Mastering Divergence in Technical AnalysisIn technical analysis, a divergence (also called a “momentum divergence” or “price/indicator disagreement”) is one of the most powerful early warning signals available to traders. In simple terms, divergence occurs when price and a momentum indicator (such as RSI, MACD, or Awesome Oscillator etc.) move in opposite directions.
This disagreement often signals that the current trend is losing strength and that a pause, pullback, or full reversal may be approaching.
1. What Is Divergence?
Normally, in a healthy trend:
In an uptrend, price makes higher highs and momentum indicators also make higher highs.
In a downtrend, price makes lower lows and momentum indicators also make lower lows.
A divergence appears when this alignment breaks.
Typical example with RSI or MACD:
Price makes a higher high,
But the indicator makes a lower high.
This tells us that, although price has pushed to a new extreme, the underlying momentum is weaker. Smart money may be taking profits, and the late participants are driving the final leg of the move.
2. Types of Divergence
There are two main families of divergence:
Regular (classic) divergence – often associated with potential trend reversals.
Hidden divergence – often associated with trend continuation after a correction.
Within each family, we have bullish and bearish versions.
2.1 Regular Bullish Divergence – Potential Trend Reversal Up
This suggests that sellers are still pushing price to new lows, but momentum is no longer confirming the strength of this selling pressure. The downtrend is weakening and a bullish reversal may develop.
Context where it’s most powerful:
After a prolonged downtrend.
At or near a higher-timeframe support level (daily/weekly support, major demand zone, trendline, or Fibonacci confluence).
2.2 Regular Bearish Divergence – Potential Trend Reversal Down
This signals that buyers are still able to push price higher, but each new high is supported by less momentum. The uptrend is aging, and a bearish reversal or deeper correction becomes more likely.
Context where it’s most powerful:
After a strong, extended uptrend.
Around major resistance levels, supply zones, or upper trendlines.
2.3 Hidden Bullish Divergence – Trend Continuation Up
Here, price structure still shows an uptrend (higher lows), but the indicator has overshot to the downside. This often appears during pullbacks within an uptrend, suggesting that the correction is driven more by short-term emotion than by real structural weakness.
Interpretation:
Hidden bullish divergence indicates trend continuation. Bulls remain in control, and the pullback may provide an opportunity to join the uptrend at a better price.
2.4 Hidden Bearish Divergence – Trend Continuation Down
Price structure still favors the bears (lower highs), but the indicator has spiked higher, often due to a sharp counter-trend rally. This suggests that the bounce is corrective rather than the start of a new uptrend.
Interpretation:
Hidden bearish divergence favors continuation of the downtrend and often appears before the next impulsive bearish leg.
3. Which Indicators to Use?
Divergence can be spotted on many oscillators, but the most commonly used are:
RSI (Relative Strength Index) – very popular for spotting overbought/oversold zones and divergences.
MACD (and its histogram) – useful for trend and momentum, especially on higher timeframes.
Stochastic Oscillator – often used in range-bound environments.
Awesome Oscillator, CCI, etc. – alternative momentum tools, depending on your preference.
The concept is the same: price and indicator should generally confirm each other. If not, you have a divergence.
4. Timeframes and Reliability
Divergences can be found on all timeframes, but their reliability increases with higher timeframes:
On M5–M15, divergences are frequent but often short-lived. Better for scalpers.
On H1–H4, signals have more weight and can lead to multi-session moves.
On Daily/Weekly, divergences can mark major tops and bottoms, but they may take longer to play out.
A good practice is to:
Identify major divergences on higher timeframes (H4, Daily).
Refine entries on lower timeframes (M15, M30, H1) using structure and price action.
5. How to Trade Divergences (Practical Framework)
Divergence by itself is not a complete trading system. It is a signal of potential imbalance, which should be combined with:
Key levels (support, resistance, supply/demand zones).
Trend structure (higher highs/lows or lower highs/lows).
Price action confirmations (reversal candles, break of structure, etc.).
Risk management (position sizing, stop loss, invalidation level).
6. Common Mistakes When Using Divergences
- Trading every divergence blindly.
Not every divergence leads to a big reversal. Many will result in only minor pullbacks.
- Ignoring the trend.
Regular divergences against a strong trend can fail multiple times before a real top or bottom forms. Hidden divergences are often more reliable in trending markets.
- Forcing divergences where they don’t exist.
Only connect clear, obvious swing highs and lows on both price and indicator. If you have to “stretch” the lines, the signal is probably weak.
- No risk management.
A divergence is just a probability edge, not a guarantee. Always define invalidation and manage position size accordingly.
7. Best Practices
Combine divergence with market structure (trendlines, channels, higher highs/lows).
Use higher-timeframe context and drop to lower timeframes for refined entries.
Pay attention to confluence:
Divergence + key level + candlestick signal is stronger than any single factor.
Keep a trading journal of divergence setups, including screenshots from your charts. Over time, you will see which conditions work best for your style.
Divergences are not magic, but they are one of the cleanest ways to see when price and momentum disagree. Used correctly, they can:
Help you avoid entering late in a trend,
Alert you to potential reversals before they are obvious to the crowd, and
Provide high-probability continuation entries via hidden divergences within strong trends.
Oscillators
A Thesis Of A Trade: Developing A Story For Each TradeThe plan is the same, but each pair has a different story and different thesis. Previously, I have reported that I open a batch of trades and closing them all when I reach a certain profit percentage based on the Stochastic Plan.
Last week the batch stayed negative, but all are still within the plan and not a single one broke the idea of the reason why they were opened. This opened the door for me to start treating each trade on its own instead of opening and closing batches. This is something that I wanted to implement but did not have the heart for it, especially that this is the first time for me to trade the scary daily time frame.
Today is Monday, and accidentally it is the 1st of the month, and the 1st of December. This month I am going to try to keep at the methodology of treating each trade independently and create a thesis for each trade.
Such a methodology with a thesis for each trade allows, as one of the comments of one of my previous videos here suggested, to create structural Stop Loss and Take Profit points. The thesis will tell a story of the pair. Why I opened the trade and where do I see it going based on the stochastic trigger and the chart elements.
The thesis will also show when is the thesis going to be negated and no more stands and therefore needs to be stopped even at a loss. A break of thesis means that the reason why a trade was opened no longer exists and I need to get out of it.
In the same manner, the thesis will look at the chart elements and see potential areas where the price might stop moving in my direction and this is again a point where I would close the trade in my favor.
Everyday now I feel closer to reaching a solid Forex trading plan that I can depend on, and the day of funding a live account is getting closer. I am looking at funding an account by the end of this month to start the year 2026 trading live.
Mastering RSI: A Complete Guide to Momentum🔵 Mastering RSI: A Complete Guide to Momentum, Regimes, Reversals & Professional Signals
Difficulty: 🐳🐳🐳🐳🐋 (Advanced)
This article goes far beyond the basic idea of “RSI = overbought/oversold.” If you want to truly master RSI as a momentum gauge, trend filter, reversal tool, and structure confirmation model, this guide is for you.
🔵 WHY MOST TRADERS MISUSE RSI
Most traders use RSI in the simplest way:
RSI above 70 = sell
RSI below 30 = buy
This leads to shorting strong trends and catching falling knives.
RSI is not a reversal button. RSI is a momentum translator.
To master RSI, you must understand:
Trend regimes
Momentum pressure
Acceleration and deceleration
Failure swings
Divergences
Trend vs range behavior
Multi-timeframe alignment
Structure confirmation
RSI shows the strength behind price, not just extremes.
🔵 1. RSI TREND REGIMES (CORE FOUNDATION)
RSI moves in predictable zones depending on the type of market environment.
Bullish RSI Regime
RSI holds between 40 and 80
Pullbacks bottom around 40–50
Breaks above 60 show trend acceleration
Bearish RSI Regime
RSI holds between 20 and 60
Pullback tops form around 50–60
Breaks below 40 confirm bearish dominance
These regimes tell you who controls the market before you even look at candles.
🔵 2. MOMENTUM PRESSURE (RSI AS A SPEEDOMETER)
RSI measures the speed and pressure of price movement.
Rising RSI with rising price = trend acceleration
Falling RSI with rising price = momentum weakening
Rising RSI with falling price = early strength
Falling RSI with falling price = continuation pressure
This is not divergence. It is momentum pressure, the earliest sign of trend shift.
🔵 3. FAILURE SWINGS (THE MOST RELIABLE RSI REVERSAL SIGNAL)
Failure swings are powerful because they show internal momentum breaking before price reacts.
Bullish Failure Swing
RSI makes a low
RSI rallies
RSI dips again but stays above previous low
RSI breaks the previous high
Bearish Failure Swing
RSI makes a high
RSI pulls back
RSI rallies but fails to break the previous high
RSI breaks the previous low
Failure swings often appear at trend tops and bottoms before candles reveal anything.
🔵 4. DIVERGENCES (REGULAR AND HIDDEN)
Regular Divergence: Reversal Clue
Bullish: price lower low, RSI higher low
Bearish: price higher high, RSI lower high
Hidden Divergence: Trend Continuation
Bullish hidden: price higher low, RSI lower low
Bearish hidden: price lower high, RSI higher high
Hidden divergence is more powerful than regular because it confirms trend continuation.
🔵 5. RANGE RSI VS TREND RSI
RSI behaves very differently in ranges versus trends.
Range Environment
RSI oscillates between 30 and 70
Reversals at extremes have high accuracy
RSI 50 is the equilibrium
Trend Environment
RSI stays above 50 in bullish trends
RSI stays below 50 in bearish trends
30 and 70 extremes lose meaning
Always identify environment first. RSI signals change depending on regime.
