "Next-Generation" storage architecture is a feat of spatial physics. By reducing warehouse footprints by nearly 40%, the technology acts as a deflationary force against rising industrial real estate costs.
High-Tech Engineering: The system uses proprietary mobile bots that operate independently of specific racking, a radical departure from legacy automation.
Physics of Density: The proprietary design maximizes cubic density, allowing companies to store more inventory in smaller, cheaper spaces close to urban centers.
Macroeconomics & Economics: The Inflation Hedge
The macroeconomic thesis for Symbotic is the spread between the cost of capital and the cost of labor. Even with interest rates elevated, the long-term cost of human labor is rising faster than the cost of robot depreciation. Symbotic’s systems provide a hedge against wage inflation, offering a fixed-cost structure in an inflationary world. This creates a predictable operational expenditure model that CFOs crave in volatile economic climates.
Business Models: The "GreenBox" Evolution
Symbotic is evolving its business model from pure hardware sales to "Warehouse-as-a-Service." The company is democratizing automation, allowing diverse sectors to access enterprise-grade logistics without massive upfront complexity. This recurring revenue model creates a stickier, more predictable cash flow profile. It commands a higher valuation multiple from investors who now view the company as a software platform rather than a hardware manufacturer.
Management & Leadership: The Owner-Operator Edge
CEO Rick Cohen leads with a "three-comma" operator mindset. As the third-generation leader of C&S Wholesale Grocers, Cohen built Symbotic to solve his own problems, not just to sell a product. This "owner-operator" culture permeates the company. Their disciplined refusal to chase growth at the expense of functionality sets them apart. His focus on "monitoring speculative trading" reflects a management team focused on long-term industrial value rather than quarterly stock jukes.
Cyber & Patent Analysis: The Digital Moat
With a massive portfolio of issued and pending patents, Symbotic has built a formidable legal moat around its "structure-independent" bot technology.
Intellectual Property: The patent wall prevents competitors from easily replicating their high-density architecture.
Cyber-Physical Security: As logistics centers become digital nodes, they become targets. Symbotic’s centralized AI "brain" offers a consolidated defense point, crucial for protecting the physical flow of goods from cyber threats.
Conclusion: The Industrial Prime
Symbotic has proven it can scale beyond its largest retail patrons. The Medline deal is the "proof of concept" the market demanded. Investors are no longer buying a grocery logistics company; they are buying the premier industrial automation platform of the decade. The stock’s surge is a delayed recognition of a simple truth: in a world of labor scarcity, the robot is not a luxury; it is a necessity.
Can Asia's Tensions Triple Your Hedge Returns?How escalating China-Japan geopolitical tensions create a compelling investment case for ProShares UltraPro Short QQQ (SQQQ), a triple-leveraged inverse ETF tracking the Nasdaq-100 Index (NDX). The Nasdaq-100's extreme concentration in technology sectors (61% weighting) and dependence on flawless global supply chains make it uniquely vulnerable to Asia-Pacific instability. SQQQ's triple-inverse structure allows investors to profit from anticipated NDX declines without traditional margin accounts, while its daily compounding mechanism is optimized for capturing the high-volatility, directional downside movements that geopolitical crises typically trigger.
The core vulnerability stems from critical supply chain chokepoints in East Asia. China controls nearly 90% of global rare earth element processing materials essential for EV motors, sensors, and defense systems, and has previously weaponized this dominance against Japan during territorial disputes. Meanwhile, Japan holds a 50% global market share in critical semiconductor materials like photoresists, making any disruption equivalent to halting chip fabrication for NDX companies. With the Nasdaq-100 deriving approximately 10% of revenues directly from Mainland China and nearly 50% internationally, escalating tensions threaten simultaneous revenue losses across multiple major markets while forcing costly supply chain regionalization that compresses profit margins.
Beyond physical supply chains, the analysis identifies state-sponsored cyber operations as the most immediate acute threat. U.S. agencies assess that Chinese cyber actors are pre-positioning themselves on critical infrastructure networks to enable disruptive attacks during major crises, with Japan reporting prior Chinese military cyberattacks against 200 companies and research institutes. Such cyber-induced production halts could generate billions in lost revenue while simultaneously degrading the innovation output that sustains NDX valuations. Geopolitical uncertainty correlates directly with reduced corporate R&D spending and demonstrable declines in patent quality and citation rates.
The convergence of these risks, supply chain weaponization, forced regionalization costs, elevated discount rates from geopolitical risk premiums, and cyber warfare threats creates an optimal environment for SQQQ's triple-inverse exposure. Corporate boards failing to incorporate robust geopolitical risk monitoring into NDX valuations represent a fundamental governance failure, as the structural shift from global efficiency to resilience-focused supply chains necessitates significant capital expenditure that undermines the high-growth valuations supporting current NDX prices.
The Dual Catalyst: Why Silver's \$50 Breakout is SustainableSilver (XAG/USD) recently broke the crucial $50 per ounce level, signaling a fundamental shift in its market dynamics. While the price edges lower in the short term, primarily due to a strengthened US Dollar (USD), its long-term trajectory is decisively bullish. This surge is not merely speculative. It is driven by an unprecedented convergence of geopolitical risks, critical industrial demand, and shifting macroeconomic policy. Analyzing these catalysts across multiple domains confirms silver's evolving role from a precious metal to a critical industrial asset.
