A High-Impact Support Zone Meets a Breakout StructureIntroduction
Markets occasionally compress into areas where structure, momentum, and historical buying pressure align with surprising precision. When that compression occurs at a major higher-timeframe floor, traders often pay closer attention—not because the future is predictable, but because the chart reveals a location where price behavior typically becomes informative.
The current case study centers on a market pressing into a high-impact support zone visible on the monthly chart, while the daily chart displays a falling wedge pattern that has gradually narrowed the range of movement. This combination often highlights moments where the auction process is nearing a decision point. The purpose here is to dissect that confluence using multi-timeframe structure, pattern logic, and broad order-flow principles—strictly for educational exploration.
Higher-Timeframe Structure (Monthly)
The monthly chart shows price approaching a well-defined support area between 0.0065425 and 0.0063330, a region that has acted in the past as a base for significant reactions. These areas often develop because markets rarely absorb all buy interest in a single pass; pockets of unfilled orders may remain, leading to renewed reactions when price returns.
This type of zone does not guarantee a reversal. However, historically, when price reaches such levels, traders tend to monitor whether selling pressure slows or becomes less efficient. In this case, the structure suggests a recurring willingness from buyers to engage at these prices, forming a foundation that has held multiple swings.
The presence of a clear, higher-frame resistance at 0.0067530 anchors the broader range. When price rotates between such boundaries, the monthly context often acts as a roadmap: major support below, major resistance above, and room in between for tactical case-study exploration.
Lower-Timeframe Structure (Daily)
Shifting to the daily chart, price action has carved a falling wedge, a pattern often associated with decelerating downside movement. In wedges, sellers continue to push price lower, but with diminishing strength, as each successive low becomes less effective.
This type of compression structure can provide early evidence that the auction is maturing. Traders studying such patterns often watch for:
tightening of the range,
shorter waves into new lows,
initial signs that buyers are defending intraday attempts to drive price lower.
The daily wedge in this case sits directly on top of the monthly support zone—an alignment that strengthens its analytical relevance. The upper boundary of the wedge sits near 0.0065030, and a break above that line is often interpreted as price escaping the compression phase.
Multi-Timeframe Confluence
Multi-timeframe confluence arises when higher-frame structure provides the background bias and lower-frame patterns offer the tactical trigger. In this case:
The monthly chart signals a historically responsive support zone.
The daily chart shows structural compression and slowing downside momentum.
The interaction between them creates a scenario where educational case studies tend to focus on breakout behavior, as the daily timeframe may provide the first evidence that higher-frame buyers are engaging.
This confluence does not imply certainty. It simply highlights a location where structure tends to become more informative, and where traders often study the transition from absorption to response.
Order-Flow Logic (Non-Tool-Specific)
From an order-flow perspective, strong support zones typically develop where prior buying activity left behind unfilled interest. When price returns to that region, two things often happen:
Sellers begin to encounter difficulty driving price lower, as remaining buy orders absorb their activity.
Compression patterns form, as the market oscillates in a tightening range while participants test whether enough liquidity remains to cause a directional shift.
A breakout of the daily wedge represents a potential change in the auction dynamic. While sellers are still active inside the wedge, a breakout suggests their pressure may have become insufficient to continue the sequence of lower highs and lower lows. Traders studying market transitions often use such moments as part of hypothetical scenarios to understand how imbalances evolve.
Forward-Looking Trade Idea (Illustrative Only)
For educational purposes, here is how a structured case study could frame a potential opportunity using the discussed charts:
Entry: A hypothetical entry could be placed above the falling wedge, around 0.0065030, once buyers demonstrate the ability to break outside the compression structure.
Stop-Loss: A logical invalidation area in this case study would be at or below the monthly support, around 0.0063330, where failure would indicate the higher-timeframe zone did not hold.
Target: A purely structural wedge projection would suggest a target near 0.0067695, aligning closely with the broader resistance region on the monthly chart.
These price points yield a reward-to-risk profile that is measurable and logically linked to structure, though not guaranteed. This case study exists solely to illustrate how support-resistance relationships and pattern logic can be combined into a coherent, rules-based plan, not as an actionable idea for trading.
Yen Futures Contract Context
The larger (6J) and micro-sized (MJY) versions of this futures market follow the same underlying price but differ in exposure and margin scale. The standard contract generally carries a greater notional value and therefore translates each price movement into a larger monetary change. The micro contract mirrors the same structure at a reduced size, allowing traders to adjust position scaling more precisely when navigating major zones or breakout structures such as the one discussed in this case study:
6J equals 12,500,000 Japanese Yen per contract, making it suitable for larger, institutional players. (1 Tick = 0.0000005 per JPY increment = $6.25. Required Margin = $2,800)
MJY equals 1,250,000 Japanese Yen per contract, making it suitable for larger, institutional players. (1 Tick = 0.000001 per JPY increment = $1.25. Required Margin = $280)
Understanding margin requirements is essential—these products are leveraged instruments, and small price changes can result in large percentage gains or losses.
Risk Management Considerations
Strong support zones can attract interest, but risk management remains the foundation of any structured approach. Traders studying these transitions typically:
size positions relative to the distance between entry and invalidation,
maintain clear exit criteria when structure fails,
avoid adjusting stops unless the market has invalidated the original reasons for the plan,
adapt to new information without anchoring to prior expectations.
These principles emphasize the importance of accepting uncertainty. Even at major support zones, markets can remain volatile, and scenarios may unfold differently than anticipated.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Falling Wedge
What’s a Wedge Pattern?What's up traders! 👋
Wedge patterns are a powerful tool in technical analysis that can give you a heads-up about potential price moves. Whether you’re spotting a falling wedge or a rising wedge, these formations can reveal key signals about market direction.
What’s a Wedge Pattern?
A wedge pattern forms when price moves between two converging trendlines, creating a shape resembling a triangle. These patterns usually appear when the market is slowing down or consolidating before making a bigger move. Wedges can slope upwards or downwards, and the key difference lies in whether the trendlines are converging in an uptrend (rising wedge) or a downtrend (falling wedge).
Falling Wedge Pattern: Bullish Reversal 📈
The falling wedge pattern is a bullish reversal signal. This formation occurs when price moves between two downward-sloping trendlines, creating a series of lower highs and lower lows. The downward momentum weakens as the trendlines converge, indicating that sellers are losing strength, which sets up the potential for a bullish breakout.
How to Trade the Falling Wedge
Entry: Wait for the price to break above the upper trendline. This is your signal to enter long.
Target: Measure the height of the wedge at its widest point and project it upwards from the breakout point.
Stop Loss: Place it just below the most recent swing low to protect your position if the breakout doesn’t happen.
The chart illustrates a falling wedge pattern on the Bitcoin / Tether US pair with a 1-hour timeframe. Price action is contained within two converging downward-sloping trendlines, suggesting weakening bearish momentum. The breakout above the upper trendline signals a bullish reversal, and the subsequent uptick in price confirms the shift in momentum.
In rare cases, a breakout failure can lead to a bearish falling wedge pattern, but this scenario is less common. Keep an eye on the price action for signs of continued upward momentum.