🔵 6. RSI AS A STRUCTURE FILTER
RSI combined with structure improves trade selection dramatically.
Price makes higher highs + RSI rising = healthy trend
Price makes higher highs + RSI flat = weak breakout
Price makes higher highs + RSI dropping = exhaustion
Support retest + RSI 40–50 = strong continuation potential
Most false breakouts are avoided simply by checking RSI pressure.
🔵 7. MULTI-TIMEFRAME RSI ALIGNMENT
Use higher timeframe RSI to validate lower timeframe setups.
HTF RSI bullish + LTF RSI pullback = high-quality entry
HTF RSI bearish + LTF RSI bounce = premium short area
HTF RSI crossing 50 = long-term regime shift
This is one of the most powerful RSI confluences.
🔵 EXAMPLE TRADING FRAMEWORK
Bullish Setup Checklist
RSI in bullish regime (above 50)
Pullback into 40–50 zone
Hidden bullish divergence or failure swing
Structure forms a higher low
Bearish Setup Checklist
RSI in bearish regime
Rejection from 50–60 zone
Hidden bearish divergence or failure swing
Structure forms a lower high
🔵 COMMON RSI MISTAKES
Trading RSI extremes without trend context
Ignoring RSI regimes
Entering on regular divergences in strong trends
Not using RSI midline (50) as a regime filter
Relying only on overbought/oversold signals
🔵 CONCLUSION
RSI is one of the most powerful indicators when used correctly. It provides a complete framework for:
Reading trend strength
Tracking momentum pressure
Identifying early reversals
Trading continuation setups
Filtering breakout strength
Aligning multi-timeframe bias
Master RSI, and you gain a clearer view of momentum than most traders ever experience.
How do you use RSI? Do you prefer divergences, trend zones, or failure swings? Share your approach below!
Examples of Using the StochRSI Indicator
Hello, fellow traders!
Follow us to get the latest information quickly.
Have a great day!
-------------------------------------
The StochRSI indicator combines the Stochastic indicator with the RSI indicator.
You can find more detailed explanations of this indicator online.
I'd like to explain how to utilize the StochRSI indicator to aid trading.
The standard way to interpret the StochRSI indicator is to interpret chart movements by touching and breaking out of overbought or oversold zones.
The method I use, utilizing this principle, is to draw a trend line.
That is, when the K value of the StochRSI indicator forms a peak in the overbought or oversold zone, I connect those points to create a trend line.
This creates a trend line like the one drawn in the example chart above.
However, when drawing a trend line, the candlestick that forms the peak in the overbought zone must be the open value of a bearish candlestick.
If not, the open value of the first bearish candlestick encountered to the right is used.
In the oversold zone, the peak is the low value.
-
I've also included a second method for interpreting the StochRSI indicator.
When the indicator is activated, the chart above will appear.
This can be intuitively seen by the StochRSI indicator appearing on the price candlestick.
To sustain an uptrend, the price must remain above the StochRSI 80 level.
Therefore, the StochRSI 80 level acts as resistance.
A decline below the StochRSI 20 level likely indicates a downtrend.
Therefore, the StochRSI 20 level acts as support.
This interpretation can be helpful when entering a trade.
However, the most important points are the support and resistance levels drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts.
Therefore, observing the movement of the StochRSI indicator near the support and resistance levels drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts can help you determine the trend.
-------------------------------
The StochRSI and RSI indicators are also indicators that utilize averages.
When interpreting indicators that utilize averages, it's important to consider the location of the average and how to interpret it accordingly.
Therefore, the StochRSI 50 indicator point can be used as an average.
Therefore, you can initiate a trade based on whether there is support at the StochRSI 50 indicator point.
As mentioned earlier, the most important points are the support and resistance levels drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts. Therefore, you should check the movement of the StochRSI indicator around these support and resistance points.
-
Thank you for reading to the end.
I wish you successful trading.
--------------------------------------------------
Improving My Win Loss Ratio In Forex TradingWell, Some good news, actually great news. The experiment worked and in this video I show how I am improving my win loss ratio in Forex trading.
From a disastrous Win Loss ratio using only SMC now with combining the classical school along with the Stochastic I have been nailing it for the past 20 days with 22 trades and 8.6% increase on my balance.
In many cases, especially with advantageous RRR, it is Ok to have the win loss ratio in favor of the Loss, as the RRR will compensate and the balance would increase, but in this case I have the win rate higher and the RRR if it was calculated is also higher.
I depend on opening multiple trades and closing them all at once once they hit an acceptable percentage. In the video I said I will close them around 2%, but to tell you the truth, even if it was 1% I would close because no business I know of would bring 1% profit in a day.
The concern now with this Forex Trading Plan is that it does not use Stop Loss nor Take Profit. I feel that I am hanging in the air, which is not a good feeling and this might get me inside an emotional imbalance in the long run.
Still, the test is going on to evaluate all that.
My Steps On how To Improve Forex Trading Win / Loss Ratio In this video we talk about the three elements of the new plan that I have designed based on different types of schools and educational sources.
The plan elements consist of SMC (Smart Money Concepts), Classical School (Support & Resistance, Trend Lines, Febonacci Retracement (not all the time)), and the Stochastic Indicator.
The stochastic is of two timeframes, One is weekly and the other is daily but both are shown on the daily timeframe. This is something that I loved here about TradingView; is the ability to show an indicator of a different timeframe.
Last week I opened a couple of positions based on the new plan, but one of them was opened with haste and not totally adhered to my trading Plan rules.
I show the exact trading rules that I am using and how this will affect my risk management plan.
Something’s Brewing at the Front EndDonald Trump wants lower interest rates. He may well get his wish soon, at least at the front of the U.S. Treasury curve. The chart you’re looking at has two panes. On the left, we have U.S. two-year Treasury futures. On the right, we have two-year U.S. Treasury yields. The former uses a weekly tick, the latter daily.
With futures coiling in a well-defined ascending triangle pattern for more than a year, you get the sense that should we see a weekly close above 104’16’0, it may act as a catalyst to spark further upside, potentially explosive. The contract has been rejected at the level six separate times since July 2024, including four failed breakout attempts over the same period. This reinforces its importance. Given its proximity to the level with RSI (14) and MACD generating bullish momentum signals, attempt number seven—if we see it—stands a decent chance of sticking.
If we see a sustained break above 104’16’0, 105’08’0, 106’06’6 and 107’06’2 loom as the levels to watch, especially the latter as it aligns with the extension target based on the triangle’s height. If it were to be achieved, it points to a nominal two-year Treasury yield of around 1.5%.
That’s obviously far lower than where it currently resides, pointing to negative real rates given the Fed’s 2% inflation target and, in all likelihood, economic conditions far weaker than recent years or monetary policy being guided by factors other than fundamentals.
While the setup is tradable, if it plays out, it will have ramifications far beyond rate futures given the economic signal it would provide. When you look at recent moves in hard assets with perceived scarcity value, it appears many investors and traders are already positioning for such an environment.
Good luck,
DS
How to Trade with Stochastics in TradingViewMaster Stochastics using TradingView’s charting tools in this comprehensive tutorial from Optimus Futures.
The Stochastic Oscillator is a momentum indicator that helps traders identify potential turning points in the market by comparing the current closing price to the recent high–low range. It’s designed to show when momentum may be shifting from buyers to sellers — or vice versa.
What You’ll Learn:
- Understanding the Stochastic Oscillator as a momentum tool plotted from 0 to 100
- How the %K line represents the current close relative to the recent high–low range
- How the %D line acts as a moving average of %K and serves as a signal line
- Key thresholds: readings above 80 suggest overbought conditions, while below 20 suggest oversold conditions
- Why overbought and oversold levels are not automatic buy or sell signals — and how strong trends can keep Stochastics extended
- Identifying bullish and bearish crossovers between %K and %D
- Spotting bullish and bearish divergence between price and momentum
- Using Stochastics to confirm trend direction across different timeframes
- How to add Stochastics on TradingView via the Indicators menu
- Understanding the default settings (14, 3, 3) and how adjusting them affects responsiveness
- Practical examples on the E-mini S&P 500 futures chart
- Applying Stochastics across multiple timeframes — daily, weekly, or intraday — for confirmation signals
This tutorial will benefit futures traders, swing traders, and technical analysts who want to incorporate Stochastics into their trading process.
The concepts covered may help you identify momentum shifts, potential reversal zones, and trend confirmations across different markets and timeframes.
Learn more about futures trading with TradingView:
optimusfutures.com
Disclaimer
There is a substantial risk of loss in futures trading. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Please trade only with risk capital. We are not responsible for any third-party links, comments, or content shared on TradingView. Any opinions, links, or messages posted by users on TradingView do not represent our views or recommendations. Please exercise your own judgment and due diligence when engaging with any external content or user commentary.
This video represents the opinion of Optimus Futures and is intended for educational purposes only.
Chart interpretations are presented solely to illustrate objective technical concepts and should not be viewed as predictive of future market behavior. In our opinion, charts are analytical tools — not forecasting instruments.