Macroeconomics and Geopolitics
Silver's price strength reflects global systemic risk and monetary policy uncertainty. Current market expectations strongly favor a Federal Reserve (Fed) rate cut by December, with a nearly 68% probability priced in by the CME FedWatch Tool. Lower interest rates reduce the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding silver, making it relatively more attractive than bonds or cash. This dovish outlook provides a powerful structural floor for the price.
From a geopolitical perspective, ongoing global tensions and elevated political risks, like recent US government funding debates, accelerate safe-haven demand. Investors seek hard assets to hedge systemic risks. While gold often leads as the primary safe haven, silver's lower cost and dual-use nature attract broader retail and institutional flows, pushing it higher. A strong, sustained rally will require the price to hold above $50 and overcome the next major resistance near the historical high of $54.50.
Technology, Science, and Patents
Industrial demand now constitutes over 50% of silver’s total annual consumption, fundamentally redefining its market. Its unmatched electrical and thermal conductivity makes it indispensable in high-growth sectors.
* Renewable Energy: Silver is critical for photovoltaics (PV), specifically in solar cells, which form the conductive paste that harvests electrons. The global push for green energy and solar capacity expansion creates structural, persistent demand that consistently tightens the market.
* High-Tech and EVs: Electric Vehicles ( EVs) require significantly more silver (25–50 grams per unit) than traditional vehicles for inverters, battery management systems, and high-voltage contacts. The expansion of 5G technology, advanced computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) further relies on silver-based components for seamless connectivity and efficiency.
Geostrategy and Supply Chain Risk
Silver is now recognized as a critical mineral by several major economies. This reclassification acknowledges its essential role in national security, advanced manufacturing, and the energy transition. This status highlights a geopolitical vulnerability: silver's supply chain is increasingly seen as a strategic concern.
The market currently runs a persistent supply deficit, depleting above-ground stockpiles to critically low levels. Mining silver often occurs as a byproduct of copper, lead, and zinc, meaning its supply cannot easily scale up based on price alone. Trade conflicts or export controls imposed by major producing nations could severely disrupt supply, immediately spiking the price due to its non-substitutable role in key high-tech applications.
Cyber and Economics: The Future Nexus
Silver’s unique properties extend into emerging fields like cybersecurity* and advanced computing. Research integrates silver nanoparticles and quantum materials into sophisticated systems. These materials enhance data processing efficiency and bolster the security of financial supply chains. Furthermore, flexible electronics using silver nanowires* will drive the next generation of wearable and flexible displays, creating entirely new demand vectors.
The long-term economic case for a $100 silver price remains dependent on this confluence of factors. Sustained high industrial consumption, a breakdown in global supply chains, and a continued environment of monetary debasement must align. Silver has truly become a dual-catalyst metal, positioned to thrive as both a financial safe haven and a fundamental building block of the twenty-first-century green and digital economy.
Can One Company Break China's Rare Earth Stranglehold?Lynas Rare Earths Limited (OTCPK: LYSCF / ASX: LYC) has emerged as the Western world's strategic counterweight to Chinese dominance in rare earth minerals, positioning itself as critical infrastructure rather than merely a mining company. As the only significant producer of separated rare earths outside Chinese control, Lynas supplies materials essential for advanced defense systems, electric vehicles, and clean energy technologies. The company's transformation reflects an urgent geopolitical imperative: Western nations can no longer tolerate dependence on China, which controls nearly 90% of global rare earth refining capacity and previously held 99% of heavy rare earth processing. This monopoly has enabled Beijing to weaponize critical minerals as diplomatic leverage, prompting the U.S., Japan, and Australia to intervene with unprecedented financial backing and strategic partnerships.
The confluence of government support validates Lynas's indispensable role in allied supply chain security. The U.S. Department of Defense awarded a $120 million contract for domestic heavy rare earth separation capability in Texas, while Japan's government provided A$200 million in financing to secure priority NdPr supply through 2038. Australia committed A$1.2 billion to a Critical Minerals Reserve, and U.S. officials are exploring equity stakes in strategic projects. This state-backed capital fundamentally alters Lynas's risk profile, stabilizing revenue through defense contracts and sovereign agreements that transcend traditional commodity market volatility. The company's recent A$750 million equity placement demonstrates investor confidence that geopolitical alignment overrides cyclical price concerns.
Lynas's technical achievements cement its strategic moat. The company successfully achieved the first production of separated heavy rare earth oxides—dysprosium and terbium—outside China, eliminating the West's most critical military supply vulnerability. Its proprietary HREE separation circuit can produce up to 1,500 tonnes annually, while the high-grade Mt Weld deposit provides exceptional cost advantages. The October 2025 partnership with U.S.-based Noveon Magnetics creates a complete mine-to-magnet supply chain using verified non-Chinese materials, addressing downstream bottlenecks where China also dominates magnet manufacturing. Geographic diversification across Australia, Malaysia, and Texas provides operational redundancy, though permitting challenges at the Seadrift facility reveal the friction inherent in forcing rapid industrial development onto allied soil.