Rising Wedge Pattern: Bearish Reversal 📉
The rising wedge pattern is a bearish reversal signal. This formation happens when price moves between two upward-sloping trendlines, creating higher highs and higher lows. The rising wedge indicates weakening buying pressure and a potential reversal to the downside.
How to Trade the Rising Wedge
Entry: Enter a short position once the price breaks below the lower trendline.
Target: Measure the height of the wedge and project it downward from the breakout point.
Stop Loss: Set it just above the most recent swing high to protect your trade.
Wedge Chart Pattern Trading: Key Tips ⚡
Context is everything when trading wedge patterns. If a bullish wedge pattern appears in an uptrend, it’s more likely to break to the upside. If a bearish wedge shows up in a downtrend, expect a breakdown.
Here are a few quick tips to improve your wedge trading pattern game:
Trendlines are key: Ensure your trendlines are drawn accurately. Properly drawn trendlines lead to better trades.
Breakout confirmation: Confirm breakouts with increased volume and, ideally, by checking for confluence with other indicators like RSI or MACD. A breakout without volume is often a false signal.
Risk management: Always use a stop loss to protect your capital.
Use other indicators: Wedge patterns work well with additional tools such as RSI, moving averages, or MACD. The more confluence, the better!
Final Thoughts 🏁
Wedge patterns, whether it’s the falling wedge pattern signaling a bullish reversal or the rising wedge pattern trading indicating bearish pressure, are some of the most reliable chart formations out there. But remember: no setup is perfect, so always use a stop loss and never rely on a single indicator.
With practice, you’ll get better at spotting these setups and timing your entries and exits like a pro. Happy trading, and may the charts be in your favor! 💰📊
Bullish Energy in Natural Gas: -DMI Extreme + Wedge BreakoutThe Spark in the Gas Market
Natural gas has been quietly simmering in recent weeks, building pressure beneath a surface of consolidation. Traders watching closely will have noticed a rare alignment — one that history shows can potentially precede outsized moves. We’re talking about the convergence of two powerful signals: a -DMI yearly extreme and a falling wedge breakout.
In the past, this combination has marked moments when bearish momentum had run its course, giving way to swift and decisive bullish reversals. Now, that same alignment is flashing again, inviting a closer look at the technical landscape and the potential opportunities it presents.
Why This Setup Matters
The -DMI (Directional Movement Index) measures the strength of downward price moves. When it pushes beyond two standard deviations above its yearly linear regression channel, it signals an overextended bearish phase. Historically, these extremes have often coincided with market bottoms in Natural Gas Futures.
Layer on top a falling wedge — a bullish reversal chart pattern — and the probability of an upside move gains weight. The wedge compresses price action into a narrowing range, reflecting reduced volatility and setting the stage for a potential explosive breakout once resistance gives way. The current breakout level sits near 3.18, with technical projections aligning closely to a well-defined UFO resistance (UnFilled Orders) zone around 3.90.
The Technical Story Unfolds
Looking at the daily chart in the present, the -DMI has recently breached the +2 standard deviation boundary of its 252-period regression channel — a rare occurrence that, as said, has preceded multiple major bullish reversals in the past year. When this condition appeared, downside momentum often faded, making room for buyers to take control.
This time, the current signal aligns with a falling wedge that has been developing for weeks. Price is about to break above the wedge’s upper boundary at approximately 3.18, suggesting a potential trend reversal.
The Trade Blueprint
Direction: Long
Entry: 3.18 (confirmed breakout above wedge resistance)
Target: 3.90 (wedge projection + UFO resistance)
Stop Loss: 2.858 (below wedge and technical support floor)
Reward-to-Risk Ratio: ~2+ to 1
This structure allows traders to define risk tightly while targeting a meaningful upside move. The setup applies equally to both Natural Gas Futures (NG) and Micro Natural Gas Futures (MNG), offering flexibility in capital allocation. For smaller accounts or those wanting to reduce margin exposure, the MNG contract delivers the same tick size precision with only one-quarter of the notional value.
The Contract Advantage
Natural Gas Futures (NG) represent 10,000 MMBtu per contract, with a minimum tick size of 0.00025 — equivalent to $2.50 per tick.
Micro Natural Gas Futures (MNG) are one-tenth the size at 1,000 MMBtu per contract, with the same 0.00025 tick size equaling $0.25 per tick.
Margin requirements vary with volatility and exchange adjustments, but at the time of writing, the CME lists initial margin for NG in the range of $3,500 per contract, while MNG margins are proportionally lower at $350 per contract. This creates flexibility for traders to scale positions or manage risk without altering the technical logic of the trade. Both contracts trade nearly 24 hours per day, Sunday through Friday, offering the ability to react to global energy market shifts in real time.
Risk Management as the Safety Valve
Defining risk is the cornerstone of any trade plan. The stop loss at 2.858 is not arbitrary — it sits below both the wedge’s lower boundary and a nearby technical support level. If price were to close below this level, it would undermine the bullish thesis and call for an exit.
Using smaller MNG contracts can help align risk with account size, allowing for partial position scaling and better drawdown control. Equally important is avoiding undefined risk scenarios, particularly in a commodity as volatile as natural gas. Precision in both entries and exits reduces exposure to intraday whipsaws while maintaining the trade’s structural integrity.
Closing the Loop
The natural gas market has aligned a rare set of conditions — a -DMI yearly extreme and a falling wedge breakout — each of which has historically preceded significant upside moves on their own. Together, they offer a compelling technical case for a defined, risk-managed long position targeting the 3.90 zone.
While no setup guarantees success, this one seems to offer clarity: a well-defined entry, stop, and target, supported by historical probability and pattern structure. In volatile markets, those moments of clarity are worth paying attention to — and acting on with discipline, and always depending on the trader’s trading plan.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Trading Divergences With Wedges in ForexTrading Divergences With Wedges in Forex
Divergence trading in forex is a powerful technique for analysing market movements, as is observing rising and falling wedges. This article explores the synergy between divergence trading and wedges in forex, offering insights into how traders can leverage these signals. From the basics to advanced strategies, learn how you could utilise this approach effectively, potentially enhancing your trading skills in the dynamic forex market.
Understanding Divergences
In forex trading, the concept of divergence plays a pivotal role in identifying potential market shifts. A divergence in forex, meaning a situation where price action and a technical indicator like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) move in opposite directions, often signals a weakening trend. This discrepancy is a valuable tool in divergence chart trading, as it may indicate a possible reversal or continuation of the current trend.
There are two primary types of divergence in forex—regular and hidden. Regular divergence occurs when the price makes higher highs or lower lows while the indicator does the opposite, often signalling a reversal. Hidden divergence, on the other hand, happens when the price makes lower highs or higher lows while the indicator shows higher highs or lower lows, typically suggesting a continuation of the current trend.
Trading Rising and Falling Wedges
Rising and falling wedges are significant patterns in forex trading, often signalling potential trend reversals. A rising wedge, formed by converging upward trendlines, often indicates a bearish reversal if it appears in an uptrend. Conversely, a falling wedge, characterised by converging downward trendlines, typically reflects a bullish reversal if it occurs in a downtrend.