Is the Bitcoin market bearish?📊 Bitcoin Market Psychology Analysis
Market psychology analysis is one of the most fascinating and practical approaches to understanding Bitcoin's current position! 🎯
🎭 Market Psychology Cycle Phases:
1. Hope Phase 🟦
Likely the current point for many assets
· 📈 Description: After a panic-driven crash, the market stabilizes and consolidates within a relatively stable range
· 💰 Price hasn't returned to previous lows and shows occasional small positive breakouts
· 😌 Sentiment: Fatigue from the downturn, but quiet hope for gradual improvement
· 👴 Experienced investors accumulate while newcomers remain cautious
· 📊 Indicator: Moderate trading volume typically
2. Optimism & Belief Phase 🟩
· 🚀 Description: Price begins breaking key resistance levels
· 📰 Media gradually starts paying attention again
· 😨 Sentiment: FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out) among experienced investors
· 😞 Regret over selling at the bottom
· 📈 Indicator: Beginning of increasing trading volume
3. Greed & Euphoria Phase 🟨
· 📈 Description: Full-blown bullish phase - price rises consistently and rapidly
· 🗞️ Positive news dominates everywhere
· 👥 Friends and acquaintances talk about massive profits
· 💭 Sentiment: Belief that "this time it's different" and "price only goes up"
· 💸 Greed for more profits and borrowing to buy
· 📊 Indicator: Very high trading volume and positive media coverage
4. Denial Phase 🟧 - Danger Point!
· 📉 Description: Price falls from the peak
· 🤦 Many investors consider this just a "temporary correction"
· 🔮 Expect a return to the peak
· ❌ Sentiment: Strong denial
· 🛒 Buying during the decline hoping for recovery
· 📊 Indicator: Trading volume remains high
5. Fear, Panic & Capitulation Phase 🟥
· 🚨 Description: Sharp and rapid decline
· 📉 Price experiences consecutive breakdowns
· 😱 Sentiment: Intense fear, panic selling
· 💔 Acceptance of heavy losses - absolute despair
· 📊 Indicator: Very high selling volume
6. Apathy & Depression Phase ⬜
· 😴 Description: Market remains stagnant with low volatility for extended periods
· 💤 Prices are low and boring
· 🚫 Sentiment: Complete disinterest in the market
· 👋 Most people have accepted defeat and exited the market
· ☠️ Talk of "Bitcoin's death" resurfaces
· 📊 Indicator: Very low trading volume and minimal media attention
---
💡 Golden Insight:
Understanding these phases can help you make the best trading decisions! ✨
---
📌 Market Psychology + Technical Analysis = Trading Success 🚀
---
💬 Let's Interact!
I'd love to hear your thoughts! 👇
· 🤔 Which phase do you think we're currently in?
· 📊 What's your market outlook for the coming months?
· 💭 Share your technical analysis perspective
· 🎯 Have you used market psychology in your trading strategy?
· 📉 What indicators do you find most reliable?
· 💡 Any successful trades based on market sentiment?
· 🔮 Where do you see Bitcoin in the next 6 months?
Let's learn from each other! Share your comments and analysis below 👇
Your experience and insights are valuable - let's build our trading knowledge together! 🌟
Feel free to ask any questions or share your trading experiences! 💪
Simple UO + ADX Futures Strategy📚 Trading Plan with UO + ADX + 9/21 MA
1. Indicator Roles
Ultimate Oscillator (UO): Measures momentum across 3 different timeframes (short, medium, long). I use the lengths 4/8/14.
Overbought: > 70
Oversold: < 30
Neutral: 30–70 range
ADX (14-period, 100 smoothed): Measures trend strength, not direction.
Weak trend: < 17~20
Building trend: 20–25
Strong trend: > 27–30, enter on pullback. A bounce from the 9 or 21 MA.
2. Core Trading Logic
We combine momentum (UO) with trend strength (ADX) to avoid false signals.
Long Setup (Buy):
ADX rising above 23 → trend gaining strength.
UO crosses above 30 from below → confirms bullish momentum.
Confirm price is above 21-day MA (optional filter for trend).
📈 Exit:
UO > 50 and turning down, or
ADX below 17, or
Trailing MA.
Short Setup (Sell):
ADX rising above 27 → trend gaining strength.
UO crosses below 70 from above → confirms bearish momentum.
Confirm price is below 9-day MA (optional filter for trend).
📉 Exit:
UO < 30 and turning up, or
ADX drops below 20, or
Trailing stop.
3. Advanced Filters
Avoid false breakouts: If ADX < 20, ignore UO signals (no strong trend).
Divergence filter: If price makes a new high but UO does not → weakening trend.
Scaling:
Add to winners if ADX > 30 and still rising.
Take partial profits if ADX flattens while UO is in extreme zone.
4. Risk Management
Position sizing: Risk 1–2% of account per trade.
Stop loss: Below recent swing low (for longs) or above swing high (for shorts).
Take profit: Risk:Reward 1:2 minimum, or trail with MA.
5. Example Workflow
Case 1 (Bullish):
ADX rises from 18 → 27 (trend forming).
UO crosses 50 → bullish signal.
Enter long.
Exit when UO > 70 and rolls over, or ADX drops < 20.
Case 2 (Bearish):
ADX rises above 25.
UO crosses below 50.
Enter short.
Exit when UO < 30 and turns up, or ADX weakens.
✅ Summary Ruleset
Trade only when ADX > 23–25 (filter out noise).
Go long: UO crosses > 50 with rising ADX.
Go short: UO crosses < 50 with rising ADX.
Exit on momentum extremes (UO < 30 or > 70) or weakening ADX.
Risk: Keep losses capped at 1–2% of equity per trade.
Options Blueprint Series [Basic]: Gold Income or Bargain Entry?The Setup: A Pullback with a Plan
Gold has been riding a strong bullish wave, yet momentum indicators suggest it's time for a breather. RSI is now overbought, and if history repeats, we could see a healthy correction of up to 9.29%, in line with prior pullbacks. This projects price near 3255, where we also find a cluster of UnFilled Orders (UFOs) acting as a potentially relevant support. It’s a key price area where buyers may step in again.
Rather than try to perfectly time the correction or the bottom, we’re applying a more forgiving approach: selling a PUT far below current price—generating income while leaving room to be wrong by over 375 points.
This is not a hedge. This is a standalone income strategy that accepts risk but frames it intelligently using technical context and options structure.
The Strategy: Selling the 3250 PUT on GC
We're using a simple but powerful strategy—selling a naked PUT—which can generate income or result in ownership of Gold at a deep discount if price dips.
Underlying Asset: GCZ2025 – using Gold Futures Options (Nov 24 2025 Expiration)
Strategy: Sell 1x 3250 PUT
Premium Collected: 10.09 points ≈ $1,009
Breakeven Price: 3240
Max Profit: $1,009 (if Gold stays above 3250 until expiration)
Max Risk: Unlimited below breakeven
There are two possible outcomes here:
Gold stays above 3250 → we keep the full premium.
Gold drops below 3250 → we get assigned and become long GC at 3250. From there, we’re exposed to downside risk in Gold, with a breakeven at 3240.
The position benefits from time decay and stable to rising prices, but it does carry the full downside exposure of long Gold futures if the trade moves against us.
We want to be very clear here—this is a naked trade with undefined risk. That doesn’t make it reckless if done with sizing discipline and technical alignment, but it’s not a beginner-friendly strategy.
Gold Contract Specs
Understanding the size and risk of what you're trading is critical—especially with naked options.
✅ GC – Gold Futures (Full Size)
Symbol: GC
Contract Size: 100 troy ounces
Tick Size: 0.10 = $10
Point Value: 1 point = $100
Initial Margin (as of Sep 2025): ~$15,000 per contract (subject to change)
Underlying for the Option: GC Futures
✅ MGC – Micro Gold Futures
Symbol: MGC
Contract Size: 10 troy ounces
Tick Size: 0.10 = $1
Point Value: 1 point = $10
Initial Margin: ~$1,500 per contract (subject to change)
Why does this matter?
Because if GC collapses below 3250 and you're assigned long, you’ll be exposed to full-size futures. That’s $100 per point of movement. A 50-point drop? That's $5,000 in unrealized loss.
That’s where MGC becomes your best ally. Micro Gold futures offer a scalable way to hedge. If price begins moving down or breaks below the support zone, one could short MGC against the Short GC 3250 PUT to cap further losses or rebalance directional exposure with reduced size and margin impact.
The Technical Confluence: Where Structure Meets Strategy
The 3250 strike isn’t just a random number—it’s calculated. Historical RSI-based corrections in Gold have shown recent worse-case scenarios around 9.29%, and projecting that from recent highs lands us precisely near the 3255 zone. This level also aligns with a clear UFO support, where institutional buyers have likely left behind unfilled orders.
That confluence—statistical retracement, technical indicator, and order flow support—gives the 3250 strike an interesting probability structure. Selling a Put beneath it means we are placing our bet below the “floor” and getting paid while we wait.
If Gold never corrects that far, we profit.
If it does, we might get long near a historically meaningful level.
There’s no need to catch the top. There’s no need to nail the bottom.
Just structure the trade where the odds are already potentially skewed in your favor.
Trade Plan: Reward, Risk & Realism
This trade isn’t about precision entry or leveraged glory—it’s about risk-defined logic with a cash-flow twist. Here's the full breakdown:
🧠 Trade Parameters
Strategy: Sell 1x Gold Futures 3250 PUT Options
Premium Collected: 10.09 points = $1,009
Point Value (GC): $100/point
Breakeven Price: 3240 (3250 – 10)
Expiration: Nov 24, 2025
🟩 If Gold Stays Above 3250
You keep the full premium → $1,009 profit
🟥 If Gold Falls Below 3250
You may be assigned 1 GC contra<ct long at 3250
Unrealized losses begin below breakeven (3240)
Losses can be significant if Gold falls aggressively
⚠️ Reward-to-Risk?
Reward is capped at $1,009
Risk is unlimited below breakeven
The trade only makes sense if you're prepared to own Gold, or hedge dynamically via MGC or using any other technique
This isn’t a “set-and-forget” income play—it’s a calculated entry into a structured exposure with a fallback plan.