The company's strategic significance is perhaps most starkly demonstrated by its targeting in the DRAGONBRIDGE influence operation, a Chinese state-aligned disinformation campaign using thousands of fake social media accounts to spread negative narratives about Lynas facilities. The U.S. Department of Defense publicly acknowledged this threat, confirming Lynas's status as a national defense proxy. This adversarial attention, combined with robust intellectual property protections and government commitments to defend operational stability, suggests that Lynas's valuation must account for factors beyond traditional mining metrics—it represents the West's collective bet on achieving mineral independence from an increasingly assertive China.
Could One Alaskan Mine Reshape Global Power?Nova Minerals Limited has emerged as a strategically critical asset in the escalating U.S.-China resource competition, with its stock surging over 100% to reach a 52-week high. The catalyst is a $43.4 million U.S. Department of War funding award under the Defense Production Act to develop domestic military-grade antimony production in Alaska. Antimony, a Tier 1 critical mineral essential for defense munitions, armor, and advanced electronics, is currently imported by the U.S. in its entirety, with China and Russia controlling the global market. This acute dependency, coupled with China's recent export restrictions on rare earths and antimony, has elevated Nova from mining explorer to national security priority.
The company's dual-asset strategy offers investors exposure to both sovereign-critical antimony and high-grade gold reserves at its Estelle Project. With gold prices exceeding $4,000 per ounce amid geopolitical uncertainty, Nova's fast-payback RPM gold deposit (projected sub-one-year payback) provides crucial cash flow to self-fund the capital-intensive antimony development. The company has secured government backing for a fully integrated Alaskan supply chain from mine to military-grade refinery, bypassing foreign-controlled processing nodes. This vertical integration directly addresses supply chain vulnerabilities that policymakers now treat as wartime-level threats, evidenced by the Department of Defense's renaming to the Department of War.
Nova's operational advantage stems from implementing advanced X-Ray Transmission ore sorting technology, achieving a 4.33x grade upgrade while rejecting 88.7% of waste material. This innovation reduces capital requirements by 20-40% for water and energy, cuts tailings volume up to 60%, and strengthens environmental compliance critical for navigating Alaska's regulatory framework. The company has already secured land use permits for its Port MacKenzie refinery and is on track for initial production by 2027-2028. However, long-term scalability depends on the proposed $450 million West Susitna Access Road, with environmental approval expected in Winter 2025.
Despite receiving equivalent Department of War validation as peers like Perpetua Resources (market cap ~$2.4 billion) and MP Materials, Nova's current enterprise value of $222 million suggests significant undervaluation. The company has been invited to brief the Australian Government ahead of the October 20 Albanese-Trump summit, where critical minerals supply chain security tops the agenda. This diplomatic elevation, combined with JPMorgan's $1.5 trillion Security and Resiliency Initiative, which targets critical minerals, positions Nova as a cornerstone investment in Western supply chain independence. Success hinges on disciplined execution of technical milestones and securing major strategic partnerships to fund the estimated A$200-300 million full-scale development.
Can China Weaponize the Elements We Need Most?China's dominance over rare earth element (REE) processing has transformed these strategic materials into a geopolitical weapon. While China controls approximately 69% of global mining, its true leverage lies in processing, where it commands over 90% of Global capacity and 92% of permanent magnet manufacturing. Beijing's 2025 export controls exploit this chokehold, requiring licenses for REE technologies used even outside China, effectively extending regulatory control over global supply chains. This "long-arm jurisdiction" threatens critical industries from semiconductor manufacturing to defense systems, with immediate impacts on companies like ASML facing shipment delays and US chipmakers scrambling to audit their supply chains.
The strategic vulnerability runs deep through Western industrial capacity. A single F-35 fighter jet requires over 900 pounds of REEs, while Virginia-class submarines need 9,200 pounds. The discovery of Chinese-made components in US defense systems illustrates the security risk. Simultaneously, the electric vehicle revolution guarantees exponential demand growth. EV motor demand alone is projected to reach 43 kilotons in 2025, driven by the prevalence of permanent magnet synchronous motors that lock the global economy into persistent REE dependency.
Western responses through the EU Critical Raw Materials Act and US strategic financing establish ambitious diversification targets, yet industry analysis reveals a harsh reality: concentration risk will persist through 2035. The EU aims for 40% domestic processing by 2030, but projections show the top three suppliers will maintain their stranglehold, effectively returning to 2020 concentration levels. This gap between political ambition and physical execution stems from formidable barriers environmental permitting challenges, massive capital requirements, and China's strategic shift from exporting raw materials to manufacturing high-value downstream products that capture maximum economic value.
For investors, the VanEck Rare Earth/Strategic Metals ETF (REMX) operates as a direct proxy for geopolitical risk rather than traditional commodity exposure. Neodymium oxide prices, which plummeted from $209.30 per kilogram in January 2023 to $113.20 in January 2024, are projected to surge to $150.10 by October 2025 volatility driven not by physical scarcity but by regulatory announcements and supply chain weaponization. The investment thesis hinges on three pillars: China's processing monopoly converted into political leverage, exponential green technology demand establishing a robust price floor, and Western industrial policy guaranteeing long-term financing for diversification. Success will favor companies establishing verifiable, resilient supply chains in downstream processing and magnet manufacturing outside China, though the high costs of secure supply, including mandatory cybersecurity auditing and environmental compliance, ensure elevated prices for the foreseeable future.