Traders often look for a breakout from these patterns as a signal to enter trades. For rising wedges, a downward breakout can be seen as a sell signal, while an upward breakout from a falling wedge is often interpreted as a buy signal. When combined with divergences, this chart pattern can add confirmation and precede strong movements.
Best Practices for Trading Divergences
Trading divergence patterns in forex requires a keen eye for detail and a disciplined, holistic approach. Here are key practices for effective trading:
- Comprehensive Analysis: Before trading on divergence and wedges, be sure to analyse overall market conditions.
- Selecting the Right Indicator: Choose a forex divergence indicator that suits your trading style. Common choices include RSI, MACD, and Stochastic.
- Confirmation Is Key: It’s best to watch for additional confirmation from price action or other technical tools before entering a trade.
- Risk Management: Traders always set stop-loss orders to manage risk effectively. Divergence trading isn't foolproof; protecting your capital is crucial.
- Patience in Entry and Exit: Be patient as the divergence develops and confirm with your chosen indicators before entering or exiting a trade.
Strategy 1: RSI and Wedge Divergence
Traders focus on regular divergence patterns when the RSI is above 70 (overbought) or below 30 (oversold), combined with a rising or falling wedge pattern. The strategy hinges on identifying highs or lows within these RSI extremes. It's not crucial if the RSI remains consistently overbought or oversold, or if it fluctuates in and out of these zones.
Entry
- Traders may observe a regular divergence where both the price highs/lows and RSI readings are above 70 or below 30.
- After the formation of a lower high (in an overbought zone) or a higher low (in an oversold zone) in the RSI, traders typically watch as the RSI crosses back below 70 or above 30. This is accompanied by a breakout from a rising or falling wedge, acting as a potential signal to enter.
Stop Loss
- Stop losses might be set just beyond the high or low of the wedge.
Take Profit
- Profit targets may be established at suitable support/resistance levels.
- Another potential approach is to exit when the RSI crosses back into the opposite overbought/oversold territory.
Strategy 2: MACD and Wedge Divergence
Regarded as one of the best divergence trading strategies, MACD divergence focuses on the discrepancy between price action and the MACD histogram. The strategy is particularly potent when combined with a rising or falling wedge pattern in price.
Entry
- Traders typically observe for the MACD histogram to diverge from the price. This divergence manifests as the price reaching new highs or lows while the MACD histogram fails to do the same.
- The strategy involves waiting for the MACD signal line to cross over the MACD line in the direction of the anticipated reversal. This crossover should coincide with a breakout from the rising or falling wedge.
- After these conditions are met, traders may consider entering a trade in anticipation of a trend reversal.
Stop Loss
- Stop losses may be set beyond the high or low of the wedge, which may help traders manage risk by identifying a clear exit point if the anticipated reversal does not materialise.
Take Profit
- Profit targets might be established at nearby support or resistance levels, allowing traders to capitalise on the expected move while managing potential downside.
Strategy 3: Stochastic and Wedge Divergence
Stochastic divergence is a key technique for divergence day trading in forex, especially useful for identifying potential trend reversals. This strategy typically employs the Stochastic Oscillator with settings of 14, 3, 3.
Entry
- Traders may look for divergence scenarios where the Stochastic readings are above 80 or below 20, mirroring the RSI approach.
- This divergence is observed in conjunction with price action, forming a rising or falling wedge.
- Entry may be considered following a breakout from the wedge, which signals a potential shift in market direction.
Stop Loss
- Setting stop losses just beyond the high or low of the wedge might be an effective approach.
Take Profit
- Profit targets may be set at key support/resistance levels.
The Bottom Line
Divergence trading, coupled with the analysis of rising and falling wedges, offers a comprehensive approach to navigating the forex market. By integrating the discussed strategies with sound risk management and market analysis, traders may potentially enhance their ability to make informed decisions in the dynamic world of forex.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
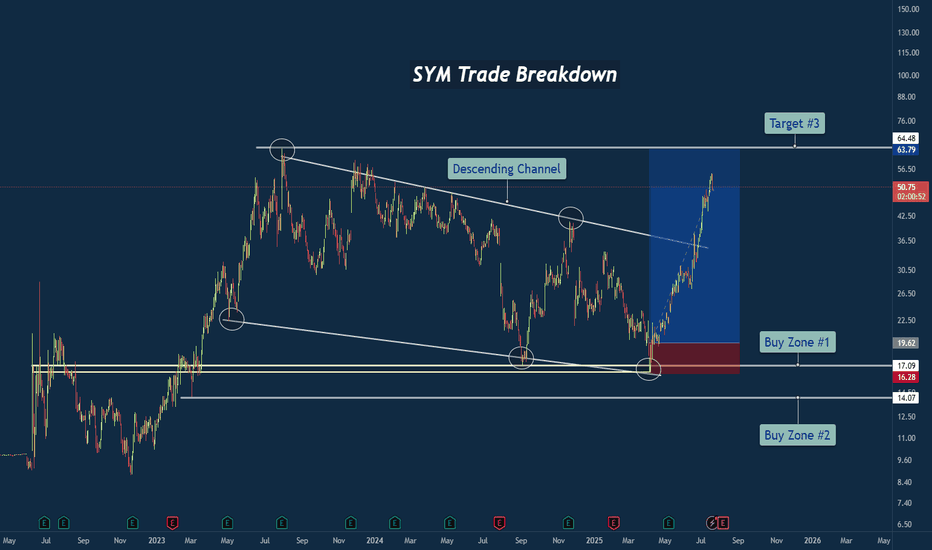
SYM Trade Breakdown – Robotics Meets Smart Technical's🧪 Company: Symbotic Inc. ( NASDAQ:SYM )
🗓️ Entry: April–May 2025
🧠 Trade Type: Swing / Breakout Reversal
🎯 Entry Zone: $16.28–$17.09
⛔ Stop Loss: Below $14.00
🎯 Target Zone: $50–$64+
📈 Status: Strong Rally in Motion
📊 Why This Trade Setup Stood Out
✅ Macro Falling Wedge Reversal
After nearly two years of compression inside a falling wedge, price finally tapped multi-year structural support and fired off with strength. This wasn’t just a bottom — it was a structural inflection point.
✅ Triple Tap at Demand Zone
Symbotic tapped the ~$17 area multiple times, signaling strong accumulation. Volume and momentum picked up with each successive test, showing institutional interest.
✅ Clean Break of Trendline
Price broke through the falling resistance trendline decisively, confirming the bullish reversal and unleashing stored energy from months of sideways structure.
🔍 Company Narrative Backdrop
Symbotic Inc. isn't just any tech stock. It’s at the forefront of automation and AI-powered supply chain solutions, with real-world robotics deployed in major retail warehouses. That kind of secular growth narrative adds rocket fuel to technical setups like this — especially during AI adoption surges.
Founded in 2020, Symbotic has quickly become a rising name in logistics and warehouse automation, serving the U.S. and Canadian markets. With robotics in demand and investors chasing future-ready tech, the price action aligned perfectly with the macro theme.