Risk Management: No Margin for Error
Selling naked options isn’t “free money.” It’s responsibility wrapped in premium. Here's what must be considered:
❗ Undefined Risk
When you sell a naked PUT, you're exposed to the full downside. If Gold drops $100 below your strike, that’s a $10,000 loss. Don’t sell naked options unless you’re ready—and capitalized—to buy the underlying or actively hedge it.
🔄 Use MGC to Hedge
If Gold breaks below 3250, using Micro Gold Futures (MGC) offers a surgical way to hedge risk without overleveraging. A simple short MGC can offset GC losses proportionally, depending on how aggressive the move becomes.
🧮 Precision Matters
Avoid entering trades too early or too large.
Place an “invalidation” point: if price violates the support zone with conviction, reduce or hedge exposure.
Never sell premium just because it’s “high”—sell where structure backs the trade.
📊 Discipline Trumps Direction
This strategy is valid only if risk is respected. The market doesn’t owe anyone consistency—but a structured, risk-controlled approach keeps you in the game long enough to see it.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Candle Metrics: BSP Guide🏛️ RESEARCH NOTES
Buying & Selling Pressure measures the internal dynamics within a candlestick that shapes the trends. It dissects each OHLC range into distinct components made of Body Range, Higher & Lower Wicks, making it possible to quantify bullish & bearish parts of bar range. BSP doesn’t just point direction, it reveals magnitude - how much buyers or sellers injected into the move, and whether that push is accelerating or running out of steam.
Unlike Average %Δ , which uses separate conditional averaging by "count", BSP processes candles through periodic averaging that makes it more responsive for important transitions like: divergence from volatility benchmarks. incentive change (spotting early reversals after impulsive move), filtering false breakouts, confirming trend strength, etc.
⚖️ Candle Metrics
Buying Pressure (BP)
Represents the degree of upward displacement relative to prior reference points.
🟢 Rising BP: Signals growing demand absorption and accumulation, often preceding sustained advances.
🟣 Falling BP: Indicates waning participation from buyers; persistent declines while price rises suggest trend fatigue and elevated risk of retracement.
Selling Pressure (SP)
Captures downward displacement relative to highs and prior closes.
🔴 Rising SP: Reflects heightened distribution activity, consistent with institutional supply or hedging flows.
🟡 Falling SP: Suggests sellers are withdrawing liquidity; commonly observed near troughs as downside momentum exhausts.
Average True Range (ATR) Rising ATR = higher volatility, falling ATR = calm markets. High BP in low ATR = stealth accumulation.
Body Range (BR) Large bodies show conviction, small bodies = indecision. Strong BR + rising BP = solid bullish trend.
Higher Wick (HW) Long HW means rejection at highs (supply). Falling HW means buyers are holding gains.
Lower Wick (LW) Long LW means rejection at lows (demand). Falling LW signals less defense from buyers.
Total Wicks (TW) More wick length = intrabar battles. Expansion of TW with small bodies often precedes reversals.
Average Wick (AW)
Rising AW = more volatility both ways. Falling AW = cleaner, directional trend.
Darkened Tops
Tracks the strongest side (BP or SP) over the lookback period. Its primary function is to dynamically highlight moments of extreme pressure. When either the Buying or Selling Pressure value reaches the level, the tops would . This provides an immediate visual cue for:
Black Colored Plot: A signal that the current buying or selling pressure has hit a significant level relative to recent history, often pointing to climactic activity or a potential exhaustion point.
◇ Practical Interpretation
Trend Confirmation BP ↑, SP ↓, BR ↑, ATR steady → sustainable directional advance.
Exhaustion BP ↓, SP steady or rising, HW ↑ = buyers tiring at resistance, overextended into supply.
Accumulation BP ↑, LW ↑, TW ↑ but ATR low = stealth buying before breakout.
Distribution SP ↑, HW ↑, TW ↑ = sellers unloading into strength. supply emerging into strength, caution warranted.
From Strength to Weakness: ETH Validates a Key Bearish PatternIntroduction (Market Context)
Ether Futures (ETH) and Micro Ether Futures (MET) have been at the center of market attention since April 2025, when prices staged a remarkable rally of more than +250%. This surge was not just a technical phenomenon—it came in the wake of major macro events such as Liberation Day and the reemergence of U.S. tariff policies under Donald Trump’s administration. Those developments sparked speculative flows into digital assets, with Ether acting as one of the prime beneficiaries of capital rotation.
Yet markets rarely move in one direction forever. After such a sharp rise, technical exhaustion often follows, and signs of that exhaustion are beginning to surface on ETH’s daily chart. Traders who enjoyed the rally now face a critical juncture: whether to protect gains or to consider new opportunities in the opposite direction. The key lies in a pattern that has appeared many times in history, often marking important reversals—the Rising Wedge.
What is a Rising Wedge?
A Rising Wedge is one of the most recognizable bearish reversal formations in technical analysis. It typically develops after a strong uptrend, where price continues to push higher but does so with diminishing momentum. On the chart, the highs and lows still point upward, but the slope of the highs is shallower than the slope of the lows, creating a narrowing upward channel.
The psychology behind the wedge is critical: buyers are still in control, but they are running out of strength with every push higher. Sellers begin to absorb demand more aggressively, and eventually, price breaks through the lower boundary of the wedge. This breakdown often accelerates as trapped buyers unwind positions.
From a measurement perspective, technicians project the maximum width of the wedge at its start, and then apply that distance downward from the point of breakdown. This projection offers a technical target for where price may gravitate in the following weeks. In the case of Ether Futures, that target points toward the 3,200 area, a level of strong technical interest and a logical area for traders to watch closely.
RSI and Bearish Divergence
Alongside the wedge, momentum indicators add further weight to the bearish case. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a widely used oscillator that measures momentum on a scale of 0 to 100. Values above 70 are generally interpreted as “overbought,” while values below 30 suggest “oversold.”
The most powerful signals often emerge not when RSI is at an extreme, but when it diverges from price action. A bearish divergence occurs when price sets higher highs while RSI forms lower highs. This is an indication that upward momentum is weakening even as price appears to climb.
Ether Futures have displayed this phenomenon clearly over the past few weeks. The daily chart shows four successive higher highs in price, yet RSI failed to confirm these moves, instead tracing a series of lower peaks. Notably, RSI pierced the overbought zone above 70 twice during this period, but momentum faded quickly after each attempt. This divergence is a classic early warning sign that a bullish run is running out of steam.
Forward-Looking Trade Idea
With the Rising Wedge breakdown and RSI divergence in place, a structured trade plan emerges. Futures traders can express this view through either the standard Ether Futures contract (ETH) or its smaller counterpart, the Micro Ether Futures contract (MET).
Contract Specs & Margins
Ether Futures (ETH): Notional = 50 Ether, Tick size = 0.50, Tick value = $25.00, Initial margin ≈ $68,800 (subject to CME updates).
Micro Ether Futures (MET): Notional = 0.1 Ether, Tick size = 0.50, Tick value = $0.05, Initial margin ≈ $140 (subject to CME updates).
Trade Plan (Bearish Setup)
Direction: Short
Entry: 4,360
Target: 3,200
Stop Loss: 4,702 (coinciding with a minor resistance level)
Reward-to-Risk Ratio: ≈ 3.39 : 1
The projected wedge target around 3,200 is not only a measured move from the pattern but also sits close to a previously established UFO support zone. While anecdotal, this confluence reinforces the credibility of the level as a potential magnet for price.
Risk Management
Regardless of how compelling a technical setup may appear, the most decisive factor in trading remains risk management. Defining risk in advance ensures that losses are limited if the market behaves unexpectedly. In this case, placing the stop at 4,702 not only keeps risk under control but also aligns with a minor resistance level, making the trade plan technically coherent.
Position sizing also plays a crucial role. The availability of Micro Ether Futures (MET) allows traders to participate with significantly reduced capital requirements compared to the full-sized ETH contract. This flexibility makes it easier to fine-tune exposure and manage account risk more precisely.
Equally important is the discipline of adhering to precise entries and exits. Chasing a trade or ignoring pre-defined stop levels can erode the edge provided by technical analysis. Markets often deliver multiple opportunities, but without sound risk management, traders may not survive long enough to benefit from them. Ultimately, capital preservation is the foundation on which consistent performance is built.
Closing
Ether’s spectacular rally since April 2025 is a reminder of the asset’s ability to deliver explosive moves under the right conditions. Yet history shows that parabolic advances rarely continue uninterrupted. The combination of a Rising Wedge breakdown and a confirmed RSI divergence provides strong evidence that the current uptrend is losing momentum, and the market may be entering a corrective phase.
For traders, this is less about predicting the future and more about recognizing when probabilities align in favor of a defined setup. With clear entry, target, and stop levels, the ETH and MET contracts offer a structured opportunity for those willing to take a bearish stance while managing their risk appropriately.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
one of the applications of RSIRSI as an indicator can be used in several ways ,
RSI is almost mirror image of the price ,
if we convert a candle stick chart into a line chart ,
and we hide which is RSI plotting and which is price plotting ,
it is difficult to identify which one is which...
But there are times where RSI due to it formula creates
divergence and confluences with prices, and there are
many articles and tutorials to explain those aspects of RSI
Motive of this article :
To see RSI as tool for range bound trading , and shape our next trade ideas using this
possibility .
After working with RSI extensively , all what I can say is RSI can be treated
almost similar with all the treatments which we can have over the price chart ,
for example : we can apply head & shoulders / cup&handle etc ... concept(s) on rsi ditto same as we do on price chart. so decoding RSI isn't just limited to divergences ...