Can Light Truly Power the Future of AI?The exponential rise of artificial intelligence has exposed the physical limits of traditional electronic infrastructure. Electrical interconnects, once the backbone of computation, now struggle under escalating data demands, generating immense heat and power inefficiency. POET Technologies emerges as a transformative force in this landscape, leveraging its Optical Interposer™ platform to integrate electronic and photonic components at the wafer level. This innovation enables data speeds of 800G to 1.6T, meeting the insatiable bandwidth needs of AI clusters and hyperscale data centers while drastically reducing energy consumption.
At the core of POET’s advantage lies its patented low-thermal budget process, which allows photonic integration without the costly, high-temperature methods typical of semiconductor manufacturing. This approach not only minimizes thermal mismatches and signal losses but also aligns perfectly with existing CMOS foundry infrastructure—forming the foundation of an “asset-light” business model. By licensing its process and forming strategic joint ventures, POET scales efficiently without massive capital expenditure. Its collaborations with Foxconn and Semtech validate the platform’s industrial readiness, while a $75 million private placement strengthens its financial capacity to accelerate research, acquisitions, and manufacturing partnerships.
Beyond technology, POET’s innovations carry profound geopolitical and environmental implications. As nations race to secure semiconductor independence and energy resilience, POET’s energy-efficient, domestically manufacturable photonics become a critical strategic asset. Optical interconnects can cut data center power consumption by up to half, directly addressing mounting sustainability and national security concerns tied to AI’s energy footprint. Moreover, photonic architectures inherently enhance cybersecurity by offering interference-resistant, ultra-low-latency communication essential for distributed AI and defense systems.
In essence, POET Technologies transcends the definition of a semiconductor company; it represents the physical infrastructure upon which the next phase of artificial intelligence, digital sovereignty, and global energy stability may rest. By turning light into the new language of computation, POET positions itself not merely as a market participant but as an indispensable enabler of AI’s sustainable and secure future.
Why Did Cheap Lumber Become a National Security Issue?Lumber prices have entered a structurally elevated regime, driven by the convergence of trade policy, industrial capacity constraints, and emerging technological demand. The U.S. administration's imposition of Section 232 tariffs - 10% on softwood lumber and up to 25% on wood products like cabinets - reframes timber as critical infrastructure essential for defense systems, power grids, and transportation networks. This national security designation provides legal durability, preventing a quick reversal through trade negotiations and establishing a permanent price floor. Meanwhile, Canadian producers facing combined duties exceeding 35% are pivoting exports toward Asian and European markets, permanently reducing North American supply by over 3.2 billion board feet annually that domestic mills cannot quickly replace.
The domestic industry faces compounding structural deficits that prevent rapid capacity expansion. U.S. sawmill utilization languishes at 64.4% despite demand, constrained not by timber availability but by severe labor shortages—the average logging contractor age exceeds 57, with one-third planning retirement within five years. This workforce crisis forces expensive automation investments while climate-driven wildfires introduce recurring supply shocks. Simultaneously, cybersecurity vulnerabilities in digitized mill operations pose quantifiable risks, with manufacturing ransomware attacks causing an estimated $17 billion in downtime since 2018. These operational constraints compound tariff costs, with new home prices increasing $7,500 to $22,000 before builder markups and financing costs amplify the final impact by nearly 15%.
Technological innovation is fundamentally reshaping demand patterns beyond traditional housing cycles. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) markets are growing at 13-15% annually as mass timber products displace steel and concrete in commercial construction, while wood-based nanomaterials enter high-tech applications from transparent glass substitutes to biodegradable electronics. This creates resilient demand for premium-grade wood fiber across diversified industrial sectors. Combined with precision forestry technologies - drones, LiDAR, and advanced logistics software—these innovations both support higher price points and require substantial capital investment that further elevates the cost baseline.
The financialization of lumber through CME futures markets amplifies these fundamental pressures, with prices reaching $1,711 per thousand board feet in 2021 and attracting speculative capital that magnifies volatility. Investors must recognize this convergence of geopolitical mandates, chronic supply deficits, cyber-physical risks, and technology-driven demand shifts as establishing a permanently elevated price regime. The era of cheap lumber has definitively come to an end, replaced by a high-cost, high-volatility environment that requires sophisticated supply chain resilience and financial hedging strategies.
Can a Small-Cap Survive the AI Data Revolution?Applied Optoelectronics (AAOI) represents a high-stakes investment proposition at the intersection of artificial intelligence infrastructure and geopolitical supply chain realignment. The small-cap optical networking company has positioned itself as a vertically integrated manufacturer of advanced optical transceivers, leveraging proprietary laser technology to serve hyperscale data centers, driving the AI boom. With 77.94% year-over-year revenue growth reaching $368.23 million in FY 2024, AAOI has successfully re-engaged a major hyperscale customer and begun shipping 400G datacenter transceivers, marking a potential turnaround from its 2017 customer loss that previously crushed its stock performance.