🧠 Lessons from the Trade
⚡ Compression = Expansion: Wedges like this build pressure. When they break, the moves are violent.
🧱 Structure Never Lies: The $17 zone was no accident — it was respected over and over.
🤖 Tech Narrative Boosts Confidence: Trading is easier when the fundamentals align with the technicals.
💬 What’s Next for SYM?
If price holds above the wedge and clears the $64 resistance, we could be looking at new all-time highs in the next cycle. Watching for consolidation and retests as opportunity zones.
#SYM #Symbotic #Robotics #Automation #AIStocks #BreakoutTrade #FallingWedge #SwingTrade #TechnicalAnalysis #TradingView #TradeRecap #SupplyChainTech
Real Success Rates of the Falling Wedge in TradingReal Success Rates of the Falling Wedge in Trading
The falling wedge is a chart pattern highly valued by traders for its potential for bullish reversals after a bearish or consolidation phase. Its effectiveness has been extensively studied and documented by various technical analysts and leading authors.
Key Statistics
Bullish Exit: In 82% of cases, the exit from the falling wedge is upward, making it one of the most reliable patterns for anticipating a positive reversal.
Price Target Achieved: The pattern's theoretical target (calculated by plotting the height of the wedge at the breakout point) is achieved in approximately 63% to 88% of cases, depending on the source, demonstrating a high success rate for profit-taking.
Trend Reversal: In 55% to 68% of cases, the falling wedge acts as a reversal pattern, signaling the end of a downtrend and the beginning of a new bullish phase.
Pullback: After the breakout, a pullback (return to the resistance line) occurs in approximately 53% to 56% of cases, which can provide a second entry opportunity but tends to reduce the pattern's overall performance.
False Breakouts: False exits represent between 10% and 27% of cases. However, a false bullish breakout only results in a true bearish breakout in 3% of cases, making the bullish signal particularly robust.
Performance and Context
Bull Market: The pattern performs particularly well when it appears during a corrective phase of an uptrend, with a profit target reached in 70% of cases within three months.
Gain Potential: The maximum gain potential can reach 32% in half of cases during a bullish breakout, according to statistical studies on equity markets.
Formation Time: The wider the wedge and the steeper the trend lines, the faster and more violent the post-breakout upward movement will be.
Comparative Summary of Success Rates:
Criteria Rate Observed Frequency
Bullish Exit 82%
Price Target Achieved 63% to 88%
Reversal Pattern 55% to 68%
Pullback After Breakout 53% to 56%
False Breakouts (False Exits) 10% to 27%
Bullish False Breakouts Leading to a Downside 3%
Points of Attention
The falling wedge is a rare and difficult pattern to correctly identify, requiring at least five contact points to be valid.
Performance is best when the breakout occurs around 60% of the pattern's length and when volume increases at the time of the breakout.
Pullbacks, although frequent, tend to weaken the initial bullish momentum.
Conclusion
The falling wedge has a remarkable success rate, with more than 8 out of 10 cases resulting in a bullish exit and a price target being reached in the majority of cases. However, it remains essential to validate the pattern with other technical signals (volume, momentum) and to remain vigilant against false breakouts, even if their rate is relatively low. When mastered, this pattern proves to be a valuable tool for traders looking for optimized entry points on bullish reversals.
Falling Wedge Trading Pattern: Unique Features and Trading RulesFalling Wedge Trading Pattern: Unique Features and Trading Rules
Various chart patterns give an indication of possible market direction. A falling wedge is one such formation that indicates a possible bullish reversal. This FXOpen article will help you understand whether the falling wedge pattern is bullish or bearish, what its formation signifies about the market direction, and how it can be used to spot trading opportunities.
What Is a Falling Wedge Pattern?
Also known as the descending wedge, the falling wedge technical analysis chart pattern is a bullish formation that typically occurs in the downtrend and signals a trend reversal. It forms when an asset's price drops, but the range of price movements starts to get narrower. As the formation contracts towards the end, the buyers completely absorb the selling pressure and consolidate their energy before beginning to push the market higher. A falling wedge pattern means the end of a market correction and an upside reversal.
How Can You Spot a Falling Wedge on a Price Chart?
This pattern is usually spotted in a downtrend, which would indicate a possible bullish reversal. However, it may appear in an uptrend and signal a trend continuation after a market correction. Either way, the falling wedge provides bullish signals. The descending formation generally has the following features.
- Price Action. The price trades lower, forming lower highs and lower lows.
- Trendlines. Traders draw two trendlines. One connects the lower highs, and the other connects the lower lows. Finally, they intersect towards a convergence point. Each line should connect at least two points. However, the greater the number, the higher the chance of the market reversal.
- Contraction. The contraction in the price range signals decreasing volatility in the market. As the formation matures, new lows contract as the selling pressure decreases. Thus, the lower trendline acts as support, and the price consolidating within the narrowing range creates a coiled spring effect, finally leading to a sharp move on the upside. The price breaks through the upper trendline resistance, indicating that sellers are losing control and buyers are gaining momentum, resulting in an upward move.
- Volume. The trading volume ideally decreases as the pattern forms, and the buying volume increases with the breakout above the upper trendline, reflecting a shift in momentum towards the buyers.
Falling and Rising Wedge: Differences
There are two types of wedge formation – rising (ascending) and falling (descending).
An ascending wedge occurs when the highs and lows rise, while a descending wedge pattern has lower highs and lows. In an ascending formation, the slope of the lows is steeper and converges with the upper trendline at some point, while in a descending formation, the slope of the highs is steeper and converges with the support trendline at some point.
Usually, a rising wedge indicates that sellers are taking control, resulting in a downside breakdown. Conversely, a descending wedge pattern indicates that buyers are gaining momentum after consolidation, generally resulting in an upside breakout.
The Falling Wedge: Trading Rules
Trading the falling wedge involves waiting for the price to break above the upper line, typically considered a bullish reversal. The pattern’s conformity increases when it is combined with other technical indicators.
- Entry
According to theory, the ideal entry point is after the price has broken above the wedge’s upper boundary, indicating a potential upside reversal. Furthermore, this descending wedge breakout should be accompanied by an increase in trading volume to confirm the validity of the signal.
The price may retest the resistance level before continuing its upward movement, providing another opportunity to enter a long position. However, the entry point should be based on the traders' risk management plan and trading strategy.
- Take Profit
It is essential to determine an appropriate target level. Traders typically set a profit target by measuring the height of the widest part of the formation and adding it to the breakout point. Another approach some traders use is to look for significant resistance levels above the breakout point, such as previous swing highs.
- Stop Loss
Traders typically place their stop-loss orders just below the lower boundary of the wedge. Also, the stop-loss level can be based on technical or psychological support levels, such as previous swing lows. In addition, the stop-loss level should be set according to the trader's risk tolerance and overall trading strategy.
Trading Example
In the chart above, there is a falling wedge. A trader opened a buy position on the close of the breakout candlestick. A stop loss was placed below the wedge’s lower boundary, while the take-profit target was equal to the pattern’s widest part.