One of such use-cases which I have been using about RSI is in range-bound trading,
if we can have a price range or a parallel channel , you can observe that either price
goes side-ways or gets reversed as per the RSI in the respective timeframe ...
here we are taking two channels ( a channel within a channel )
1w candles , and 1D candles .. and you can see RSI going from 30 to 70 to 30 to 70 ,
all alongwith the boundaries of the price range in either 1w or 1d channels ...
Just two images and it is clearly visible what we are discussing here ,
1w candles : see the candles having a range of channel and rsi also behaving in same way between 70-30 levels :
1d candles : see the candles having a range of channel and rsi also behaving in same way between 70-30 levels :
So the whole logic over here is , if in case we can make out a range bound behaviour ,
or a price range in channels , then we can align our next trade idea in accordance
with the RSI behaviour i.e.
if it is around 70 levels in 1D timeframe , then we can try to observe if there is any chart pattern or price action which is showing a sell side trade ...
and if it is around 30 levels in 1D timeframe , then we can try to observe if there a buy side trade based on price action / or chart patterns . . .
same goes with 1W candles ....
( I am not focussing on 1M because it becomes very much slow process and we always have lots of scrips to trade with on D and W basis .. so omitting it for M candles ... but i am much much sure this can work with M candles as well ... )
Now one of the aspect is to check whether there is an alignment of RSI on both timeframes D & W , if both time frames are having rsi around 30 , and the prices are range bound in both timeframes ... we can have a much much high conviction on buy-side or the trade ....
And at last please note three things about RSI which i have observed and discovered
while talking with lots of fellow trades ....
1) RSI follows CLOSE prices , and not the wicks ( high and low ) so while detecting divergences consider the close price and now the high or low ..
2) RSI hitting 70 is not an assurance of prices reversing , it can either reverse or just go side-ways .... RSI at any level 70 or 30 is not an guarantee of " Price reversal "
3) RSI can remain above 70 for a much much time period than usual expectation, and RSI can remain below 30 for much much time ... there are index charts which shows this ...
Bonus point : read some where from a veteran of the market , prices can remain irrational for a longer period of time , just make sure you remain solvent till then ...
happy investing and joyful trading wishes to all
Deep Dive Into Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)🗓 The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is one of the most popular momentum indicators in technical analysis. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding how the MACD works can significantly enhance your trading decisions.
📚 Introduction: What Is MACD and Why It Matters
The MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is one of the most powerful and widely used momentum indicators in technical analysis. It was developed by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s and has since become a staple in the toolkit of traders and investors across markets — from stocks and forex to cryptocurrencies.
At its core, MACD helps traders understand the relationship between two moving averages of an asset’s price, providing insight into both trend direction and momentum strength. By analyzing how these averages converge and diverge, the indicator offers valuable signals for entries, exits, and trend reversals.
What makes MACD especially popular is its versatility — it works well in trending markets, can be used across all timeframes, and combines both leading and lagging components. Whether you're a day trader or a long-term investor, understanding how MACD works gives you an edge in making timely and informed trading decisions.
📚 How the MACD Is Calculated: The Components Explained
The MACD is built from three core components: MACD line, Signal line and MACD histogram.
🔹 Calculating the MACD Line:
The MACD line is the difference between two Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs), typically 12-period EMA (fast) and 26-period EMA (slow). The formula is:
MACD Line = EMA(12) − EMA(26)
This line captures momentum by tracking how the shorter-term average diverges from the longer-term average. When the MACD line rises, the short-term momentum is increasing faster than the longer-term trend — a sign of bullish acceleration. The reverse implies bearish momentum.
🔹 Calculating the Signal Line:
To reduce noise and provide clearer signals, a 9-period EMA of the MACD line is plotted on top. This is the Signal Line, and it acts as a trigger:
When the MACD line crosses above the signal line → bullish signal (buy)
When the MACD line crosses below the signal line → bearish signal (sell)
Signal Line = EMA(9)(MACD Line)
🔹 Calculating the MACD Histogram:
The Histogram shows the difference between the MACD Line and the Signal Line:
Histogram = MACD Line − Signal Line
It provides a visual representation of momentum strength. The histogram bars expand when momentum strengthens and contract as it fades. It helps you spot shifts in momentum earlier than a basic crossover.
📚 How to Use MACD in Trading Strategies
⚡️MACD Signal Line Crossover
Buy Signal:
MACD Line crosses above the Signal Line from below (bullish crossover)
Preferably when both lines are below the zero line (early in the trend)
Price closes above the long-term trend approximation, in our case we use 200-period EMA
Sell Signal:
MACD Line crosses below the Signal Line from above (bearish crossover)
Preferably when both lines are above the zero line (early in the trend)
Price closes below the long-term trend approximation, in our case we use 200-period EMA
📈Long Trading Strategy Example
1. Wait until MACD line crosses over the Signal line from down to up. In our example we use 1D time frame for BITMART:BTCUSDT.P . Open long trade if point 2 will be completed.
2. Price candle shall be closed above the 200-period EMA. This is long-term trend filter to increase the probability that trades will be open only in the direction of the main trend.
3. Close the long trade when the MACD line crosses under the Signal line. This is an approximation that short-term impulse is over and correction is about to start.
In our case we have +20% return on this long trade, but, please, notice that we have not used initial stop-loss in this strategy. Trade was closed according to the technical condition, this approach can violate the risk management rules, but also can be applicable if you trade the amount ready to lose using this strategy. We will talk about stop-loss later.
📉Short trading strategy example
1. Wait until MACD line crosses under the Signal line from up to down. In our example we use 1D time frame for BITMART:ETHUSDT . Open short trade if point 2 will be completed.
2. Price candle shall be closed below the 200-period EMA. This is long-term trend filter to increase the probability that trades will be open only in the direction of the main trend.
3. Close the short trade when the MACD line crosses over the Signal line. This is an approximation that short-term impulse is over and correction is about to start.
In this case we have +15% return on the short trade. Again, strategy used the technical condition to close the trade and now let's cover how to place the stop-loss. There is no right answer how to use stop-losses. The first and the most obvious way to place stop-loss is using recent swing low/high, but the problem is that all traders are seeing them and do the same. Price tends to reach such levels to collect liquidity.
Another one way to place stop-loss is using the signal candle's high/low. This is so-called 1 candle stop-loss. Usually it's very tight and can allow to have the fantastic risk to reward ratio, but we are now recommend to use it if you are not a professional trader because win rate of such strategy decreases.
Third approach in placing stop-loss which we often use in our algorithmic strategies is the Average True Range (ATR). ATR is the volatility measurement, it allows to take into account the current volatility. Sometimes it helps to avoid the stop-loss hit when trade finally goes in your direction. You can just simply subtract (in case of long trade) or add (in case of short trade) ATR value to the entry price and obtain the dynamic stop loss based on current market condition. Also multiplier can be used for ATR. You shall choose the approach which is more comfortable for you, backtest all these approached to make your choice.
🧪Important: we used the long signals only below the zero-line and short signals above it in the attempt to catch the beginning of a trend and have large potential move. On the picture below you can see the same BITMART:BTCUSDT.P , but what will happen if we open long on the lines crossover above zero line? This trade will not be profitable because of restricted potential.
⚡️MACD Zero Line Crossover
Buy Signal:
MACD Histogram crosses above the zero line (momentum shifts from bearish to bullish)
Price closes above the long-term trend approximation, in our case we use 200-period EMA
Sell Signal:
MACD Histogram crosses below the zero line (momentum shifts from bullish to bearish)
Price closes below the long-term trend approximation, in our case we use 200-period EMA
📈Long Trading Strategy Example
1. Wait until MACD Histogram crosses over zero line. Open long trade if point 2 will be completed.
2. Price candle shall be closed above 200-period EMA. This is long-term trend filter to increase the probability that trades will be open only in the direction of the main trend.
3. Take profit when price reaches 3:1 risk to reward ratio according to the stop-loss from point 4.
4. Stop-loss shall be placed below recent swing low. This point can be discussed, you can use any stop-loss technique described earlier in this article. We demonstrate the simplest one, the key here is using at least 3:1 RR.
📉Short trading strategy example
1. Wait until MACD Histogram crosses under zero line. Open short trade if point 2 will be completed.
2. Price candle shall be closed below 200-period EMA. This is long-term trend filter to increase the probability that trades will be open only in the direction of the main trend.
3. Take profit when price reaches 3:1 risk to reward ratio according to the stop-loss from point 4.
4. Stop-loss shall be placed above recent swing high. This point can be discussed, you can use any stop-loss technique described earlier in this article. We demonstrate the simplest one, the key here is using at least 3:1 RR.
⚡️MACD Divergence Strategy
MACD Divergence is a strategy that helps traders identify potential reversals in market direction before they become obvious on the price chart. This makes it a favorite tool among swing traders and crypto enthusiasts looking to catch major moves early.
But what exactly is a divergence? In simple terms, divergence occurs when price and momentum (MACD) are moving in opposite directions — signaling that the current trend may be losing strength and preparing for a reversal. There are two main types of divergence.
🐂 Bullish Divergence
Price makes a lower low
MACD Histogram makes a higher low
This suggests that while price is still falling, downward momentum is weakening. The bears are losing control, and a bullish reversal may be near. Trading signal is very simple, when bullish divergence happens wait for the first increasing column on MACD histogram and open long trade. Place stop-loss under recent swing low and take profit at 3:1 RR.
🐻Bearish Divergence
Price makes a higher high
MACD makes a lower high
This suggests that while price is still falling, downward momentum is weakening. The bears are losing control, and a bullish reversal may be near. Trading signal is very simple, when bearish divergence happens wait for the first decreasing column on MACD histogram and open short trade. Place stop-loss above recent swing high and take profit at 3:1 RR.