The company's strategic pivot centers on transitioning from lower-margin products to high-performance 800G and 1.6T transceivers while simultaneously relocating manufacturing capacity from China to Taiwan and the United States. This supply chain realignment, formalized through a 15-year lease for a New Taipei City facility signed in September 2025, positions AAOI to benefit from domestic sourcing preferences and potential government incentives like the CHIPS Act. The optical transceiver market, valued at $13.6 billion in 2024 and projected to reach $25 billion by 2029, is driven by substantial tailwinds, including AI workloads, 5G deployment, and hyperscale data center expansion.
However, AAOI's financial foundation remains precarious despite impressive revenue growth. The company reported a net loss of $155.72 million in 2024 and carries over $211 million in debt while facing ongoing share dilution from equity offerings that increased outstanding shares from 25 million to 62 million. Customer concentration risk persists as a fundamental vulnerability, with data centers representing 79.39% of revenue. External scrutiny has questioned the viability of the Taiwan expansion, with some reports characterizing the 800G production story as an "optical illusion" and raising concerns about the readiness of manufacturing facilities.
The investment thesis ultimately hinges on execution risk and competitive positioning in a rapidly evolving technology landscape. While AAOI's vertical integration and proprietary laser technology provide differentiation against giants like Broadcom and Lumentum, emerging co-packaged optics (CPO) technology threatens to disrupt traditional pluggable transceivers. The company's success depends on successfully ramping 800G production, operationalizing the Taiwan facility, achieving consistent profitability, and maintaining its re-engaged hyperscale customer relationships. For investors, AAOI represents a classic high-risk, high-reward opportunity, where strategic execution could deliver significant returns; however, financial vulnerabilities and operational challenges present substantial downside risks.
Can Innovation Survive Strategic Drift?Lululemon Athletica's shares plummeted 18% in premarket trading on September 5, 2025, following a dramatic reduction in annual sales and profit guidance that marked the second guidance cut of the year. The company's stock has declined by 54.9% year-to-date, resulting in a market capitalization of $20.1 billion. This drop in stock value comes as a reaction from investors to disappointing Q2 results, which showed only 7% revenue growth, reaching $2.53 billion. Additionally, there was a concerning 3% decline in comparable sales in the Americas, despite strong international growth of 15%.
The perfect storm hitting Lululemon stems from multiple converging forces. The Trump administration's removal of the *de minimis* exemption on August 29, 2025, eliminated duty-free treatment for shipments under $800, creating an immediate $240 million gross profit headwind in fiscal 2025 that's projected to reach $320 million in operating margin impact by 2026. This policy change particularly damages Lululemon's supply chain strategy, as the company previously fulfilled two-thirds of its U.S. e-commerce orders from Canadian distribution centers to bypass duties, while relying heavily on Vietnam (40% of manufacturing) and China (28% of fabrics) for production.
Beyond geopolitical pressures, Lululemon faces internal strategic failures that have amplified external headwinds. CEO Calvin McDonald acknowledged the company had become "too predictable with our casual offerings" and "missed opportunities to create new trends," which led to prolonged product life cycles, especially in lounge and casual wear, accounting for 40% of sales. The company is facing increasing competition from emerging brands such as Alo Yoga and Vuori in the premium segment. At the same time, it is dealing with pressure from private-label imitations that provide similar fabric technology at much lower prices. This trend is especially challenging in markets where consumers are more price-sensitive.
Despite maintaining an impressive portfolio of 925 patents globally, protecting unique fabric blends, and investing in next-generation bio-based materials through partnerships with companies like ZymoChem, Lululemon's core challenge lies in the disconnect between its robust intellectual property and innovation capabilities versus its inability to translate these strengths into timely, trend-setting products. The company’s future strategy requires decisive actions in three key areas: refreshing our products, implementing strategic pricing to counteract tariff costs, and optimizing the supply chain. All of this must be done while navigating a challenging macroeconomic environment, where American consumers are cautious and Chinese consumers are increasingly opting for local brands over premium foreign alternatives.
Can the World's Most Critical Company Survive Its Own Success?Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) stands at an unprecedented crossroads, commanding 67.6% of the global foundry market while facing existential threats that could reshape the entire technology ecosystem. The company's financial performance remains robust, with Q2 2025 revenue reaching $30.07 billion and over 60% year-over-year net income growth. Yet, this dominance has paradoxically made it the world's most vulnerable single point of failure. TSMC produces 92% of the world's most advanced chips, creating a concentration risk where any disruption could trigger global economic catastrophe exceeding $1 trillion in losses.
The primary threat comes not from a direct Chinese invasion of Taiwan, but from Beijing's "anaconda strategy" of gradual economic and military coercion. This includes record-breaking military flights into Taiwan's airspace, practice blockades, and approximately 2.4 million daily cyberattacks on Taiwanese systems. Simultaneously, U.S. policies create contradictory pressures—while providing billions in CHIPS Act subsidies to encourage American expansion, the Trump administration has revoked export privileges for TSMC's Chinese operations, forcing costly reorganization and individual licensing requirements that could cripple the company's mainland facilities.