Falling Wedge and Other Patterns
Here are chart patterns that can be confused with a falling wedge.
Falling Wedge vs Bullish Flag
These are two distinct chart formations used to identify potential buying opportunities in the market, but there are some differences between the two.
A descending wedge is a bullish setup, forming in a downtrend. It is characterised by two converging trendlines that slope downward, signalling decreasing selling pressure. A breakout above the upper trendline suggests a bullish move.
A bullish flag appears after a strong upward movement and forms a rectangular shape with parallel trendlines that slope slightly downward or move sideways. This formation represents a brief consolidation before the market resumes its upward trajectory.
While the falling wedge indicates a potential shift in a downtrend, the bullish flag suggests a continuation of an uptrend.
Falling Wedge vs Bearish Pennant
The falling wedge features two converging trendlines that slope downward, indicating decreasing selling pressure and often signalling a bullish reversal when the price breaks above the upper trendline.
Conversely, the bearish pennant forms after a significant downward movement and is characterised by converging trendlines that create a small symmetrical triangle. This pattern represents a consolidation phase before the market continues its downward trend upon breaking below the lower trendline.
While the falling wedge suggests a potential bullish move, the bearish pennant indicates a continuation of the bearish trend.
Falling Wedge vs Descending Triangle
The falling wedge consists of two downward-sloping converging trendlines, indicating decreasing selling pressure and often signalling a bullish reversal when the price breaks above the upper trendline. In contrast, the descending triangle features a flat lower trendline and a downward-sloping upper trendline, suggesting a buildup of selling pressure and typically signalling a bearish continuation when the price breaks below the flat lower trendline.
While the falling wedge is associated with a potential bullish move, the descending triangle generally indicates a bearish trend.
Falling Wedge: Advantages and Limitations
Like any technical pattern, the falling wedge has both limitations and advantages.
Advantages
- High Probability of a Reversal. The falling wedge is often seen as a strong, bullish signal, especially when it occurs after a downtrend. It suggests that selling pressure is subsiding, and a reversal to the upside may be imminent.
- Clear Entry and Exit Points. The pattern provides clear points for entering and exiting trades. Traders often enter when the price breaks out above the upper trendline and set stop-loss orders below a recent low within the formation.
- Versatility. The wedge can be used in various market conditions. It is effective in both continuation and reversal scenarios, though it is more commonly associated with bullish reversals.
- Widely Recognised. Since the falling wedge is a well-known formation, it is often self-fulfilling to some extent, as many traders recognise and act on it, further driving the market.
Limitations
- False Breakouts. Like many chart patterns, the falling wedge is prone to false breakouts. Prices may briefly move above the resistance line but then fall back below, trapping traders.
- Dependence on Market Context. The effectiveness of the falling wedge can vary depending on broader market conditions. In a strong downtrend, it might fail to result in a significant reversal.
- Requires Confirmation. The wedge should be confirmed with other technical indicators or analysis tools, such as volumes or moving averages, to increase the likelihood of an effective trade. Relying solely on the falling wedge can be risky.
- Limited Use in Low-Volatility Markets. In markets with low volatility, the falling wedge may not be as reliable, as price movements might not be strong enough to confirm the falling wedge's breakout.
The Bottom Line
The falling wedge is a powerful chart pattern that can offer valuable insights into potential trend reversals or continuations, depending on its context within the broader market. By understanding and effectively utilising the falling wedge in your strategy, you can enhance your ability to identify many trading opportunities. As with all trading tools, combining it with a comprehensive trading plan and proper risk management is crucial.
FAQ
Is a Falling Wedge Bullish?
Yes, the falling wedge is a bullish continuation pattern in an uptrend, and it acts as a bullish reversal formation in a bearish market.
What Does a Falling Wedge Pattern Indicate?
It indicates that the buyers are absorbing the selling pressure, which is reflected in the narrower price range and finally results in an upside breakout.
What Is the Falling Wedge Pattern Rule?
The falling wedge is a technical analysis formation that occurs when the price forms lower highs and lower lows within converging trendlines, sloping downward. Its rule is that a breakout above the upper trendline signals a potential reversal to the upside, often indicating the end of a downtrend or the continuation of a strong uptrend.
How to Trade Descending Wedge Patterns?
To trade descending wedges, traders first identify them by ensuring that the price is making lower highs and lows within converging trendlines. Then, they wait for the price to break out above the upper trendline, ideally accompanied by increased trading volume, which confirms the breakout. After the breakout, a common approach is to enter a long position, aiming to take advantage of the anticipated upward movement.
What Is the Target of the Descending Wedge Pattern?
The target for a descending wedge is typically set by measuring the maximum width of the wedge at its widest part and projecting that distance upwards from the breakout point. This projection gives a potential price target.
What Is the Entry Point for a Falling Wedge?
The entry point for a falling wedge is ideally just after the breakout above the upper trendline. Some traders prefer to wait for a retest of the broken trendline, which may act as a new support level, before entering a trade to confirm the breakout.
*Important: At FXOpen UK, Cryptocurrency trading via CFDs is only available to our Professional clients. They are not available for trading by Retail clients. To find out more information about how this may affect you, please get in touch with our team.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
Falling Wedge Pattern: Cocoa FuturesThis is the map of how to trade this rare chart pattern.
This is a textbook sample of Falling Wedge continuation pattern that played out with impressive accuracy.
We have a strong uptrend in 2024 that has been changed
by a large consolidation that took place for the rest of 2024
as it has built the large Falling Wedge (continuation) pattern.
One should focus on the following crucial points and measurements:
1. breakout point where price rises above trendline resistance
it acts as a buy entry trigger (green segment)
2. stop loss - it is located below the lowest valley preceding breakout (red segment)
3. widest part of the pattern - use it to measure the distance to the target adding it to breakout point (blue arc)
4. target (yellow dashed segment)
all of above key parameters are highlighted on the chart.
It's amazing how accurately the price grew towards the target booking over 60% profit.
Next time you can use this map as a guidance.
Uptrend & Downtrend Bullish Falling Wedge Pattern TutorialA bullish falling wedge is a charting pattern that signals a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend. Here's a breakdown of its key characteristics:
Shape: The pattern forms a wedge that slopes downward, with the upper trendline connecting the highs and the lower trendline connecting the lows. The key is that the highs and lows get closer together as the pattern develops.
Trend: It typically forms during a downtrend, indicating that selling pressure is decreasing.
Breakout: The pattern is bullish when the price breaks above the upper trendline. This breakout suggests that the downward trend is losing momentum, and an upward trend may follow.
Volume: During the falling wedge formation, volume tends to decrease, which supports the idea that selling pressure is diminishing.
Retest: After the breakout, it's common for the price to retest the upper trendline, and if it holds, it provides further confirmation of the bullish reversal.
Example
Imagine a stock that has been falling for several months. The price forms lower highs and lower lows, creating a narrowing wedge. Suddenly, the price breaks above the upper trendline with increased volume, signaling a potential reversal and the start of an upward trend.