🧪 Important hint: MACD histogram shall cross the zero line between two lows/high to create the most reliable divergence signals. We are not recommend to use it without zero-line crossover to decrease number of false signals.
📈Long Trading Strategy Example
1. MACD Histogram shall create higher low.
2. Price shall create lower low.
3. MACD Histogram shall cross the zero line between lows.
4. MACD Histogram shall show the first increasing column.
5. Put stop-loss under the recent swing low.
6. Put take profit at 3:1.
🧪 You can enhance the long signal with the MACD Line divergence. In our case we have both divergences: with MACD Histogram and MACD Line.
📉Short trading strategy example
1. MACD Histogram shall create lower high.
2. Price shall create higher high.
3. MACD Histogram shall cross the zero line between lows.
4. MACD Histogram shall show the first decreasing column.
5. Put stop-loss above the recent swing high.
6. Put take profit at 3:1.
🧪Divergence is extremely strong signal, but when price continue it's move in the direction of a trend and it's not reversing it can also be the signal for the trend continuation. This situation is called "Baskerville Hound" signal, this name was given by famous trader Alexander Elder. We don't recommend to use it for novice traders, but it's useful to know about it.
📚 Conclusion
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is more than just a crossover tool — it's a powerful momentum indicator that offers deep insight into the strength, direction, and timing of market trends. By understanding how the MACD line, Signal line, and Histogram interact, traders can uncover early trend shifts, spot momentum divergences, and time entries and exits with greater confidence.
Whether you're a short-term trader using fast crossovers for scalping or a long-term investor watching for weekly divergences, MACD can adapt to your style when used thoughtfully. Like all indicators, it works best when combined with price action, support/resistance levels, and other indicators — not in isolation.
Ultimately, mastering MACD is not about memorizing patterns, but about learning to read the story of momentum that unfolds beneath the surface of price. With disciplined application and practice, MACD can become a reliable compass in your trading strategy.
Mastering the RSI - How to use it in trading?What will be discussed?
- What is the RSI?
- RSI overbought
- RSI oversold
- RSI divergences
- How to use the RSI
- How to trade with the RSI
What is the RSI?
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a popular momentum oscillator used in technical analysis to measure the speed and change of price movements. Developed by J. Welles Wilder Jr., it ranges from 0 to 100 and helps traders evaluate whether a security is overbought or oversold. The RSI typically uses a 14-period timeframe and is calculated based on the average gains and losses over that period. A rising RSI suggests increasing buying momentum, while a falling RSI indicates growing selling pressure.
RSI overbought
When the RSI rises above 70, the asset is generally considered overbought. This condition indicates that the price may have risen too quickly and could be due for a correction or pullback. However, being overbought doesn't automatically mean a reversal will occur, it signals that bullish momentum is strong, and traders should be cautious of potential trend exhaustion.
RSI oversold
Conversely, an RSI reading below 30 is typically seen as a sign that the asset is oversold. This condition suggests the price may have fallen too sharply and could be primed for a rebound. Just like with the overbought condition, an oversold RSI doesn’t guarantee an immediate reversal but serves as a warning that bearish momentum may be overextended.
RSI divergences
Divergences occur when the RSI and the price of the asset move in opposite directions. A bullish divergence happens when the price makes a lower low, but the RSI forms a higher low, potentially signaling a reversal to the upside. A bearish divergence occurs when the price makes a higher high, but the RSI creates a lower high, possibly indicating a downward reversal. Divergences are often used to spot early signs of trend changes.
How to use the RSI?
To use the RSI effectively, traders typically look for overbought and oversold conditions to time entries and exits, combine it with other technical indicators for confirmation, and watch for divergences as a sign of potential reversals. RSI can also be adapted for different timeframes or strategies, depending on whether the trader is looking for short-term swings or long-term trend analysis. While it’s a powerful tool, RSI should not be used in isolation, it works best as part of a broader trading plan that considers market context and risk management.
How to trade with the RSI?
The RSI can be a powerful tool for identifying potential trade setups. When the price approaches a key support zone while the RSI remains in overbought territory, this may signal an early warning of a possible market reversal. However, rather than acting immediately, it's wise to wait for confirmation. A clear candlestick reversal pattern, such as a bullish engulfing candle or a pin bar, a provide stronger evidence that momentum is shifting. By combining RSI readings with price action and support levels, traders can improve the accuracy and timing of their entries.
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
Thanks for your support.
- Make sure to follow me so you don't miss out on the next analysis!
- Drop a like and leave a comment!
Example of how to draw a trend line using the StochRSI indicator
Hello, traders.
If you "Follow", you can always get new information quickly.
Have a nice day today.
-------------------------------------
We use the StochRSI indicator to draw a trend line.
We draw a trend line by connecting the peaks of the StochRSI indicator, i.e. the K line, when they are created in the overbought area or when they are created in the overbought area.
That is, when the K line of the StochRSI indicator forms a peak in the overbought area, the trend line is drawn by connecting the Open values of the falling candles.
If the candle corresponding to the peak of the StochRSI indicator is a rising candle, move to the right and use the Open value of the first falling candle.
When drawing the first trend line, draw it from the latest candle.
Since the third trend line indicates a new trend, do not draw anything after the third trend line.
The currently drawn trend line corresponds to the high-point trend line.
-
Therefore, you should also draw the low-point trend line.
The low-point trend line is drawn by connecting the K line of the StochRSI indicator when the top is formed in the oversold zone.
The low-point trend line uses the low value of the candle when the K line of the StochRSI indicator forms the top in the oversold zone.
That is, it doesn't matter whether the candle is a bearish candle or a bullish candle.
The drawing method is the same as when drawing the high-point trend line, drawing from the latest candle.
The top of the best K line of the StochRSI indicator was not formed within the oversold zone.
(The top is indicated by the section marked with a circle.)
Since the trend line was not formed, the principle is not to draw it.
If you want to draw it and see it, it is better to display it differently from the existing trend line so that it is intuitively different from the existing trend line.
-
The chart below is a chart that displays the trend line drawn separately above as a whole.
It is also good to distinguish which trend line it is by changing the color of the high-point trend line and the low-point trend line.
The chart below is a chart that distinguishes the high-point trend line in blue (#5b9cf6) and the low-point trend line in light green (#00ff00).
The low-point trend line is a line drawn when the trend has changed, so it does not have much meaning, but it still provides good information for calculating the volatility period.
-
To calculate the volatility period, support and resistance points drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts are required.
However, since I am currently explaining how to draw a trend line, it is only drawn on the 1M chart.
-
I use the indicators used in my chart to indicate support and resistance points.
That is, I use the DOM(60), DOM(-60), HA-Low, HA-High, and OBV indicators to indicate support and resistance points.
Since the DOM(-60) and HA-Low indicators are not displayed on the 1M chart, I have shown the 1W chart as an example.
The indicators displayed up to the current candle correspond to the main support and resistance points.
Although it is not displayed up to the current candle, the point where the horizontal line is long is drawn as the sub-support and resistance point.
It is recommended to mark them separately to distinguish the main support and resistance point and the sub-support and resistance point.
The trend line drawn in this way and the support and resistance points are correlated on the 1D chart and the volatility period is calculated.
(For example, it was drawn on the 1M chart.)
The sections marked as circles are the points that serve as the basis for calculating the volatility period.
That is,
- The point where multiple trend lines intersect
- The point where the trend line and the support and resistance points intersect
Select the point that satisfies the above cases at the same time to display the volatility period.
When the point of calculating the volatility period is ambiguous, move to the left and select the first candle.
This is because it is meaningless to display it after the volatility period has passed.
If possible, the more points that are satisfied at the same time, the stronger the volatility period.
If the K-line peak of the StochRSI indicator is formed outside the overbought or oversold zone, it is better to exclude it when calculating the volatility period.
-
The chart below is a chart drawn on a 1D chart by summarizing the above contents.
The reason why there are so many lines is because of this reason.
For those who are not familiar with my charts, I have been simplifying the charts as much as possible these days.
However, when explaining, I have shown all the indicators to help you understand the explanation.
-
Thank you for reading to the end.
I hope you have a successful trade.
--------------------------------------------------
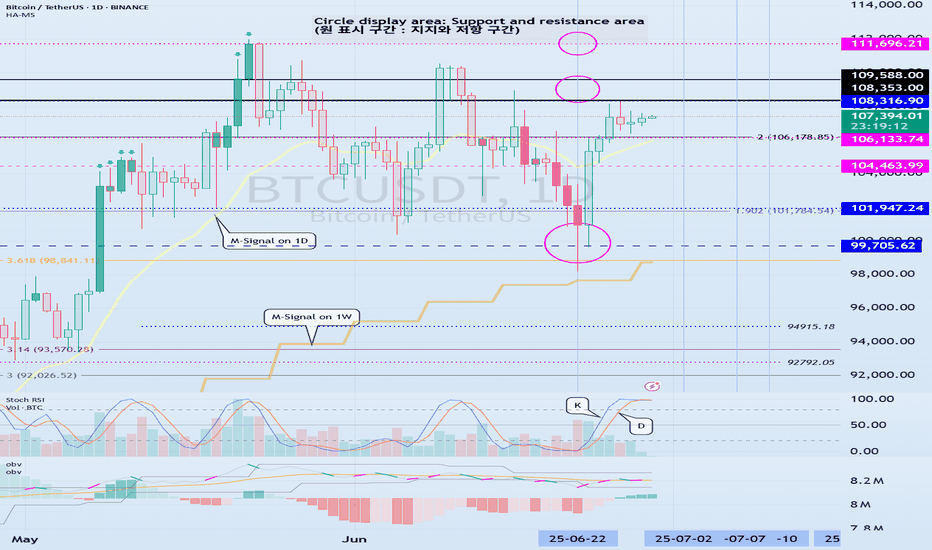
StochRSI indicator and support and resistance levels
Hello, traders.