Beyond geopolitical risks, TSMC faces an invisible war in cyberspace, with over 19,000 employee credentials circulating on the dark web and sophisticated state-sponsored attacks targeting its intellectual property. The recent alleged leak of 2nm process technology highlights how China's export control restrictions have shifted the battleground from equipment access to talent and trade secret theft. TSMC's response includes an AI-driven dual-track IP protection system, which manages over 610,000 cataloged technologies and extends security frameworks to global suppliers.
TSMC is actively building resilience through a $165 billion global expansion strategy, establishing advanced fabs in Arizona, Japan, and Germany while maintaining its technological edge with superior yields on cutting-edge nodes. However, this de-risking strategy comes at a significant cost - Arizona operations will increase wafer costs by 10-20% due to higher labor expenses, and the company must navigate the strategic paradox of diversifying production while keeping its most advanced R&D concentrated in Taiwan. The analysis concludes that TSMC's future hinges not on current financial performance, but on successfully executing this complex balancing act between maintaining technological leadership and mitigating unprecedented geopolitical risks in an increasingly fragmented global order.
Can One Idaho Mine Break China's Grip on America's Defense?Perpetua Resources Corp. (NASDAQ: PPTA) has emerged as a critical player in America's quest for mineral independence through its Stibnite Gold Project in Idaho. The company has secured substantial backing with $474 million in recent financing, including investments from Paulson & Co. and BlackRock, plus over $80 million in Department of Defense funding. This support reflects the strategic importance of the project, which aims to produce both gold and antimony while restoring legacy mine sites and creating over 550 jobs in rural Idaho.
The geopolitical landscape has dramatically shifted in Perpetua's favor following China's export restrictions on antimony imposed in September 2024. With China controlling 48% of global antimony production and 63% of U.S. imports, Beijing's ban on sales to America has exposed critical supply chain vulnerabilities. The Stibnite Project represents America's only domestic antimony source, positioning Perpetua to potentially supply 35% of U.S. antimony needs and reduce dependence on China, Russia, and Tajikistan, which collectively control 90% of global supply.
Antimony's strategic significance extends far beyond its typical use as a mining commodity, serving as an essential component in defense technologies, including missiles, night vision equipment, and ammunition. The U.S. currently maintains stockpiles of just 1,100 tons against annual consumption of 23,000 tons, highlighting the critical supply shortage. Global antimony prices surged 228% in 2024 due to these shortages, while conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East have amplified demand for defense-related materials.
The project combines economic development with environmental restoration, employing advanced technologies for low-carbon operations and partnering with companies like Ambri to develop liquid metal battery storage systems. Analysts have set an average price target of $21.51 for PPTA stock, with recent performance showing a 219% surge reflecting market confidence in the company's strategic positioning. As clean energy transitions drive demand for critical minerals and U.S. policies prioritize domestic production, Perpetua Resources stands at the intersection of national security, economic development, and technological innovation.
Can Rivian Survive the Perfect Storm of Challenges?Rivian Automotive reported mixed Q2 2025 results that underscore the electric vehicle startup's precarious position. While the company met revenue expectations with $1.3 billion in consolidated revenue, it significantly missed earnings forecasts with a loss per share of $0.97 versus the anticipated $0.66 loss - a 47% deviation. Most concerning, gross profit returned to negative territory at -$206 million after two consecutive positive quarters, highlighting persistent manufacturing inefficiencies and cost management challenges.
The company faces a confluence of external pressures that threaten its path to profitability. Geopolitically, China's dominance over rare earth elements - controlling 60% of production and 90% of processing capacity - creates supply chain vulnerabilities, while new Chinese export licensing rules complicate access to critical EV components. Domestically, the impending expiration of federal EV tax credits on September 30, 2025, combined with the effective end of CAFE fuel economy standards enforcement, eliminates key demand-side and supply-side incentives that have historically supported EV adoption.
Rivian's strategic response centers on three critical initiatives: the R2 model launch, the transformative Volkswagen partnership, and aggressive manufacturing scale-up. The R2 represents Rivian's pivot from niche, high-cost premium vehicles to mainstream, higher-volume products designed to achieve positive gross margins. The $5.8 billion Volkswagen joint venture provides essential capital and manufacturing expertise, while the Illinois plant expansion to 215,000 annual units by 2026 aims to deliver the economies of scale necessary for profitability.
Despite maintaining a strong cash position of $7.5 billion and securing the Volkswagen investment, Rivian's widened EBITDA loss guidance of $2.0-2.25 billion for 2025 and target of EBITDA breakeven by 2027 represent a high-stakes race against time and capital burn. The company's success hinges on flawless execution of the R2 launch, achieving planned production scale, and leveraging its software capabilities and patent portfolio in V2X/V2L technologies to diversify revenue streams beyond traditional vehicle sales in an increasingly challenging regulatory and competitive environment.