Rising and Falling Wedges ExplainedWelcome to the world of trading patterns. If you appreciate our charts, give us a quick 💜💜
Today, we'll explore two important ones: the Rising Wedge and the Falling Wedge . These patterns can signal shifts in market trends. Let's dive in and see how they work.
Rising Wedge:
In an uptrend, the Rising Wedge hints at a bearish turn. It takes shape as prices find a middle ground between two upward-sloping lines, one as support and the other as resistance, both inching closer. As the price inches towards the wedge's tip, its upward push tends to fade, suggesting a potential shift to a downward trend.
Your sell signal triggers with a bearish break beneath the wedge's support.
Set a stop loss just above the wedge's highs.
Aim for the next significant support level.
Falling Wedge:
Unlike the Rising Wedge, the falling wedge spells optimism in a downtrend. It emerges as prices consolidate between two downward-sloping lines, one providing support and the other resistance, both drawing nearer. As prices approach the wedge's apex, the downward momentum loses steam, hinting at a potential shift towards an upward trend.
Your buy signal activates with a bullish breakout beyond the wedge's resistance.
Place a stop loss just below the wedge's lows.
Target the next notable resistance.
Feel free to let us know your thoughts and if you have any questions. Your feedback is valuable and helps us improve. Happy trading!
Wealth Unleashed: Wedge Pattern Power - Hidden Gem Revealed!Introduction:
Are you looking to skyrocket your trading profits? Look no further! Today, we will uncover the hidden gem of trading patterns: the Wedge Pattern. This powerful tool has the potential to transform your trading strategy and help you achieve financial success. Let's dive into the world of wedge patterns and explore how you can capitalize on their power.
What are Wedge Patterns?
Wedge patterns are popular among traders due to their high probability of forecasting trend reversals. These patterns appear when the price of an asset consolidates between converging support and resistance lines. There are two primary types of wedge patterns: the rising wedge and the falling wedge.
Rising Wedge:
In an upward trend, the rising wedge is considered a bearish pattern. It forms when the price consolidates between an upward-sloping support line and an upward-sloping resistance line that are converging. As the price approaches the apex of the wedge, the upward momentum weakens, signaling a potential trend reversal to the downside.
Falling Wedge:
Contrary to the rising wedge, the falling wedge is a bullish pattern. It appears in a downward trend when the price consolidates between a downward-sloping support line and a downward-sloping resistance line that are converging. As the price nears the apex of the wedge, the downward momentum loses strength, indicating a possible trend reversal to the upside.
Trading Strategies:
To capitalize on the power of wedge patterns, follow these steps:
✅Identify the pattern: Observe the chart for converging support and resistance lines to spot a rising or falling wedge pattern.
✅Confirmation: Wait for a breakout from the wedge pattern, either above the resistance line (for falling wedges) or below the support line (for rising wedges).
✅Entry point: Open a long position after a breakout above the resistance line in a falling wedge, or a short position after a breakout below the support line in a rising wedge.
✅Stop-loss and take-profit: Set your stop-loss order below the breakout level (for falling wedges) or above the breakout level (for rising wedges). Establish your take-profit target at a level that aligns with your risk-reward ratio and trading plan.
Conclusion:
The wedge pattern is a hidden gem that can potentially boost your trading profits when used correctly. By mastering the art of identifying and trading wedge patterns, you can strengthen your technical analysis skills and increase your chances of success in the market. Remember, no single tool guarantees success, so always use additional technical indicators and maintain a disciplined approach to risk management. Happy trading!
Uncovering Wyckoff Accumulation Secret PatternWyckoff Accumulation & Distribution is a trading strategy that was developed by Richard Wyckoff in the early 1900s. It is based on the premise that markets move in cycles and that traders may recognize and use these cycles.
In accumulation phase Wyckoff strategy involves identifying a Trading Range where buyers are accumulating shares of a stock before it moves higher. This allows traders to enter into positions at lower prices and benefit from the eventual price increase. Wyckoff Accumulation is an effective way for traders and investors to gain on market movements and make profits from their trades.
The Wyckoff Trading Ranges feature a chart pattern called Descending Wedge. This pattern involves two trendlines, one falling and one rising, which converge to form a wedge shape.
This pattern indicates that the price of an asset is likely to break out in the direction of the falling trendline.
In my understanding, "Continuous Weakness" means a shift away from selling towards buying. Sellers fail to hold the pressure, so buyers take the lead leading in D,E: MARKUP phases.
Kind regards
Artem Shevelev
Please check out my older Education Ideas
Consider put like and follow my page for more updates)
How to understand the falling wedge and rising wedgeHello dear traders,
Here are some educational chart patterns you must know in 2022 and 2025.
I hope you find this information educational and informative.
We are new here so we ask you to support our views with your likes and comments,
Feel free to ask any questions in the comments, and we'll try to answer them all, folks.
What Is a Wedge?
A wedge is a price pattern marked by converging trend lines on a price chart. The two trend lines are drawn to connect the respective highs and lows of a price series over the course of 10 to 50 periods. The lines show that the highs and the lows are rising or falling at differing rates, giving the appearance of a wedge as the lines approach a convergence. Wedge-shaped trend lines are considered useful indicators of a potential reversal in price action by technical analysts.
Understanding the Wedge Pattern:-
A wedge pattern can signal either bullish or bearish price reversals. In either case, this pattern holds three common characteristics: first, the converging trend lines; second, a pattern of declining volume as the price progresses through the pattern; third, a breakout from one of the trend lines. The two forms of the wedge pattern are a rising wedge (which signals a bearish reversal) and a falling wedge (which signals a bullish reversal).
Falling Wedge pattern:-
When a security's price has been falling over time, a wedge pattern can occur just as the trend makes its final downward move. The trend lines drawn above the highs and below the lows on the price chart pattern can converge as the price slide loses momentum and buyers step in to slow the rate of decline. Before the lines converge, the price may breakout above the upper trend line.
When the price breaks the upper trend line, the security is expected to reverse and trend higher. Traders identifying bullish reversal signals would want to look for trades that benefit from the security’s rise in price.
Rising Wedge pattern:-
This usually occurs when the security's price has been rising over time, but it can also occur in the midst of a downtrend.
Trend lines drawn above and below a price chart pattern can converge to help a trader or analyst anticipate breakout reversals. While the price can break out of either trend line, the wedge pattern has a tendency to break out from the trend line in the opposite direction.
Therefore, the ascending wedge pattern indicates a higher probability of further downside in the price after the breakdown of the lower trend line. Traders can enter bearish trades on the basis of a charted security after a breakout, either by selling the security short or by using derivatives such as futures or options. These trades will seek to profit from the possibility of a fall in prices.
Trading Profits for the Wedge Pattern:-
As a general rule, price pattern strategies for trading systems rarely produce returns that outperform buy-and-hold strategies over time, but some patterns nevertheless appear to be useful in predicting general price trends. Huh. Some studies suggest that a wedge pattern will break out toward reversal (a bullish breakout for falling wedges and a bearish breakout for rising wedges) more than two-thirds of the time, with a falling wedge being followed by a rising wedge. Is a more reliable indicator than the wedge. ,
Because wedge patterns converge in a smaller price channel, the distance between the price at the entry of the trade and the price for the stop loss is relatively smaller than at the beginning of the pattern. This means that the stop loss can be placed closer to the time the trade is initiated, and if the trade is successful, can result in a return greater than the amount of risk initially placed on the trade.