If you "follow" me, you can always get the latest information quickly.
Have a nice day today.
-------------------------------------
The StochRSI indicator on the left chart is slightly different from the StochRSI indicator on the right.
The StochRSI indicator on the left chart is the StochRSI indicator provided by default in TradingView, and the StochRSI indicator on the right chart is an indicator with a modified formula.
The StochRSI indicator is a leading indicator that is reflected almost in real time.
Therefore, it reacts sensitively to price changes.
Although it is advantageous because it reacts sensitively, it also increases the possibility of being caught in a fake, so I thought that a slight delay(?) was necessary, and so I created the StochRSI indicator on the left chart.
If you look at the relationship between the K and D of the StochRSI indicators on the two charts, you can see that there is a big difference.
In the end, you can predict the movement by checking whether the movement of the K line has escaped the overbought or oversold section.
However, I think that you will receive information that can determine the sustainability of the trend depending on the positional relationship between K and D.
Therefore, it is important to distinguish the inflection points that occur in the StochRSI indicator.
This is because these inflection points provide important information for drawing trend lines.
Therefore, the StochRSI indicator on the left chart, which better expresses the inflection point, is being used to draw the trend line.
(Unfortunately, this indicator was not registered on TradingView because I did not explain it well.)
-
As a new candle was created, the StochRSI indicator on the left chart is showing an inflection point on the K line.
The StochRSI indicator on the right chart is showing a transition to a state where K < D.
We will have to check whether the inflection point was created only when today's candle closes, but I think that the fact that it is showing this pattern means that there is a high possibility of a change in the future trend.
Since the next volatility period is expected to start around July 2nd (July 1st-3rd), I think it has started to show meaningful movements.
-
It is true that you want to buy at the lowest price possible and sell at the highest price.
However, because of this greed, one mistake can lead to a loss that can overturn nine victories, so you should always be careful.
Therefore, if possible, it is better to check for support and respond.
In that sense, I think it is worth referring to the relationship between K and D of the StochRSI indicator on the left chart.
This is because the actual downtrend is likely to start when K < D.
-
In order to check for support, you definitely need support and resistance points drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts.
Ignoring this and checking for support at the drawn support and resistance points can result in not being able to apply the chart you drew to actual trading.
Therefore, you should draw support and resistance points first before starting a trade.
Otherwise, if you draw support and resistance points after starting a trade, you are more likely to set support and resistance points that reflect your subjective thoughts, so as I mentioned earlier, you are more likely to lose faith in the chart you drew.
If this phenomenon continues, it will eventually lead to leaving the investment market.
-
It is important to determine whether there is support by checking the correlation between the StochRSI indicator and other indicators at the support and resistance points drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts.
Even if the inflection point of the StochRSI indicator or other indicators occurs at a point other than the support and resistance points you drew, you should consider it as something that occurred beyond your ability to handle.
In other words, you should observe the price movement but not actually trade.
As I mentioned earlier, if you start to violate this, you will become less and less able to trust the chart you drew.
-
Accordingly, the basic trading strategy I suggest is to buy near the HA-Low indicator and sell near the HA-High indicator.
However, since the HA-Low and HA-High indicators are expressed as average values, they may move in the opposite direction to the basic trading strategy.
In other words, if the HA-Low indicator is resisted and falls, there is a possibility of a stepwise downward trend, and if the HA-High indicator is supported and rises, there is a possibility of a stepwise upward trend.
Therefore, the basic trading strategy mentioned above can be considered a trading strategy in the box section.
In the case of deviating from this box section, it is highly likely to occur before and after the volatility period indicated by the relationship between the trend line using the StochRSI indicator mentioned above and the support and resistance points drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts.
Therefore, special care is required when conducting new transactions during the volatility period.
This is because there is a high possibility of being caught in a fake when trading during the volatility period.
-
The DOM(60) and DOM(-60) indicators are good indicators to look at together with the HA-Low and HA-High indicators.
The DOM indicator is an indicator that comprehensively evaluates the DMI, OBV, and MOMENTUM indicators.
Therefore, the DOM(60) indicator is likely to be at the end of the high point range, and the DOM(060) indicator is likely to be at the end of the low point range.
In the explanation of the HA-Low and HA-High indicators,
- I said that if the HA-Low indicator receives resistance and falls, there is a possibility that a stepwise downtrend will begin,
- and if the HA-High indicator receives support and rises, there is a possibility that a stepwise uptrend will begin.
In order for an actual stepwise downtrend to begin, the price must fall below DOM(-60), and in order for a stepwise uptrend to begin, it must rise above DOM(60).
In other words, the DOM(-60) ~ HA-Low section and the HA-High ~ DOM(60) section can be seen as support and resistance sections.
-
If these correlations start to appear, I think you will be able to create a trading strategy that fits your investment style without being swayed by price volatility and proceed with trading.
The reason for analyzing charts is to trade.
Therefore, the shorter the time for chart analysis, the better, and you should increase the start of creating a trading strategy.
-
Thank you for reading to the end.
I hope you have a successful trade.
--------------------------------------------------
Skeptic | RSI Masterclass: Unlock Pro-Level Trading Secrets!Hey traders, it’s Skeptic ! 😎 Ready to transform your trading? 95% of you are using the Relative Strength Index wrong , and I’m here to fix that with a game-changing strategy I’ve backtested across 200+ trades. This isn’t a generic RSI tutorial—it’s packed with real-world setups, myth-busting insights, and precise rules to trade with confidence. Join me to master the art of RSI and trade with clarity, discipline, and reason. Big shoutout to TradingView for this epic free tool! 🙌 Let’s dive in! 🚖
What Is RSI? The Core Breakdown
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) , crafted by Welles Wilder, is a momentum oscillator that measures a market’s strength by comparing average gains to average losses over a set period. Here’s the formula:
G = average gains over n periods, L = average losses.
Relative Strength (RS) = | G / L |.
RSI = 100 - (100 / (1 + RS)).
Wilder used a 14-period lookback , and I stick with it—it’s smooth, filters noise, and gives a crystal-clear read on buyer or seller momentum. Let’s get to the good stuff—how I use RSI to stack profits! 📊
My RSI Strategy: Flipping the Script
Forget what you’ve read in books like The Handbook of Technical Analysis by Mark Andrew Lim— overbought (70) and oversold (30) aren’t just for shorting or buying. I go long when RSI hits overbought, and it’s been a goldmine. I’ve backtested over 200 trades with this approach, and it’s my go-to confirmation for daily setups. Why does it work? When RSI hits overbought on my 15-minute entry chart, it signals explosive buyer momentum. Here’s what you get:
Lightning-Fast R/R: I hit risk/reward targets in 30 minutes to 2 hours on 15-minute entries (longer for 1-hour entries, depending on your timeframe).
Massive R/R Potential: An overbought RSI on 15-minute can push 1-hour and 4-hour RSI into overbought, driving bigger moves. I hold for R/Rs of 5 or even 10, not bailing early. 🚀
Rock-Solid Confirmation: RSI confirms my entry trigger. Take BTC/USD:
BTC bounces off a key support at 76,000, sparking an uptrend.
It forms a 4-hour box range, but price tests the ceiling more than the floor, hinting at a breakout.
Trigger: Break above the box ceiling at 85,853.57.
On 15-minute, a powerful candle breaks the ceiling, and RSI hits overbought—that’s my green light. I open a long.
Soon, 1-hour and 4-hour RSI go overbought, signaling stronger momentum. I hold, and BTC pumps hard, hitting high R/R in a short window.
This keeps trades fast and efficient—quick wins or quick stops mean better capital management and less stress. Slow trades? They’re a mental grind, pushing you to close early for tiny R/Rs. 😴
Pro Rules for RSI Success
Here’s how to wield RSI like a trading weapon:
Stick to the Trend : Use RSI in the direction of the main trend (e.g., uptrend = focus on longs).
Confirmation Only: Never use RSI solo for buy/sell signals. Pair it with breakouts or support/resistance triggers.
Fresh Momentum: RSI is strongest when it just hits overbought/oversold. If the move’s already rolling, skip it—no FOMO, walk away!
Customize Zones: Overbought (70) and oversold (30) can shift—it might show reactions at 65 or 75. Adjust to your market’s behavior.
Backtesting RSI: Your Path to Mastery
To make RSI yours, backtest it across at least 30 trades in every market cycle— uptrend, downtrend, and range. Test in volatile markets for extra edge. 😏 Key takeaways:
Range Markets Kill RSI: Momentum oscillators like RSI (or SMA) are useless in ranges—no momentum, no signal. Switch to ROC (Rate of Change) for ranges—I use it, and it’s a beast. Want an ROC guide? Hit the comments!
Overextended RSI Zones: On your entry timeframe (e.g., 15-minute), check higher timeframes (e.g., 4-hour) for past RSI highs/lows. These are overextended zones—price often rejects or triggers a range. Use them to take profits.
Final Vibe Check
This RSI masterclass is your key to trading like a pro—fast R/Rs, big wins, and unshakable confidence . At Skeptic Lab, we live by No FOMO, no hype, just reason. Guard your capital— max 1% risk per trade, no excuses. Want an ROC masterclass or more tools? Drop a comment! If this fired you up, smash that boost—it means everything! 😊 Got a setup or question? Hit me in the comments. Stay sharp, fam! ✌️
Best Free Volatility Indicator on TradingView for Gold Forex
This free technical indicator will help you easily measure the market volatility on Forex, Gold or any other market.