Is Samsung's Chip Bet Paying Off?Samsung Electronics is navigating a complex global landscape, marked by intense technological competition and shifting geopolitical alliances. A recent $16.5 billion deal to supply advanced chips to Tesla, confirmed by Elon Musk, signals a potential turning point. This contract, set to run until late 2033, underscores Samsung's strategic commitment to its foundry business. The agreement will dedicate Samsung's new Texas fabrication plant to producing Tesla's next-generation AI6 chips, a move Musk himself highlighted for its significant strategic importance. This partnership aims to bolster Samsung's position in the high-stakes semiconductor sector, particularly in advanced manufacturing and AI.
The deal's economic and technological implications are substantial. Samsung's foundry division has faced profitability challenges, experiencing estimated losses exceeding $3.6 billion in the first half of the year. This large-scale contract is expected to help mitigate those losses, providing a much-needed revenue stream. From a technological standpoint, Samsung aims to accelerate its 2-nanometer (2nm) mass production efforts. While its 3nm process faced yield hurdles, the Tesla collaboration, with Musk's direct involvement in optimizing efficiency, could be crucial for improving 2nm yields and attracting future clients like Qualcomm. This pushes Samsung to remain at the forefront of semiconductor innovation.
Beyond the immediate financial and technological gains, the Tesla deal holds significant geopolitical and geostrategic weight. The dedicated Texas fab enhances U.S. domestic chip production capabilities, aligning with American goals for supply chain resilience. This deepens the U.S.-South Korea semiconductor alliance. For South Korea, the deal strengthens its critical tech exports and may provide leverage in ongoing trade negotiations, particularly concerning potential U.S. tariffs. While Samsung still trails TSMC in foundry market share and faces fierce competition in High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM) from SK Hynix, this strategic alliance with Tesla positions Samsung to solidify its recovery and expand its influence in the global high-tech arena.
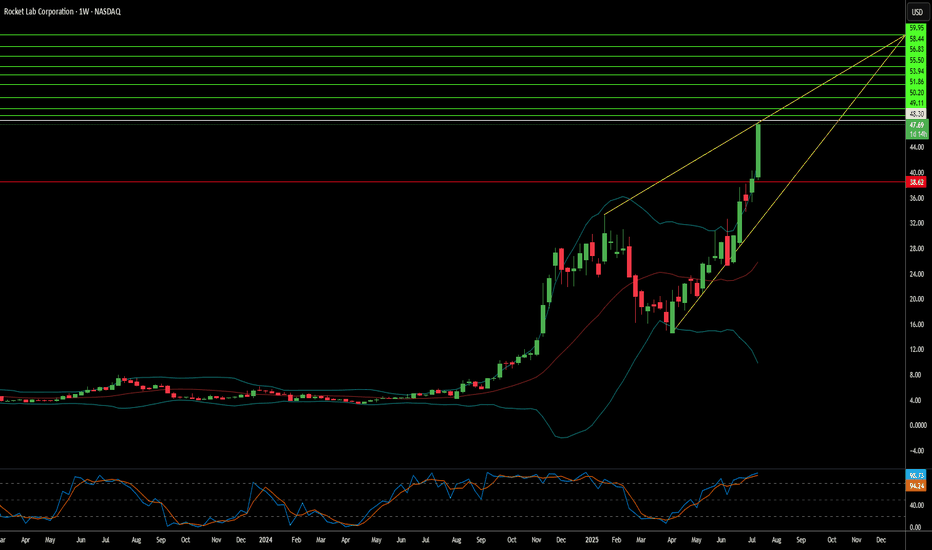
Is Rocket Lab the Future of Space Commerce?Rocket Lab (RKLB) is rapidly ascending as a pivotal force in the burgeoning commercial space industry. The company's vertically integrated model, spanning launch services, spacecraft manufacturing, and component production, distinguishes it as a comprehensive solutions provider. With key operations and launch sites in both the U.S. and New Zealand, Rocket Lab leverages a strategic geographic presence, particularly its strong U.S. footprint. This dual-nation capability is crucial for securing sensitive U.S. government and national security contracts, aligning perfectly with the U.S. imperative for resilient, domestic space supply chains in an era of heightened geopolitical competition. This positions Rocket Lab as a trusted partner for Western allies, mitigating supply chain risks for critical missions and bolstering its competitive edge.
The company's growth is inextricably linked to significant global shifts. The space economy is projected to surge from $630 billion in 2023 to $1.8 trillion by 2035, driven by decreasing launch costs and increasing demand for satellite data. Space is now a critical domain for national security, compelling governments to rely on commercial entities for responsive and reliable access to orbit. Rocket Lab's Electron rocket, with over 40 launches and a 91% success rate, is ideally suited for the burgeoning small satellite market, vital for Earth observation and global communications. Its ongoing development of Neutron, a reusable medium-lift rocket, promises to further reduce costs and increase launch cadence, targeting the expansive market for mega-constellations and human spaceflight.
Rocket Lab's strategic acquisitions, such as SolAero and Sinclair Interplanetary, enhance its in-house manufacturing capabilities, allowing greater control over the entire space value chain. This vertical integration not only streamlines operations and reduces lead times but also establishes a significant barrier to entry for competitors. While facing stiff competition from industry giants like SpaceX and emerging players, Rocket Lab's diversified approach into higher-margin space systems and its proven reliability position it strongly. Its strategic partnerships further validate its technological prowess and operational excellence, ensuring a robust position in an increasingly competitive landscape. As the company explores new frontiers like on-orbit servicing and in-space manufacturing, Rocket Lab continues to demonstrate the strategic foresight necessary to thrive in the dynamic new space race.