Wedge a Continuation or a Reversal Pattern:-
The wedge pattern signals a reversal. The reversal is either bearish or bullish, depending on where the trend line meets, what the trading volume is, and whether the wedge is falling or rising.
Trade with care.
If you like our content, please feel free to support our page with a like, comment
Hit the like button if you like it and share your charts in the comments section.
Thank you
📈 4 Common Bullish Patterns🟢 RISING THREE
"Rising three methods" is a bullish continuation candlestick pattern that occurs in an uptrend and whose conclusion sees a resumption of that trend.
This can be contrasted with a falling three method. The first bar of the pattern is a bullish candlestick with a large real body within a well-defined uptrend.
🟢 FALLING WEDGE
The falling wedge pattern occurs when the asset’s price is moving in an overall bullish trend before the price action corrects lower.
Within this pull back, two converging trend lines are drawn. The consolidation part ends when the price action bursts through the upper trend line, or wedge’s resistance.
🟢 BULL PENNANT
A pennant is a type of continuation pattern formed when there is a large movement in a security, known as the flagpole, followed by a consolidation period with converging trend line.
Pennants, which are similar to flags in terms of structure, have converging trend lines during their consolidation period and last from one to three weeks.
🟢 ASCENDING TRIANGLE
An ascending triangle is a chart pattern used in technical analysis. It is created by price moves that allow for a horizontal line
to be drawn along the swing highs and a rising trendline to be drawn along the swing lows. The two lines form a triangle.
Traders often watch for breakouts from triangle patterns. The breakout can occur to the upside or downside
👤 @AlgoBuddy
📅 Daily Ideas about market update, psychology & indicators
❤️ If you appreciate our work , Please like, comment and follow ❤️
Forget about chart patterns! Hello, my dear friends and happy New Year!
I wish you to be healthy and reach all your goals in trading and not only! Never give up on this difficult way which we are going to overcome together!
Today we have a very important topic. How to use Elliott waves instead of classical chart patterns. This is the natural exposure why the chart patterns are garbage. I remember my third year at university when we have the trading lessons. Our teacher gave us a lot of useless knowledges about support, resistance and chart patterns. I have not understood why it should working and it was not soo intereting subject for me. That’s why I returned back to trading much later using self-education. Now I have the clear understanding why Elliott waves is the best tool and why it’s working. Most of traders even don’t understand that chart patterns is just the special case of Elliott waves. That’s why today I decided to explain you how you can change the first one to the second one. Let’s go!
Double Top(Bottom)
On the chart above I drew the different types of double tops. Generally we have 3 types of this pattern
Double top with the second top higher than the first one. In this case we can interpret it in two ways. It could be the classical waves 3, 4, 5 and the corrective wave A at the ending stage. In this case we can anticipate waves B and C. Also it could be the irregular correcton ABC inside wave 4 (rarely in wave 2). In this case we should wait for the wave 5 after that. Traders usually execute short position on the neckline breakdown and suffer when the wave 5 smashed their stop-loss. They are wondering why double top does not working.
Double top with the equal highs has the same possible outcomes. The only one difference that correction called flat instead of irregular.
Double top with the second top lower than the first one. Here is the most common variant is the end of the ABC correction. In this case we have the low potential for shorting the market becuase the new impulsive wave to the upside can hit all stop losses.
Head & Shoulders
This is the easiest pattern for analysis. The right sholder usually is the wave 4, the head, obviously is the wave 5 and the right shoulder is the wave B. On the neckline breakdown we have the shorting potential only in the rest part of the wave C. You could correctly count waves and short that the bearish reversal bar of the wave 5 or, as a last resort, at wave B potential top. Shorting at the neckline has sence only if you are sure that the wave B was the the wave 1 of the impulsive wave to the downside if higher degree and now the market is in wave 3. We have to learn how to count waves in a correct way. I would recommend you to read the Trading Chaos book by Bill Williams because it has the best explanation how do waves work.
Triangles and Wedges
This part is common for all types of triangles (ascending, descending, symmetrical) and wedges (falling and rising). This patterns have the similar structure. If we faced with one of these patterns we have 4 possible scenarios.
Triangle in the downtrend after the wave 3. In this case triangle is the wave 4, which is represented as the triangle correction. This correction type consists of 5 waves A, B, C, D and E. When the wave E is finished market will continue it’s move in the direction of a trend, printing the wave 5.
The same, but in the uptrend.
When the market showed us the 5 waves cycle to the upside and the correction is in progress. Triangle can appears in the wave B. In this case the price will continue the corrective move in the wave C after it’s finished.
The same with the downtrend.
Guys, of course there are much more types of chart patterns. For example, tripple tops and bottoms and so on. The purpose of this article is giving you another view of the market structure and to motivate you studying the Elliott waves theory. Believe me, it has much more potential than it seems on the first glimplse.
Best regards, Ivan
________________________________________________________________________________________________
If you like my educational ideas, please smash the boost button to stimulate me make more quality articles!
A Guide about Falling & Rising Wedge PatternsHello every one
🟡WHAT IS A FALLING WEDGE PATTERN?
The falling wedge pattern is a continuation pattern formed when price bounces between two downward sloping, converging trendlines. It is considered a bullish chart formation but can indicate both reversal and continuation patterns – depending on where it appears in the trend.
🌳HOW TO IDENTIFY A FALLING WEDGE PATTERN
The falling wedge pattern is interpreted as both a bullish continuation and bullish reversal pattern which gives rise to some confusion in the identification of the pattern. Both scenarios contain different market conditions which must be taken into consideration.
The differentiating factor that separates the continuation and reversal pattern is the direction of the trend when the falling wedge appears. A falling wedge is a continuation pattern if it appears in an uptrend and is a reversal pattern when it appears in a downtrend.
(Example)
🔵WHAT IS A RISING WEDGE PATTERN?
The rising wedge (also known as the ascending wedge) pattern is a powerful consolidation price pattern formed when price is bound between two rising trend lines. It is considered a bearish chart formation which can indicate both reversal and continuation patterns – depending on location and trend bias. Regardless of where the rising wedge appears, traders should always maintain the guideline that this pattern is inherently bearish in nature
🌳HOW TO IDENTIFY A RISING WEDGE PATTERN
The rising wedge pattern is interpreted as both a bearish continuation and bearish reversal pattern which gives rise to some confusion in the identification of the pattern. Both scenarios contain a different set of observation dynamics which must be taken into consideration.
(Example)
How to trade Rising Wedge patternWhat is a rising wedge?
A rising wedge is a technical pattern, suggesting a reversal in the trend . This pattern shows up in charts when the price moves upward with higher highs and lower lows converging toward a single point known as the apex.