It will show you when the market is quiet , when it's active and when it's dangerous .
We will go through the settings of this indicator, and you will learn how to set it up on TradingView.
Historical Volatility Indicator
This technical indicator is called Historical Volatility.
It is absolutely free and available on TradingView, MetaTrader 4/5 and other popular trading terminals.
TradingView Setup
Let me show you how to find it on TradingView and add it to your price chart.
Open a technical price chart on TradingView and open the "Indicators" menu (you will find it at the top of the screen).
Search "Historical Volatility" and click on it.
It will automatically appear on your chart.
"Length" parameter will define how many candles the indicator will take for measuring the average volatility. (I recommend keeping the default number, but if you need longer/shorter-term volatility, you can play with that)
Timeframe drop-down list defines what time frame the indicator takes for measuring the volatility. (I recommend choosing a daily timeframe)
And keep the checkboxes unchanged .
How to Use the Indicator
Now, let me show you how to use it properly.
Wider the indicator and analyse its movement at least for the last 4 months.
Find the volatility range - its low levels will be based on the lower boundary of the range, high levels will be based on its upper boundary.
This is an example of such a range on USDCAD pair.
When the volatility stays within the range, it is your safe time to trade.
When volatility approaches its lows, it may indicate that the market might be slow .
Highs of the range imply that the market is very active
In-between will mean a healthy market.
The Extremes
The violation of a volatility range to the downside is the signal that the market is very slow . This would be the recommended period to not trade because of high chance of occurrence of fakeouts.
An upward breakout of a voliatlity range is the signal of the extreme volatility . It will signify that the market is unstable , and it will be better to let it calm down before placing any trade.
Volatility Analysis
That is how a complete volatility analysis should look.
At the moment, volatility reached extreme levels on CADJPY pair.
The best strategy will be to wait till it returns within the range.
Remember This
With the current geopolitical uncertainty and trade wars, market volatility reaches the extreme levels.
Such a volatility is very dangerous , especially for newbie traders.
Historical volatility technical indicator will help you to easily spot the best period for trading and the moment when it is better to stay away.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
Altcoins in Focus: Aptos, KAIA, and Ravencoin (RVN)Amid Bitcoin’s rapid growth and renewed interest in Ethereum, investors are increasingly turning their attention to altcoins—alternative cryptocurrencies showing strong potential for sharp gains. As of early June 2025, Aptos (APT), KAIA, and Ravencoin (RVN) stand out for their price surges and growing interest from major exchanges and analysts.
Aptos, a next-generation blockchain platform developed by former Meta (ex-Diem) engineers, has secured its place among the top 50 by market cap. In recent days, the token broke through a resistance level at $9.20, signaling a possible continuation of the uptrend. Its appeal lies in its scalability and its unique MoveVM architecture, which makes it attractive for developers in DeFi and NFT applications.
KAIA, a new token in the AI and metaverse ecosystem, gained over 15% this week following a Binance listing and integration with several major Web3 projects. Investors see KAIA as a potential “new Render,” focusing on neural computation and digital identity infrastructure.
Ravencoin (RVN), a long-time presence in the crypto space, is regaining popularity. With its focus on asset tokenization and copyright protection on the blockchain, RVN surged 14% after announcing partnerships with several independent music platforms.
The rise of these altcoins demonstrates that there is room in the crypto world not just for the giants, but also for innovative, purpose-driven projects capable of capturing market and user interest.
HA-RSI + Stochastic Ribbon: The Hidden Gem for Trend & MomentumNavigating volatile markets requires more than just raw price action. The Heikin Ashi RSI Oscillator blends the power of smoothed candlesticks with momentum insights to give traders a clearer picture of trend strength and reversals.
At Xuantify , we use the Heikin Ashi RSI Oscillator as a hybrid momentum and trend tool. While the indicator calculations are based on Heikin Ashi values to smooth out noise and better capture trend dynamics, the chart itself displays standard candlesticks (real price data) . This ensures that all signals are aligned with actual market structure, making it easier to execute trades with confidence and clarity.
This dual-layer approach gives us the best of both worlds: clarity from smoothing and precision from real price action. MEXC:SOLUSDT.P
🧠 How We Use It at Xuantify
At Xuantify , we integrate the Heikin Ashi RSI Oscillator into our multi-layered strategy framework. It acts as a trend confirmation filter and a momentum divergence detector , helping us avoid false breakouts and time entries with greater precision. We pair it with volume and volatility metrics to validate signals and reduce noise. Note the Stochastic Ribbon Overlay as shown in the chart, very accurate for momentum.
⭐ Key Features
Heikin Ashi Smoothing : Filters out market noise for clearer trend visualization.
RSI-Based Oscillation : Measures momentum shifts with precision.
Color-Coded Bars : Instantly identify bullish/bearish momentum.
Dynamic Signal Zones : Customizable overbought/oversold thresholds.
Stochastic Ribbon Overlay : A powerful multi-line stochastic system that enhances momentum analysis and trend continuation signals.
💡 Benefits Compared to Other Indicators
Less Whipsaw : Heikin Ashi smoothing reduces false signals common in traditional RSI.
Dual Insight : Combines trend and momentum in one visual.
Better Divergence Detection : Easier to spot hidden and regular divergences.
Visual Simplicity : Clean, intuitive design for faster decision-making.
⚙️ Settings That Matter
RSI Length : Default is 14, but we often test 10 or 21 for different timeframes.
Smoothing Type : EMA vs. SMA – EMA reacts faster, SMA is smoother.
Overbought/Oversold Levels : 70/30 is standard, but 80/20 can reduce noise in trending markets.
📊 Enhancing Signal Accuracy
Combine with Volume Oscillators to confirm momentum strength.
Use Price Action Zones to validate oscillator signals.
Look for Divergences between price and oscillator for early reversal clues.
🧩 Best Combinations with This Indicator
MACD : For cross-confirmation of momentum shifts.
Bollinger Bands : To identify volatility squeezes and breakouts.
Support/Resistance Levels : For contextual trade entries and exits.
⚠️ What to Watch Out For
Lag in Strong Trends : Like all smoothed indicators, it may react slightly late.
Over-Optimization : Avoid curve-fitting settings to past data.
Standalone Use : Best used in conjunction with other tools, not in isolation.
🚀 Final Thoughts
The Heikin Ashi RSI Oscillator is a powerful hybrid tool that simplifies complex market behavior into actionable insights. At Xuantify, it’s a core part of our strategy toolkit, helping us stay ahead of the curve with clarity and confidence.
🔔 Follow us for more educational insights and strategy breakdowns!
We regularly share deep dives into indicators, trading psychology, and backtested strategies. Stay tuned and level up your trading game with us!
SMI vs. Stochastic: Which One Gives You the Edge?Momentum indicators are essential tools in every trader’s arsenal—but not all are created equal. While the Stochastic Oscillator has been a go-to for decades, the Stochastic Momentum Index (SMI) offers a more refined and reliable way to read market momentum.
In this post, we’ll break down the key differences between these two indicators, how we use them at Xuantify , and why the SMI might just give you the edge you’ve been looking for.
🧠 How We Use It at Xuantify
We’re always looking for tools that offer greater precision and less noise . While the Stochastic Oscillator is one of the most commonly used tools for spotting overbought and oversold conditions, the Stochastic Momentum Index (SMI) gives us a clearer, smoother view of momentum —especially in volatile or choppy markets.
We use the SMI to refine our entries and exits , particularly when trading breakouts or reversals. MEXC:ETHUSDT.P
⭐ Key Features
Stochastic Oscillator : Measures the closing price relative to the high-low range. Simple and responsive. Great for spotting short-term reversals.
Stochastic Momentum Index (SMI) : Measures the distance of the current close from the midpoint of the high-low range. Smoother and more centered around zero. Better at filtering out false signals.
💡 Benefits Compared to Other Indicators
Stochastic Oscillator vs. SMI:
Signal Smoothness: Moderate vs. High
Noise Filtering: Low vs. Excellent
Centered Oscillation: No vs. Yes (around 0)
Best Use Case: Range-bound markets vs. Trend shifts & momentum confirmation
False Signal Risk: Higher vs. Lower
The SMI is especially useful when you want to avoid whipsaws and get a more reliable read on momentum .
⚙️ Settings That Matter
Stochastic Oscillator : %K = 14, %D = 3
SMI : Length = 14, Signal Smoothing = 3, Double Smoothing = 3
You can adjust the SMI smoothing values to match the volatility of the asset— lower smoothing for fast markets , higher for slower ones.
📊 Enhancing Signal Accuracy
Enhance SMI signals by combining them with:
Trend filters like EMAs or Supertrend
Volume confirmation
Support/resistance zones
Divergence spotting for early trend reversals
This layered approach helps us avoid false positives and stay aligned with the broader trend .
🧩 Best Combinations with This Indicator
SMI + EMA Crossovers: Confirm momentum with trend direction
SMI + RSI Divergence: Spot early reversals with confluence
SMI + Volume Profile: Validate momentum near key price levels
⚠️ What to Watch Out For
Lag in fast markets: SMI’s smoothing can delay signals slightly
Over-optimization: Avoid excessive tweaking of parameters
Not ideal alone: Best used with confluence tools for confirmation
🚀 Final Thoughts
The Stochastic Oscillator is a classic for a reason—but the Stochastic Momentum Index is a refined evolution . We’ve found that SMI gives us cleaner signals , better momentum clarity , and fewer false alarms —especially when paired with smart filters.
If you're looking to upgrade your momentum toolkit , the SMI might just be your edge.
🔔 Follow us for more educational insights and strategy breakdowns!
We break down indicators, strategies, and market psychology to help you trade smarter—not harder.