Soaring High: What Fuels GE Aerospace's Ascent?GE Aerospace's remarkable rise reflects a confluence of strategic maneuvers and favorable market dynamics. The company maintains a dominant position in the commercial and military aircraft engine markets, powering over 60% of the global narrowbody fleet through its CFM International joint venture and proprietary platforms. This market leadership, coupled with formidable barriers to entry and significant switching costs in the aircraft engine industry, secures a robust competitive advantage. Furthermore, a highly profitable aftermarket business, driven by long-term maintenance contracts and an expanding installed engine base, provides a resilient, recurring revenue stream. This lucrative segment buffers the company against cyclicality and ensures consistent earnings visibility.
Macroeconomic tailwinds also play a crucial role in GE Aerospace's sustained growth. Global air travel is steadily increasing, driving higher aircraft utilization rates. This directly translates to greater demand for new engines and, more importantly, consistent aftermarket servicing, which is a core profit driver for GE Aerospace. Management, under CEO Larry Culp, has also strategically navigated external challenges. They localized supply chains, secured alternate component sources, and optimized logistics costs. These actions proved critical in mitigating the impact of new tariff regimes and broader trade war tensions.
Geopolitical developments have significantly shaped GE Aerospace's trajectory. Notably, the U.S. government's decision to lift restrictions on exporting aircraft engines, including LEAP-1C and GE CF34 engines, to China's Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China (COMAC) reopened a vital market channel. This move, occurring amidst a complex U.S.-China trade environment, underscores the strategic importance of GE Aerospace's technology on the global stage. The company's robust financial performance further solidifies its position, with strong earnings beats, a healthy return on equity, and positive outlooks from a majority of Wall Street analysts. Institutional investors are actively increasing their stakes, signaling strong market confidence in GE Aerospace's continued growth potential.
Can Strategic Minerals Transform National Security?MP Materials has experienced a significant market revaluation, with its stock surging over 50% following a pivotal public-private partnership with the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD). This multi-billion-dollar agreement, which includes a $400 million equity investment, substantial additional funding, and a $150 million loan, aims to rapidly establish a robust, end-to-end U.S. rare earth magnet supply chain. This strategic collaboration is designed to curtail the nation's reliance on foreign sources for these critical materials, which are indispensable for advanced technology systems across both defense and commercial applications, from F-35 fighter jets to electric vehicles.
The partnership underscores a profound geopolitical imperative: countering China's near-monopoly over the global rare earth supply chain. China dominates rare earth mining, refining, and magnet production, a leverage it has demonstrably used through export restrictions amidst escalating trade tensions with the U.S. These actions highlighted acute U.S. vulnerabilities and the imperative for domestic independence, propelling the DoD's "mine to magnet" strategy aimed at achieving self-sufficiency by 2027. The DoD's substantial investment and its new position as MP Materials' largest shareholder signal a decisive shift in U.S. industrial policy, directly challenging China's influence and asserting economic sovereignty in a vital sector.
Central to the deal's financial attractiveness and long-term stability is a 10-year price floor of $110 per kilogram for key rare earths, significantly higher than historical averages. This guarantee not only ensures MP Materials' profitability, even against potential market manipulation, but also de-risks its ambitious expansion plans, including new magnet manufacturing facilities expected to produce 10,000 metric tons annually. This comprehensive financial and demand certainty transforms MP Materials from a commodity producer vulnerable to market whims into a strategic national asset, attracting further private investment and setting a powerful precedent for securing other critical mineral supply chains in the Western Hemisphere.
Why Your Orange Juice Costs More?The price of orange juice is surging, impacting consumers and the broader economy. This increase stems from a complex interplay of geopolitical tensions, macroeconomic pressures, and severe environmental challenges. Understanding these multifaceted drivers reveals a volatile global commodity market. Investors and consumers must recognize the interconnected factors that now influence everyday staples, such as orange juice.
Geopolitical shifts significantly contribute to the rising prices of orange juice. The United States recently announced a 50% tariff on all Brazilian imports, effective August 1, 2025. This politically charged move targets Brazil's stance on former President Jair Bolsonaro's prosecution and its growing alignment with BRICS nations. Brazil dominates the global orange juice supply, providing over 80% of the world's trade share and 81% of U.S. orange juice imports between October 2023 and January 2024. The new tariff directly increases import costs, squeezing margins for U.S. importers and creating potential supply shortages.
Beyond tariffs, a convergence of macroeconomic forces and adverse weather conditions amplify price pressures. Higher import costs fuel inflation, potentially compelling central banks to maintain tighter monetary policies. This broader inflationary environment impacts consumer purchasing power. Simultaneously, orange production faces severe threats. Citrus greening disease has devastated groves in both Florida and Brazil. Extreme weather events, including hurricanes and droughts, further reduce global orange yields. These environmental setbacks, coupled with geopolitical tariffs, create a robust bullish outlook for orange juice futures, suggesting continued price appreciation in the near term.