There are 4 ways to trade wedges like shown on the chart
(1) Your entry point when the price breaks the lower bound of the wedge, place your stop loss above the last peak, your target range is the distance between the upper and lower bound of the wedge at the start point.
(2) Your entry point when the price breaks the neckline of the double top pattern inside the wedge pattern, place your stop loss above the double top, place your target as same as shape (1)
(3) Your entry point when the price retest the lower bound of the wedge, place your stop loss above the last peak inside the wedge pattern, place your target as same as shape (1)
(4) a false breakout may occur in the rising wedge pattern, wait the price to go inside the pattern again and your entry point should be after breaking the last trough and your stop loss should be placed above the last peak that has been formed within the wedge, your target should be placed as same as shape (1).
We wish you the best of luck!
price action patterns you need to know ( part 4 ) hi my friends , i'll share with you some patterns which can help you in trading ( part 4 )
Falling Wedge appear in downtrend and it indicates that the sellers are losing momentum in the market, and the buyers are gaining momentum ( long ) you can go long after the break or the retest of the trendline .
rising Wedge appear in uptrend and it indicates that the buyers are losing momentum in the market, and the sellers are gaining momentum ( short ) you can go short after the break or the retest of the trendline
note : Usually we find there is a divergence in the RSI indicator and this can be used as confirmation .
please support me with like and follow me for more ideas .
What are Falling and Rising Wedge Patterns?What Is the Wedge Pattern and Its Common Characteristics?
1. Wedge patterns have converging trend lines that come to an apex with a distinguishable upside or downside slant.
a. Wedge with an upside slant is called a rising wedge
b. Wedge with downside slant is called falling wedge
2. It has declining volumes as the pattern progresses.
3. It breaks out from one of the trend lines.
Why We Should Pay Attention to Wedge Patterns?
Some studies suggest that a wedge pattern will breakout towards a reversal rather than a continuation more often than two-thirds of the time. Therefore as the rule of thumb, people generally treat a falling wedge as a bullish pattern and a rising wedge as a bearish pattern, especially a falling wedge would be a more reliable reversal indicator than a rising wedge.
Since we know a wedge pattern has a higher probability to reverse and due to the fact that the price of wedge pattern converges to a smaller area, we can trade the reversal set up with a relatively close stop loss to its entry price, which provides us with a good trading opportunity with a decent Risk:Reward ratio.
Examples of a Bullish Rising Wedge and Bearish Falling Wedge.
Sadly, there is nothing that works 100% in trading. Not every rising or falling wedge will reverse as one might expect. Every trader must properly manage their risk by setting stop losses and not just trading based on price patterns. Below are two examples.
Bullish Rising Wedge (ETHUSDT during 15/NOV/20 - 28/DEC/20)
In the early stages of the epic 20-21 bull market, if traders blindly treat the rising wedge as a bearish signal and trade accordingly, they would pay a heavy price.
Bearish Falling Wedge (LTCUSD during 14/AUG/18 - 14/NOV/18)
On the contrary, in the late stage of the 2018 bear market, any trader who blindly trades the falling wedge to bet on a reversal would also learn a hard lesson.
Comment down your thoughts on Ascending Triangle Pattern in the comment section.
Disclaimer:
This is just an educational post. Never trade just any pattern. And please do your research before making any trades.
Happy Trading!
Closer look into Rising/Falling Wedge, Reversal Price Action
Closer look into Rising/Falling Wedge, Reversal Price Action structures/patterns
Hi traders:
Today I will go more in detail on rising/falling wedge correction in price action structures/patterns.
You might have already heard about these types of correctional structures, and many traders who utilize them.
Certainly there are many ways of traders identifying them and taking advantage of these kinds of price action, so it's ideal for you to understand them in your analysis.
We first need to understand that a rising/falling wedge is a REVERSAL price action. Meaning when the correction completes, there's a higher probability of the price to reverse.
You might have already seen multiple price action videos from me that go over all sorts of continuation and reversal price action (I will share links below),
and I always talk about when combining multiples of different price action structures/patterns will give you a better edge at entering positions that work out in your favor.
Same idea here, so let's take a look at how rising/falling wedges are, how to identify them, and how to effectively use them in your analysis.
Rising/falling wedge, just as the name suggests, is an ascending/descending type of correction where the price is getting squeezed into a “wedge”.
As the price gets narrower and narrower, there's a higher probability of the price to “reverse” from the wedge.
Now about entries, certainly many traders have their own method of entering, so I will share my point of view and the way how I like to enter them.
Any questions, comments or feedback welcome to let me know :)
Thank you
Risk Management: 3 different entries on how to enter the impulsive phrase of price action
Multi-time frame analysis
Identify a correction for the next impulse move in price action analysis
Continuation and Reversal Correction
Continuation Bull/Bear Flag
Parallel Channel (Horizontal, Ascending, Descending)
Reversal Ascending/Descending Channel
Reversal Double Top/Bottom
Reversal Head & Shoulder Pattern
Reversal “M” and “W” style pattern
Reversal Impulse Price Action
Continuation/Reversal Expanding Structure/Pattern
EDUCATION - Rising & Falling Wedges - Reversal PatternsWhat is an ascending/descending correction?
The most common reversal pattern is the rising and falling wedge, which typically occurs at the end of a trend. The pattern consists of two trendiness which contract price leading to an apex and then a breakout appears.
Rising Wedge – Bearish Reversal
The ascending reversal pattern is the rising wedge which consists of higher highs and higher lows whilst losing momentum to the upside. Price contracts and eventually has a bearish break.
Falling Wedge – Bullish Reversal
The falling wedge reversal pattern occurs at the end bear run and indicates that price is ready to reverse. Again, price contracts and then eventually breaks out upwards.
There are 2 types of ways we can trade wedge patterns; Risky Entry & Safe Entry. See below for the pros and cons for both and how to enter them
__________________________________________________________________
Risk Entry:
The reason why it is called a risk entry is because we haven't got many confirmations apart from the third touch of the trendline (as indicated in the chart above). Price may have the potential to go past the trendline for a deeper correction before moving up hence why this is called a risk entry. Whereas for the safe entry, the confirmation would be the break of the wedge.
How to trade using Risk Entry:
Wait for price to bounce off the trendline and then enter with stops below/above the correction depending on whether it’s a rising wedge or falling wedge.
One of the advantages of doing a risk entry is that we can have small stop loss and have a great risk:reward ratio. Also, we can gain an entry at the start of the move and have massive gains!
Safe Entry:
Safe entry requires more than one confluence and requires confirmation. One of the confirmations of the safe entry is the third touch bounce and then another confirmation is when price breaks the correction which confirms that the structure has changed and that we are in a reversal.
How to trade using Safe Entry:
For a safe entry, enter when price has broken the correction with stops above/below the correction. Please note that with this entry method, the stoploss will be greater.
The disadvantage to using a safe entry is that we require a bigger stop loss which makes the risk:reward ratio not as great as the risk entry. However, the probability of the trade succeeding is higher.
RISING WEDGE EXAMPLES
RISK ENTRY
SAFE ENTRY
FALLING WEDGE EXAMPLES
RISK ENTRY
SAFE ENTRY